This topic describes common issues and solutions for Cloud Backup when you use the Database Backup feature.
List of questions
Database instance issues
Client issues
Backup issues
What are the network requirements for local database backup?
What is the minimum interval for real-time backup? Can it be configured with an incremental backup?
How do I change the username and password for a database backup?
RMAN reports a non-fatal error during an Oracle incremental backup
What do I do if browsing database details fails when I back up SQL Server 2019?
Are there limits on the supported MySQL database versions and operating systems for backup?
Why are there duplicate or unexpectedly timed records in the backup history?
Why does a backup fail and the backup plan status show "Error"?
Restore issues
Backup vault issues
Database instance issues
What do I do if instance registration for Database Backup fails?
First, confirm whether the Database Backup client is installed on the server (local server or ECS instance). If it is, see Uninstall the client to uninstall the client and clear its configuration files. Then, try to register the instance again.
What do I do if the database instance status is "Inactivated"?

MySQL
The Database Account or Password entered during registration is incorrect, or the user account has insufficient permissions. Verify that the username and password are correct, and grant sufficient permissions to the backup account. Alternatively, create a dedicated user for backups and try again.
For more information, see Create a MySQL backup account and configure permissions.
Run the
systemctl restart dbackup3-agentcommand to restart the backup client.If the instance is still inactive after you restart the backup client, collect the relevant logs for further analysis.
The client log path is
/var/log/dbackup3/agent.log.
Oracle
The Database Account or Password entered during registration is incorrect, or the user account has insufficient permissions. Confirm that the username and password are correct and that the backup account has sufficient permissions. You can also create a dedicated user for backups and try again.
For more information, see Create an Oracle backup account and configure permissions.
Restart the backup client.
Linux: Run the
systemctl restart dbackup3-agentcommand to restart the backup client.Windows:
Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog box.Enter
services.mscand press Enter to open the Services interface.In the services list, find the
dbackup3-agentservice.Check whether the service status is "Running". If it is not, right-click the
dbackup3-agentservice and select "Restart" to start it.
If the instance is still inactive after you restart the backup client, collect the relevant logs for further analysis.
The client log path on Linux is
/var/log/dbackup3/agent.log.The client log path on Windows is
Local Disk (C) > ProgramData > scutech > dbackup3 > agent > log > dbackup3-agent.log.
SQL Server
The Database Account or Password is incorrect, or the user account has insufficient permissions. To resolve this issue, verify that the username and password are correct and grant sufficient permissions to the backup account. As a best practice, create a dedicated user for backups and try the operation again.
For more information, see Create an SQL Server backup account and configure permissions.
Restart the
dbackup3-agentservice.Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog box.Enter
services.mscand press Enter to open the Services interface.In the services list, find the
dbackup3-agentservice.Check whether the service status is "Running". If it is not, right-click the
dbackup3-agentservice and select "Restart" to start it.
If the instance is still inactive after you restart the service, collect the relevant logs for further analysis.
The client log path is
Local Disk (C) > ProgramData > scutech > dbackup3 > agent > log > dbackup3-agent.log.
What do I do if the database instance status is "Database Offline"?
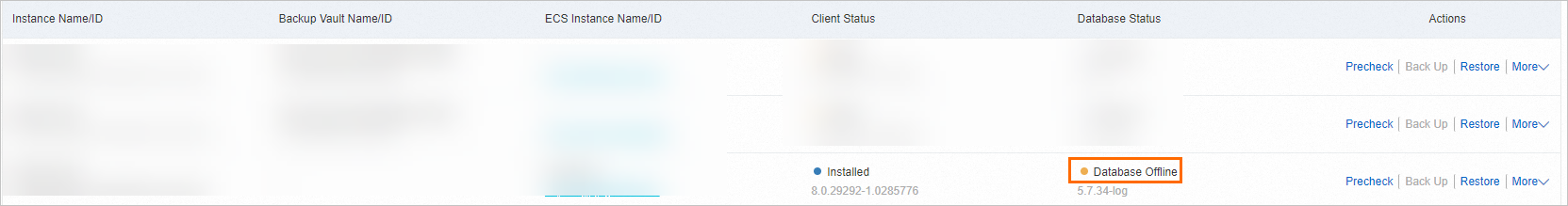
MySQL
Query the MySQL database status.
Log on to the ECS instance and run the
systemctl status mysqldcommand to query the MySQL database status. If the process status is inactive, the MySQL database service is not started.Restart the MySQL service.
After you run the
systemctl start mysqldcommand to restart the MySQL service, the Database Status in the console changes to Online.
Oracle
Query the Oracle database listener status.
