Configuring an HTTPS certificate for an accelerated domain name on CDN encrypts communication between clients and CDN points of presence (POPs). This prevents data from being intercepted or tampered with during transmission, enhancing your business security.
You can deploy certificates that you purchase from Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service to the CDN platform in batches. For more information, see Deploy HTTPS certificates in batches.
Before you start
To ensure a successful deployment, review these requirements and limitations:
Purchase a certificate: If you do not have a certificate, you can go to the SSL Certificates Service console to purchase a commercial certificate.
Private key requirements: If you upload a custom certificate, the private key must not be password-protected. You must first verify that password protection is removed from the private key file.
Procedure
Log on to the CDN console.
In the left navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the target domain name and click Manage in the Actions column.
In the domain's navigation pane, click HTTPS.
In the HTTPS Certificate section, click Modify.
On the Modify HTTPS Settings page, turn on the HTTPS Secure Acceleration switch, and configure the certificate parameters.
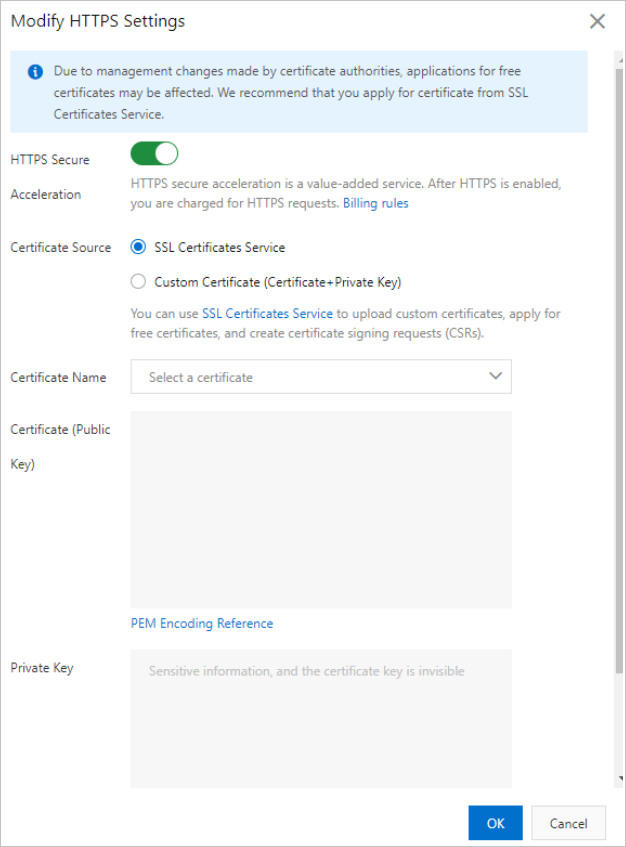
If you purchased a certificate from Certificate Management Service (formerly SSL Certificates Service), select SSL Certificates Service. Then, in the Certificate Name field, select your purchased certificate.
NoteIf you cannot select your purchased certificate, check whether the domain name bound to the certificate is the same as the accelerated domain name.
If you use a certificate issued by a third-party service provider, select Custom Certificate (Certificate+Private Key). Specify a Certificate Name, and then upload the Certificate (Public Key) and Private Key. The certificate is saved to Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service. You can view it on the My Certificates page.
Uploading a custom certificate has strict format requirements for the Certificate (Public Key) and Private Key. If a configuration fault occurs or you do not understand the configuration example, see Upload a custom certificate for instructions about how to prepare the Certificate (Public Key) and Private Key for upload.
Parameter
Description
Certificate Name
Set a name for the certificate that you want to upload.
The name can contain only letters, periods, numbers, underscores (
_), and hyphens (-), and must be unique.Certificate (Public Key)
Enter the PEM-encoded content of the certificate file.
Private Key
Enter the PEM-encoded content of the private key. Because the private key is sensitive information, you cannot view or export it from the console after it is uploaded. Store the private key in a secure location.
Click OK.
Verify the HTTPS configuration
By browser: In a browser, access
https://your-accelerated-domain-name. The configuration is successful if a security lock icon appears in the address bar and you can view the correct certificate information after you click the icon.
By command-line: Run the
curl -I https://your-accelerated-domain-namecommand. The HTTPS service is active if a200status code is returned.
Disable HTTPS secure acceleration
If you no longer require HTTPS secure acceleration, you can disable the feature in the CDN or console. The change takes effect immediately. After you disable the feature, clients can no longer access resources over HTTPS, and the certificate and private key are not retained.
To enable HTTPS secure acceleration again, you must reselect a certificate.
Upload custom certificate
If you have a certificate that is issued by a third-party service provider or is self-signed, you must first prepare the certificate and private key in a format that CDN supports, and then upload them.
Certificate (public key)
CDN supports only certificates in PEM format. If your certificate is in another format, convert it to the PEM format. For more information, see Convert the format of a certificate. The requirements for uploading certificate content vary based on the certification authority:
Certificates issued by a root certificate authority (one certificate file)
Open the PEM certificate file in a text editor. Upload the entire content, including the lines that start with
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----and end with-----END CERTIFICATE-----.-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- [Certificate content] -----END CERTIFICATE-----Certificates issued by an intermediate authority (multiple certificate files)
Concatenate the server certificate and all intermediate CA certificates in order into a single certificate chain file. The file content must follow this format:-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- [Server certificate content] -----END CERTIFICATE----- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- [Intermediate CA certificate content] -----END CERTIFICATE-----
Private key
The file extension for a private key is typically.keyor.pem. Open the private key file in a text editor. The upload requirements differ for various private key formats:Upload an RSA private key directly
If the private key starts with
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----and ends with-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----, upload the private key content directly.-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- [Private key content] -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----Convert other private key formats before uploading
If your private key starts with
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----and ends with-----END PRIVATE KEY-----, first convert the key using an OpenSSL command. Then, upload the content of the converted private key. In the command,old_server_key.pemis the original private key andnew_server_key.pemis the converted private key.# Private key to be converted -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- [Private key content] -----END PRIVATE KEY-----# Conversion command openssl rsa -in old_server_key.pem -out new_server_key.pem
Billing
Enabling the HTTPS secure acceleration feature incurs additional fees.
Billable item: HTTPS requests for static content. This fee is charged independently of CDN data transfer fees. You are charged for the total number of HTTPS requests for static content that are initiated from all accelerated domain names under your account.
Billing methods: Both pay-as-you-go supported.
Billing note: CDN outbound data transfer plans do not cover charges for HTTPS requests.
References
Document | Description |
You can configure the force redirect to HTTPS feature to redirect HTTP requests from clients to POPs to more secure HTTPS requests. | |
Enable the HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) feature to force clients, such as browsers, to use HTTPS to connect to POPs. This improves security. | |
POPs cache the online certificate validation results in advance and send the results to clients. This way, browsers do not need to query the certificate status from the CA website, which reduces the verification time for users. |
FAQ
Related APIs
API | Description |
Creates a CSR file. | |
Queries the certificate information about a specified accelerated domain name. | |
Enables or disables the certificate feature for a domain name and updates the certificate information. | |
Configures an HTTPS certificate for a specified domain name. | |
Queries accelerated domain names based on certificate information. | |
Queries the details of a CDN certificate. | |
Queries a list of certificates. | |
Queries the information about a specified certificate. | |
Queries all certificate information of a user. | |
Queries the number of domain names whose certificates have expired. | |
Enables or disables the SM certificate feature for a domain name. | |
Queries the list of SM certificates for a specified accelerated domain name. | |
Queries the details of an SM certificate. |