ASM instances of version 1.16.4 and later allow you to use CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) fields to define an egress traffic policy. This topic describes how to use an egress traffic policy to manage egress traffic.
Background
Principle
ASM supports egress traffic management by creating multiple resources such as ServiceEntry, VirtualService, Gateway, and Destination, and ensuring that these resources are interconnected. Upon completion of the configuration, it achieves transparent redirection of traffic to the egress gateway, which then forwards it to external services.
These configurations are complex and require a deep understanding of the relevant fields, making them prone to errors. To lower the threshold for egress traffic configuration, ASM introduces the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy resource.
ASMEgressTrafficPolicy abstracts and simplifies egress traffic configuration. Instead of manually configuring resources like ServiceEntry, VirtualService, Gateway, and Destination, you only need to add some necessary configurations to achieve transparent redirection of traffic to the egress gateway and send it to external services through HTTP/HTTPS protocols.
Since ASMEgressTrafficPolicy simplifies native resources of ASM, it may not meet some of your advanced needs (such as proportional routing of egress traffic, initiating mTLS from the egress gateway, and others). If you need to use advanced features, such as adding custom configurations, see Configure an egress gateway to route all outbound traffic in ASM.
Feature
ASM provides a unified way to connect, manage, and protect communication between applications. Unlike IP-based methods, ASM uses an application-centric approach without requiring modifications to existing application code. ASMEgressTrafficPolicy defines how to manage and access external traffic through the egress gateway. By combining the ASM egress gateway and AuthorizationPolicy, you can more flexibly control egress traffic. 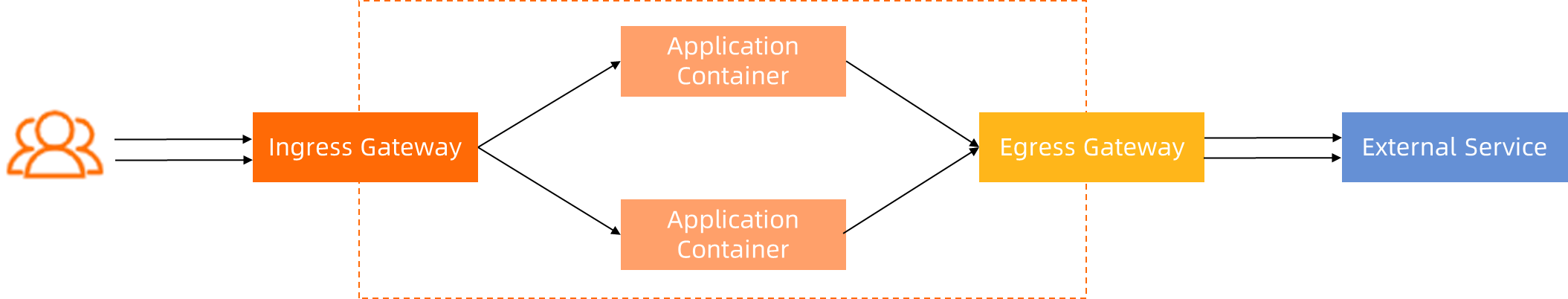
The traffic paths in this example can be categorized into two types:
1. Communication between sidecar proxies and between sidecar proxies and gateways: By default, mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS) is enabled for the communication, and certificates are managed by ASM.
2. Communication between applications and sidecar proxies and between gateways and external services:
a. To ensure that advanced Layer 7 capabilities of ASM can function properly, applications and sidecar proxies communicate in plaintext as much as possible. In this way, sidecar proxies can obtain Layer 7 information of the traffic and support more advanced features. Due to some special reasons, if applications must send HTTPS requests directly, only Layer 4 capabilities of ASM can be used.
b. You can configure the communication protocol between an egress gateway and an external service, either plaintext or HTTPS.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance of a commercial edition (Enterprise Edition or Ultimate Edition) is created. The version of the instance is 1.16.4 or later. For more information, see Create an ASM instance. For information about upgrading an instance, see Upgrade an ASM instance.
Automatic sidecar injection is enabled for the default namespace. For more information, see Enable automatic sidecar proxy injection.
Preparations
Set an egress traffic policy for the ASM instance
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the global tab, click Outbound Traffic Policy, click REGISTRY_ONLY on the right of External Access Policy, and click Update Settings.
Create a namespace
Create the istio-egress namespace. For more information, see Manage global namespaces.
On the Global namespace page, click Sync Automatic Sidecar Injection to Kubernetes Cluster to sync the namespace to the ACK cluster managed by the ASM instance.
Create an egress gateway
Create an egress gateway named egressgateway-a in ASM, set Port Mapping to HTTP 80, HTTPS 443, and HTTPS 444, and enable Support two-way TLS authentication. For more information, see Create an egress gateway.
Ensure that the spec field in the generated YAML file contains the following content. If not, add such content:
spec:
podLabels:
security.istio.io/tlsMode: istioCreate services
Create a namespace named mytest for the ASM instance and enable automatic sidecar proxy injection. For more information, see Manage global namespaces.
In the ACK cluster, deploy the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace and deploy the NGINX service in the default namespace.
Create a file named test.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
In the ACK cluster, run the following command to deploy the sleep-a and NGINX services:
kubectl apply -f test.yaml
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a and NGINX services:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.org kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
502, indicating access failure.
Use the sleep-a service to access an external service over HTTP
Solution 1: Use HTTP plaintext for communication between the sidecar proxy and the egress gateway

This solution is not reasonable in a real environment. The communication between sidecar container and egress gateway over HTTP plaintext may result in unavailable client authentication. Currently, ASMEgressTrafficPolicy does not support using HTTP plaintext to access the egress gateway.
Traffic management is implemented in sidecar proxies on the client side and does not require egress gateways.
Observability does not rely on egress gateways.
Security capabilities depend on egress gateways. However, without mTLS, all authorization capabilities based on client identities are unavailable. In this case, egress gateways can only deny all requests indiscriminately.
(Recommended) Solution 2: Use mTLS for communication between the sidecar proxy and the egress gateway

Create an egress traffic policy.
Configure through the console
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the gateway name to enter the Gateway overview page. Click Outbound Traffic Policy on the left. Configure parameters as shown in the following figure.