Log on to the ECS instance and run the following commands:
su - oracle lsnrctl statusIf the service is started, its status is running. If the service is not started, the message TNS: no listener appears.
Query the Oracle database running status.
su - oracle sqlplus /nolog conn /as sysdba SELECT name, status FROM v$instance;The v$instance view provides information about the database instance. The status column shows the instance status. If the status is OPEN, the database is open and can accept connections.
Restart the Oracle listener.
Start the Oracle listener service to listen for connection requests from clients.
su - oracle lsnrctl startRestart the Oracle database instance.
In SQL*Plus, log on as a system administrator and start the Oracle instance.
sqlplus / as sysdba; STARTUP;After startup, the Database Status in the console is Online.
SQL Server
Query the SQL Server database status.
Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog box.Enter
services.mscand press Enter to open the Services interface.In the services list, find the SQL Server service. For example, "SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)".
Check the service status. The status can be "Running", "Stopped", or "Paused".
Restart the SQL Server service.
If the SQL Server database status is Stopped or Paused, right-click the SQL Server service and select Start. If the Start option is dimmed, reopen Windows Services Manager as an administrator and try again. After the service starts, the Database Status on the console is Online.
Why do multiple database instances appear on the ECS Database Instance tab after I register an instance?
If multiple database instances are deployed on an ECS instance, the Cloud Backup console scans and displays all of them during registration.
What do I do if the database status cannot be obtained after instance registration?
Symptom
After you register a database instance, the Cloud Backup console cannot retrieve the database status.
Cause
The operating system is not supported by the database.
Solution
Switch to a supported operating system and try again.
Client issues
How to check the client process status, find the log path, and restart the client
Linux
Check the process status of the backup client.
Run the
systemctl status dbackup3-agentorservice dbackup3-agent statuscommand to check the process status of the Database Backup client.A status of active or
dbackup3-agent is running...indicates that the client is running properly.● dbackup3-agent.service - dbackup3 agent daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/dbackup3-agent.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-12-11 13:47:34 CST; 1min 13s ago Main PID: 22192 (dbackup3-agent) CGroup: /system.slice/dbackup3-agent.service └─22192 /opt/scutech/dbackup3/bin/dbackup3-agent -f /etc/opt/scutech/dbackup3/agent/svc.conf.d Dec 11 13:47:34 iZbp1******gktZ systemd[1]: Started dbackup3 agent daemon.Restart the backup client.
Run the
systemctl restart dbackup3-agentorservice dbackup3-agent restartcommand to restart the client process. The client status returns to normal when the Client Status for the database in the console is Installed.
The client log path is:
/var/log/dbackup3/agent.logWindows
Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog box.Enter
services.mscand press Enter to open the Services interface.In the services list, find the
dbackup3-agentservice.Check whether the service status is "Running". If it is not, right-click the
dbackup3-agentservice and select "Restart" to start it.
The client log path is:
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.log
What do I do if the database client status is "Offline"?
Symptom
The Client Status of the database is Offline.

Cause
The "Offline" status indicates that Cloud Backup has not received a heartbeat signal from the client process. This can happen for several reasons, such as the client being automatically stopped because of an out of memory error, or the device where the client is located being shut down.
Solution
Follow the instructions in How to view the client process status, log path, and restart the client to check and restart the client. After the client status changes to Running, wait for the database Client Status in the console to be displayed as Installed. This indicates that the client has returned to normal.
What do I do if the "Failed to run install script:exit status 4" error occurs when I install the backup client for a local SQL Server?
This error occurs because the local security policy setting "Admin Approval Mode for the Built-in Administrator account" is not enabled. This policy must be set to Enabled.
Press Win+R to open the Run dialog box, enter
gpedit.msc, and then run the Local Group Policy Editor.In the Local Group Policy Editor pane, navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options. In the right-side pane, find User Account Control: Admin Approval Mode for the Built-in Administrator account and change its status to Enabled.
What do I do if the backup client fails to install for a local SQL Server?
Log on to the server and view the backup log.
Windows client log path:
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.logIn the log, check the entries around the time the task failed.
If the backup log contains the error message Failed to install dbackup3-agent service, errno=1783, The stub received bad data, the system may have rejected the installation. Check whether any antivirus or security software has blocked the installation and review the block records. Add the installation program to the whitelist or temporarily disable the security software before you try to install it again.
What do I do if the Database Backup client fails to install on an ECS instance?
Check the following two items to ensure that the client can be installed successfully:
Cloud Assistant status: Confirm that Cloud Assistant is installed correctly and is running.
If the installation fails, find a failed command record in the Cloud Assistant console. Copy the command and run it manually on the ECS host. During manual installation, if network connectivity issues or system script execution errors occur, specific error messages appear on the screen. Use these messages to resolve the issues, for example, by adjusting network settings.
After you resolve all issues and the script runs successfully, the client is installed. Then, trigger the installation again in the console to complete the process.
C drive space: Ensure that there is enough free space on the C drive. Insufficient space can prevent the client from being installed.
Backup issues
How can I get a free trial for local database backup?
The free trial for local database backup is the same as the free trial for ECS database backup. For more information about the free trial, see 30-day Free Trial.
What are the network requirements for local database backup?
The local database server must be connected to the Alibaba Cloud virtual private cloud (VPC) through a leased line or VPN. The routing must be configured from on-premises to the cloud at 100.64.0.0/10 or 100.64.0.0/11, 100.96.0.0/11.
What is the minimum interval for real-time backup? Can it be configured with incremental backup?
Real-time backup can theoretically achieve a recovery point objective (RPO) of seconds and currently supports MySQL and Oracle databases. After you enable real-time backup, you cannot configure a separate traditional log backup. However, you can still use it with an incremental backup to further enhance your data protection policy.
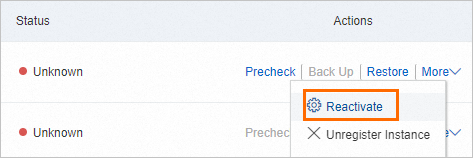
How do I change the username and password for a database backup?
During the backup process, use Reactivate to change the username and password for your backups, for example, if a password expires. Reactivation does not affect existing backup plans. However, it does affect backup jobs that are in progress. We recommend the following:
On the Backup Plans tab, pause any real-time log backups.
In the Actions column for the database, choose More > Reactivate.
What do I do if a database backup fails?
MySQL database backup fails
In the Job History, the job status is Error.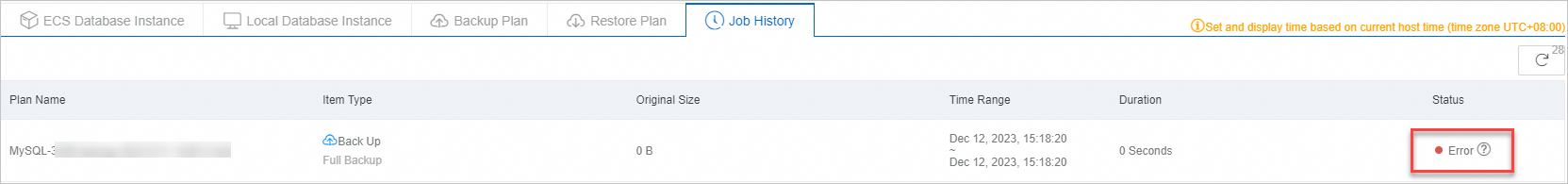
Follow these steps:
Log on to the ECS instance or local server and check the MySQL service status.
Use the command
systemctl status mysqld. A normal service status is "active". A status of "inactive" is abnormal. If the status is "inactive", restart the service and try again.Confirm that the database username, password, and permissions are configured correctly. This issue can also be caused by an expired password or insufficient permissions after a user's permissions are changed.
If the Database Account or Password entered during registration is incorrect, or if the user account has insufficient permissions, ensure that the username and password are correct and grant the required permissions to the backup account. We recommend creating a dedicated user for backups.
The minimum required permissions are RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION, and PROCESS.
Log on to the server and view the backup log.
Linux client log path:
/var/log/dbackup3/agent.logIf the keyword uploadPart SecurityTokenExpired appears, the local time is incorrect. Correct the local time.
If the keyword ib_logfile0 appears, a restore operation was performed while another restore job was not yet complete. This caused ib_logfile0 to be deleted but not recreated, which leads to subsequent backup failures.
If the message Error: failed to execute query LOCK TABLES FOR BACKUP: Access denied; you need (at least one of) the RELOAD privilege(s) for this operation appears, the account that is used for the backup has insufficient permissions. To perform a backup job, the account needs at least the following permissions: RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION, and PROCESS. In MySQL 8.0, the BACKUP_ADMIN permission is also required.
If the message no space left on device appears, a restore job fails for MySQL backup client version 29292 because of insufficient disk space. Incremental backup files need to be restored to the cache. Create a symbolic link to point the storage path to another disk to resolve the space shortage.
If the log backup status in the console is "Error" and the log contains the keyword @LM_ERROR@agent|To backup binlog in slave node needs to set log_slave_updates to ON, the backup node is a slave node. To perform log backups correctly, set the configuration item
log_slave_updates=1to enable this setting. After you change this configuration, you must perform a full backup before you perform a log backup.
Oracle database backup fails
Log on to the server and view the backup log.
Linux client log path:
/var/log/dbackup3/agent.logWindows client log path:
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.logIn the log, check the entries around the time the task failed. If the backup log contains any of the following error messages, use the corresponding solution:
If the keyword ORA-12560: TNS:protocol adapter error appears, check whether the ORACLE_SID environment variable is not set or is set incorrectly. An incorrect setting prevents a connection to Oracle. Try to log on using the sqlplus command with sysdba permissions. If you can log on successfully after you correctly configure the ORACLE_SID environment variable, the issue is resolved.
If the keyword sbtclose2 returned error-failed to close file appears, the local time differs significantly from the server time, or the system time zone is set incorrectly. Change the time on the database server and restart the dbackup3-agent service. For more information about how to restart the service, see How do I check the client process status, find the log path, and restart the client?.
If the keyword Failed to probe oracle instances appears, there are two possible causes:
The Oracle instance was not started when the client was installed.
Restart the dbackup3-agent service. For more information about how to restart the service, see How do I check the client process status, find the log path, and restart the client?.
The ORACLE_HOME environment variable is not configured correctly.
For Linux: Run
/etc/init.d/dbackup3-agent config oracleand enter the actual $ORACLE_HOME path.Restart the dbackup3-agent service. For more information about how to restart the service, see How do I check the client process status, find the log path, and restart the client?.
If the keyword ORA-12154: TNS:could not resolve the connect identifier specified appears, your password contains special characters that cause validation to fail. This results in a backup failure.
If the keyword ORA-01017: invalid username/password; logon denied appears, reactivate the instance with the correct username and password and then perform the backup again.
If the keyword The difference between the request time and the current time is too large appears, the time on the server where the Cloud Backup client is installed does not match the time on the Cloud Backup server.
Solution:
Check and sync the time: To ensure that the server time is synchronized with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) service for automatic synchronization. On Linux, use the
ntpdateorchronycommand to sync the time. Run thesudo ntpdate pool.ntp.orgcommand for manual synchronization.Check the time zone settings: To ensure that the time zone is set correctly, use the
timedatectlcommand to view and set the time zone.Restart the backup client and then run the backup operation again in the Cloud Backup console. For more information about how to restart the client, see How do I check the client process status, find the log path, and restart the client?.
SQL Server database backup fails
If a backup fails when you use Cloud Backup to back up an SQL Server, follow these steps:
Log on to the server and view the backup log.
The Windows client log path is:
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.logIn the log, find and analyze the entries around the time the task failed based on the time range (start time and end time) from the error record in the console. If the backup log contains any of the following error messages, use the corresponding solution:
Error: The login has insufficient permissions.
Analysis: The SQL Server backup user has insufficient permissions.
Solution: Check the backup account and its permissions. For more information, see Step 2: Create a backup account and configure permissions.
Error: Login failed for user 'xxx'.
Analysis: The password for the SQL Server backup user has expired (Error Code: 18487, SQL State: 28000).
Solution: Change the backup user's password in SQL Server. Then, log on to the Cloud Backup console and in the Actions column for the database, choose More > Reactivate.
Error: Cannot overwrite file.
Analysis: The SQL Server database restore path is occupied by another database.
Solution: Create a new restore job. When you restore from a specified backup, double-click to modify the restore path.
Error: The target SQL Server database does not exist. Make sure you have entered the name correctly.
Analysis: The target SQL Server database does not exist.
Solution: Confirm that the target database exists. If the database no longer exists, edit the backup plan and remove the corresponding database.
Error: The database is participating in a database mirroring session or an availability group. Some operations are not allowed on a database that is participating in a database mirroring session or an availability group.
Analysis: SQL Server AlwaysOn is enabled for the SQL Server database.
Solution: The target instance is not attached to an AlwaysOn cluster. Select the corresponding cluster.
Error: The database is configured for database mirroring or is joined to an availability group. If you want to restore the database, use ALTER DATABASE to remove mirroring or remove the database from its availability group.
Analysis: SQL Server AlwaysOn is enabled for the SQL Server database.
Solution: The target instance is not attached to an AlwaysOn cluster. Select the corresponding cluster.
Error:
The backup job fails in the console with the message "Job failed, error: -1 Backup or restore of database ""xxx"" failed, VDI error "0x80770004"".
Troubleshooting steps:
Go to the
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.logdirectory and open the log file. Locate the logs around the time the task failed based on the time range (start time and end time) from the error record in the console.If the log contains "Failed to receive WebSocket data from x.x.x.x:60305, errno=10054, connection reset" or "Failed to open socket x.x.x.x:60305, errno=10060, connection timed out", the connection between the client and the backup server was interrupted. Check the network connectivity.
When "Channel xxxxxxxxxxxxxx is registered" appears in subsequent logs, the client has reconnected to the server after it retries. Trigger a new backup job or wait for the next scheduled job to run and check whether the backup proceeds normally.
If the backup still fails or other errors occur, join the internal support group or contact a service expert for further technical support. You can send logs using DingTalk.
Cloud Backup Technical Support Group
Obtain quick answers to questions about costs, features, and usage. Search for the public DingTalk group and join. The DingTalk group number is 88650005148.
Cloud Backup Expert Support
Technical experts provide on-site analysis to quickly resolve product issues. Click to contact Cloud Backup support. We recommend that you use Chrome. Add the DingTalk contact. The DingTalk ID is d37_g935gslgo.
What do I do if the time taken for an incremental backup of Oracle data is equal to or greater than the time for a full backup?
Symptom
The time that is taken for an incremental backup and a log backup is close to or even exceeds the time for a full backup.
Solution
Enable Block Change Tracking (BCT) in the Oracle database. BCT is a feature that is used to speed up RMAN incremental backups by tracking changes to data blocks. This reduces backup time. This setting is disabled by default. You must manually enable it to take advantage of its ability to accelerate RMAN incremental backups.
Scenarios where we recommend that you enable BCT:
Frequent incremental backups: systems that perform daily or hourly RMAN incremental backups.
Large databases: optimization of incremental backup time for terabyte-scale databases.
High availability requirements: production environments that require fast recovery and rely on incremental backups.
Scenarios where you should enable BCT with caution:
Very small databases: for databases smaller than 1 GB, the benefits of BCT may not be significant.
Extreme high-write loads: for OLTP systems with tens of thousands of transactions per second, the performance impact needs to be considered.
Limited storage space: if disk space is limited, the storage requirements of the BCT file need to be evaluated.
RMAN reports a non-fatal error during an Oracle incremental backup
Symptom
Oracle full backups are successful, but incremental backups consistently fail. The following error message is reported:
oracle.phxxdb.18472|RMAN reports a non-fatal error: ORA-19505: failed to identify file "/arch/1_5137021_976544044.dbf" ORA-27037: unable to obtain file status Linux-x86_64 Error: 2: No such file or directory Additional information: 3Cause
The required archived logs cannot be found. This issue can occur if another script or backup job moves the archived logs. If other backup scripts or software run concurrently with Cloud Backup, these external processes can change the location of the archived logs. This causes the Cloud Backup incremental backup to fail because it cannot find the necessary files.
Solution
Do not use Cloud Backup concurrently with other backup software or scripts. This can cause backups to fail or become unrecoverable.
What do I do if browsing database details fails when I back up SQL Server 2019?
Symptom
When you create or edit a backup plan for SQL Server 2019 and select a database instance, the console displays the error message: "Failed to list unibackup instance detail".
Cause
When you back up SQL Server 2019, if other backup software or scripts are performing backup operations at the same time, browsing database details may fail when you create or edit a backup plan and select a database instance.
Solution
In the SQL Server database, query the number of databases and backup sets.
select count(database_id) from master.sys.databases select count(backup_set_id) from msdb.dbo.backupsetDelete the backup records in msdb.dbo.backupset.
ImportantDeleting backup records affects you. If you have your own backups, the backup records are purged, and you cannot restore these records through the normal process. However, this does not affect your data backups because the next backup is automatically converted to a full backup. Note that when you back up SQL Server 2019, you cannot use it with other backup software or scripts at the same time.
use msdb; exec sp_delete_backuphistory @oldest_date = '04/10/2024' ---Retain records from 4/10 onwards, delete all before 4/9. You need to confirm the retention period.
What to do if the IP address for a local SQL Server database is incorrect in the Cloud Backup console
Symptom
After you register a local SQL Server database with Cloud Backup, the IP address displayed in the Cloud Backup console does not match the IP address of the local machine. This issue can occur even if the local client status is Normal and the IP address of the local machine has not been changed.
Cause
This issue occurs in an environment with multiple network interface cards because Cloud Backup retrieves the IP address from an unused network interface card.
Solution
Disable the unused network interface card and then reinstall the client.
Can I back up an SQL Server database to Alibaba Cloud after enabling Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)?
No.
What do I do if the client goes offline, cannot be uninstalled, and the anti-ransomware policy fails to be deleted after deploying the anti-ransomware service for an SQL Server database?
Symptom
After you deploy the anti-ransomware service for an SQL Server database, the client is offline, the anti-ransomware policy cannot be deleted, and the client cannot be uninstalled.
At this point, the dbackup3-agent service in Windows Task Manager is stopped, and the agent log contains entries similar to "Stopping all jobs".

Cause
The client is blocked by antivirus software. Check the antivirus software for any related block records at the corresponding time.
Solution
Add the client to the trusted list in the antivirus software, and then restart the client service or reinstall the client.
What do I do if I cannot install or use the Database Backup feature after transferring an ECS instance from its original Alibaba Cloud account to a new one?
When you transfer an ECS instance from its original Alibaba Cloud account to a new one, the ECS metadata is not automatically synchronized to the Cloud Backup service. You must first complete the synchronization in the Cloud Backup service backend before installing and use the feature. For specific steps, contact "Cloud Backup Support" or join the "Cloud Backup Online Support" DingTalk group for assistance.
Cloud Backup Technical Support Group
Obtain quick answers to questions about costs, features, and usage. Search for the public DingTalk group and join. The DingTalk group number is 88650005148.
Cloud Backup Expert Support
Technical experts provide on-site analysis to quickly resolve product issues. Click to contact Cloud Backup support. We recommend that you use Chrome. Add the DingTalk contact. The DingTalk ID is d37_g935gslgo.
Are there limits on the supported MySQL database versions and operating systems for backup?
Yes, there are. Limits apply to the supported database versions, operating systems, and backup features. For example, MySQL databases that are deployed in Windows are not supported. For more information, see Compatibility list and limits.
How do I back up a newly created database in MySQL?
MySQL backups are performed at the database instance level. You do not need to manually configure backups for new databases. The next backup automatically includes the new database.
How do I cancel a database backup?
Cancel a MySQL database backup
After you completely and correctly cancel a database backup, no extra fees are incurred and no resources are occupied.
When you cancel a database backup, your backup data is deleted and cannot be recovered. You must evaluate the impact before you proceed.
Delete the backup plan.
Unregister the instance. When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled.
If the MySQL database is installed on a local server, log on to the local service and uninstall the client.
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-mysql" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-mysql" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Delete the following directories:
Linux:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Delete the backup vault.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Vault Management, and then find and delete the backup vault.
Cancel an Oracle database backup
After you completely and correctly cancel a database backup, no extra fees are incurred and no resources are occupied.
When you cancel a database backup, your backup data is deleted and cannot be recovered. You must evaluate the impact before you proceed.
Delete the backup plan.
Unregister the instance. When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled.
If the Oracle database is installed on a local server, log on to the local service and uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the command.
.\uninstall-unibackup.exe /S /NCRC
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-oracle" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-oracle" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Clear the configuration files.
Windows:
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.Linux:
Delete the following directories:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Delete the backup vault.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Vault Management, locate the target backup vault, and delete it.
Cancel an SQL Server database backup
After you completely and correctly cancel a database backup, no extra fees are incurred and no resources are occupied.
When you cancel a database backup, your backup data is deleted and cannot be recovered. You must evaluate the impact before you proceed.
Delete the backup plan.
Unregister the instance. When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled.
If the SQL Server database is installed on a local server, log on to the local service and uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the
uninstall-unibackup.execommand and follow the wizard to complete the uninstallation.
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.Delete the backup vault.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Vault Management. Find and delete the corresponding backup vault.
Why are there duplicate or unexpectedly timed records in the backup history?
This issue usually occurs when the server (local server or ECS instance) on which the Database Backup client is installed is cloned, or when a new ECS instance or local server is created from an image that contains the same backup client. Because the cloned server retains some of the client information from the original server, duplicate backup records may be generated. To resolve this issue, log on to the cloned server and uninstall the client. For more information about how to uninstall the backup client, see the following steps:
Uninstall the MySQL backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the MySQL database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-mysql" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-mysql" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Delete the following directories:
Linux:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Uninstall the Oracle backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the Oracle database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the command.
.\uninstall-unibackup.exe /S /NCRC
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-oracle" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-oracle" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Clear the configuration files.
Windows:
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.Linux:
Delete the following directories:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Uninstall the SQL Server backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the SQL Server database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the
uninstall-unibackup.execommand and follow the wizard to complete the uninstallation.
Clear the configuration files.
Windows:
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.
Why does a backup fail and the backup plan status show "Error"?
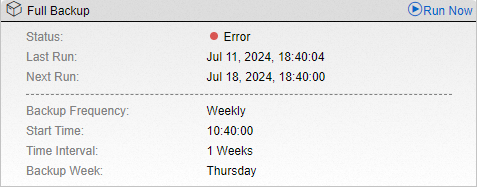
If a backup plan status is "Error" and the backup fails, first check whether the server (local server or ECS instance) where the client is installed has been cloned, had its operating system reinstalled, or had its system disk reset. These operations can invalidate the association between the backup plan and the client. To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
Make sure that you have uninstalled the client and its configuration files from the cloned server. For more information, see Uninstall the client.
Make sure that the client status on the current server is "Installed".

After you complete the preceding steps, delete the original backup plan from the console and create a new one.
Why is the alert time different from the actual error time?
Text message alerts have a nighttime suppression feature that delays alerts that are triggered between 8:00 PM and 8:00 AM the next day until after 8:00 AM. Email alerts are not affected by this feature and are sent immediately.
Why do I receive a failure alert email or text message, but the backup history shows both a successful and a failed backup record at the same time?
This issue usually occurs when the server (local server or ECS instance) on which the Database Backup client is installed is cloned, or when a new ECS instance or local server is created from an image that contains the same backup client. Because the cloned server retains some of the client information from the original server, duplicate backup records may be generated. To resolve this issue, log on to the cloned server and uninstall the client. For more information about how to uninstall the backup client, see the following steps:
Uninstall the MySQL backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the MySQL database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-mysql" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-mysql" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Delete the following directories:
Linux:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Uninstall the Oracle backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the Oracle database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the command.
.\uninstall-unibackup.exe /S /NCRC
Linux:
CentOS
sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent-oracle" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-agent" sudo rpm --erase "dbackup3-common"Ubuntu
sudo dpkg -r "dbackup3-agent-oracle" "dbackup3-agent" "dbackup3-common"
Clear the configuration files.
Windows:
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.Linux:
Delete the following directories:
/etc/default/dbackup3* /opt/scutech /var/opt/scutech/ /var/log/dbackup3/ /etc/opt/scutech/
Uninstall the SQL Server backup client
When you unregister an ECS instance database, the installed backup client is automatically uninstalled. If the SQL Server database is installed on a local server, uninstall the client as follows:
Uninstall the client.
Windows:
Go to the backup client installation directory (PowerShell). For example,
C:\Program Files\aliyun\unibackup>.Run the
uninstall-unibackup.execommand and follow the wizard to complete the uninstallation.
Clear the configuration files.
Windows:
Delete all configuration files under
c:\programdata\scutech.
Restore issues
Description of the "View Offline Instances Only" feature
The View Offline Instances Only feature is useful in scenarios where a client can no longer connect to its original instance server or restore backup data. This can happen if the operating system of the client machine is reinstalled, or if the client process and configuration are deleted by malicious software. If you install a new client in this situation, the system assigns a new instance ID to distinguish the new client from the offline one and prevent confusion. Then restore data from the offline instance to the new client instance. For more information about the restore steps, see Restore MySQL, Restore Oracle, and Restore SQL Server.
What do I do if an SQL Server database restore fails?
Log on to the server and view the backup log.
Windows client log path:
C:\ProgramData\scutech\dbackup3\agent\log\dbackup3-agent.logIn the log, check the entries around the time the task failed.
If the backup log contains the keyword RestoreContainer::ValidateTargetForCreation, it indicates that when you restored a database with the same name, you changed only the path but not the database name. This caused a name conflict and the restore operation failed. To successfully restore the database, you must change both the database name and the path.
What do I do if a SQL Server recovery fails and the agent log indicates a file initialization error?
Symptom
When a SQL Server recovery fails, the agent log indicates that a file failed to initialize. The log contains the following details:
2025-11-10 11:25:53.967@iZrxhug********@2208@LM_INFO@dbackup3-agent|[SQLSERVER] output: 100 percent processed. 2025-11-10 11:25:53.968@iZrxhug********@2208@LM_INFO@dbackup3-agent|[SQLSERVER] output: Processed 51595000 pages for database 'xxx', file 'xxx' on file 1. 2025-11-10 11:25:53.985@iZrxhug********@2208@LM_INFO@dbackup3-agent|[SQLSERVER] output: Processed 3865 pages for database 'xxx', file 'xxx_log' on file 1. 2025-11-10 11:25:53.987@iZrxhug********@2208@LM_INFO@dbackup3-agent|[SQLSERVER] output: File "xxx_log" failed to initialize correctly. See the error log for details. 2025-11-10 11:25:53.989@iZrxhug********@2208@LM_INFO@dbackup3-agent|[SQLSERVER] output: RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally.Additionally, the SQL Server error log reports the message
the file "xxx_log" failed to initialize correctly.
Cause
If a source database on SQL Server 2008 R2 was previously encrypted, disabling encryption can leave residual information. When you back up this database and restore the backup set to another instance, an initialization error occurs. The analysis process is as follows:
NoteIf the source database is SQL Server 2008 R2 and has transparent data encryption (TDE) enabled, the recovery operation fails even if the target instance is a later version, such as SQL Server 2014. The error message "Certificate not found" is returned. To complete the recovery, you must manually restore the certificate and private key.
Confirm the database version from the SQL Server error log.

This issue is likely related to TDE. Confirm whether TDE is enabled on the source database. Also, check if operations such as disabling encryption were recently performed.
Execute the following SQL statement on the source database. If the
key_algorithmandkey_lengthfields in the query result are not NULL, the database was likely encrypted in the past.USE master; SELECT d.name, d.is_encrypted, drs.database_id, drs.encryption_state, drs.percent_complete, drs.key_algorithm, drs.key_length FROM sys.databases AS d LEFT JOIN sys.dm_database_encryption_keys AS drs ON d.database_id = drs.database_id;The following figure shows a sample query result.

Solution
Upgrade the source database to a later version and create a new backup. Use the new backup set to perform the recovery. Previous backup sets are invalid.
Restore the private key and certificate from the source instance to the target instance, and then perform the recovery operation.
After the recovery is complete, delete the TDE encryption certificate and database encryption key from the target instance. Then, back up the target instance. Subsequent backup and recovery operations on the target instance will function correctly.
NoteEven if the data backup was created after TDE was disabled, the recovery process still requires the private key and certificate. These are required to process the residual encrypted metadata in the backup. However, the restored database is not encrypted. You can then use the database normally without the certificate.
# Perform the following operations on the source instance USE master; # 1. Query the certificate name for the TDE-encrypted database SELECT d.name AS DatabaseName, k.encryption_state, c.name AS CertificateName FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys AS k JOIN sys.certificates AS c ON k.encryptor_thumbprint = c.thumbprint JOIN sys.databases AS d ON k.database_id = d.database_id # Assume the CertificateName in the result is TDECert. Back up the TDE certificate and private key to a custom path. BACKUP CERTIFICATE TDECert TO FILE = 'C:\Backup\TDECert.cer' -- Specify a custom file path WITH PRIVATE KEY ( FILE = 'C:\Backup\TDECert_PrivateKey.pvk', -- Specify a custom file path ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'Strong_Password_123!' -- Remember this password ); -- Copy the certificate and private key from the path above to the target instance # 2. Perform the following operations on the target instance USE master; # Restore the master key. If the message 'The master key already exists in the database. Drop the master key before you perform this statement.' is returned, skip this step. CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'Another_Strong_Password_456!'; # Restore the TDE certificate CREATE CERTIFICATE TDECert -- Specify a custom certificate name. You will use it later for deletion. FROM FILE = 'C:\TDE_Test\TDECert.cer' -- The path where the copied files are located WITH PRIVATE KEY ( FILE = 'C:\TDE_Test\TDECert_PrivateKey.pvk', DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'Strong_Password_123!' -- The password used to back up the private key ); # 3. Perform the recovery steps in the Cloud Backup console as usual # 4. After recovery, delete the database encryption key USE TDE_TestDB_Restore -- The name of the target database DROP DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY; # 5. Delete the certificate USE master; DROP CERTIFICATE TDECert;
How do I perform a cross-database restore between a local database and an ECS database?
Direct mutual restoration is not supported. Register the database on the ECS instance as a local database instance. After registration, restore data between different local database instances.
Backup vault issues
What is a database backup vault?
You must create a database backup vault before you create a database backup plan.
A database backup vault is a storage vault that stores your database backup data. The cost of a database backup is determined by the vault rental fee and the vault capacity. For more information, see Billing methods and billable items.
How does a database backup vault purge expired data?
Incremental backups, cumulative incremental backups, and log backups depend on a complete preceding backup chain. The backup chain includes the preceding full backup and any incremental, cumulative incremental, or log backups. In a backup chain that includes a full backup and incremental, cumulative incremental, and log backups, all backups on which the complete backup chain depends are retained in the backup vault and occupy backup space until the last backup in the chain expires. You must configure the backup cycle and expiration time in a reasonable manner.
For example, you perform a full backup on September 1 and an incremental backup every day from September 2 to September 7. The retention period is 7 days. The seven backups from September 1 to September 7 are automatically deleted after all data expires on September 14.
How do I view the backup data size and backup vault usage? What is the billing basis?
Source Data Size is the total amount of data that has been backed up. For example, if you back up a 1 TB file twice, the source data size is 2 TB. Cloud BackupCloud Backup uses deduplication and compression to reduce backup vault usage and lower your costs. Billing is based on the actual Storage Vault Data Size. View the Source Data Size and Storage Vault Data Size of a database backup vault on the Vault Management page.