Configure through kubectl
Create the egress-by-egressgateway.yaml file that contains the following content:
For more information about the fields, see ASMEgressTrafficPolicy CRD.
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: ASMEgressTrafficPolicy metadata: name: egress-by-egressgateway # The format of this value is egress-by-{Name of the egress gateway}. This value corresponds to the name of the egress gateway. namespace: istio-egress # This value is fixed to istio-egress. spec: byEgressGateway: name: egressgateway egressRules: - from: - namespace: mytest workloadSelector: app: sleep-a to: - name: httpbin-service-http hosts: - www.httpbin.org # The IP addresses of multiple domain names after DNS resolution must be the same. - httpbin.org # The IP addresses of multiple domain names after DNS resolution must be the same. port: name: http number: 80 protocol: HTTP byEgressGateway: port: 80 # Sidecar → 80 Gateway → 80 Service (httpbin.org)In the ACK cluster, run the following command to create the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy resource:
kubectl apply -f egress-by-egressgateway.yaml
Verify whether the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration takes effect.
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service in the default namespace.kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
200as expected.Run the following command to delete egress-by-egressgateway, and access
http://www.httpbin.orgagain through the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace.kubectl -n istio-egress delete ASMEgressTrafficPolicy egress-by-egressgateway kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service fails after the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration is deleted.
The output indicates that the egress traffic policy takes effect.
Use the sleep-a service to access an external service over HTTPS
(Recommended) Solution 1: Use mTLS for communication between the sidecar proxy and the egress gateway

Create an egress traffic policy.
Configure through the console
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the gateway name to enter the Gateway overview page and click Outbound Traffic Policy on the left. Configure parameters as shown in the following figure.

Configure through kubectl
Update the egress-by-egressgateway.yaml file with the following content:
The spec field is updated to include the httpsUpgrade field and the definition for direct access to
https://www.httpbin.org. For more information about the fields, see ASMEgressTrafficPolicy CRD description.apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: ASMEgressTrafficPolicy metadata: name: egress-by-egressgateway # The format of this value is egress-by-{Name of the egress gateway}. This value corresponds to the name of the egress gateway. namespace: istio-egress # This value is fixed to istio-egress. spec: byEgressGateway: name: egressgateway egressRules: - from: - namespace: mytest workloadSelector: app: sleep-a to: - name: httpbin-service-http hosts: - www.httpbin.org # The IP addresses of multiple domain names after DNS resolution must be the same. - httpbin.org # The IP addresses of multiple domain names after DNS resolution must be the same. port: name: http number: 80 protocol: HTTP byEgressGateway: port: 80 # Sidecar → 80 Gateway → 80 Service (httpbin.org) httpsUpgrade: enabled: true # If this value is set to false, the value of the port parameter under httpsUpgrade does not take effect. port: 443 # Sidecar → 80 Gateway → 443 Service (httpbin.org)In the ACK cluster, run the following command to create the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy resource:
kubectl apply -f egress-by-egressgateway.yaml
Verify whether the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration takes effect.
Verify the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace.
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://httpbin.orgThe output returns
200, indicating successful access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.Run the following command to request the
anythingAPI ofhttpbin.orgto verify whether the egress gateway upgrades the HTTP request to an HTTPS request:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- sh -c "curl -s http://httpbin.org/anything |grep url"Expected output:
"url": "https://httpbin.org/anything"You can see that the
urlfield information starts withhttps, indicating that the egress gateway successfully upgrades the request tohttpsand then forwards it tohttpbin.org.Run the following command to access
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
200, indicating successful access tohttps://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.
Verify the NGINX service in the default namespace.
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service.kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to access
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service:kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgThe output shows that the request connection is refused, indicating that access to
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to view the access logs of the sidecar proxy in the NGINX service workload and obtain the rejection reason:
kubectl -n default logs -f deployment/nginx -c istio-proxy --tail=1Expected output:
{"authority":"-","bytes_received":"0","bytes_sent":"0","downstream_local_address":"52.86.XX.XX:443","downstream_remote_address":"172.16.0.199:56748","duration":"0","istio_policy_status":"-","method":"-","path":"-","protocol":"-","request_id":"-","requested_server_name":"-","response_code":"0","response_flags":"UH","route_name":"-","start_time":"2023-04-11T02:00:07.409Z","trace_id":"-","upstream_cluster":"BlackHoleCluster","upstream_host":"-","upstream_local_address":"-","upstream_service_time":"-","upstream_transport_failure_reason":"-","user_agent":"-","x_forwarded_for":"-"}The expected output indicates that the request is forwarded to
BlackHoleCluster, resulting in the connection being refused.
Run the following command to delete egress-by-egressgateway, and access
http://www.httpbin.orgagain through the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace.kubectl -n istio-egress delete ASMEgressTrafficPolicy egress-by-egressgateway kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.org kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgWhen accessing
http://www.httpbin.org,502is returned. When accessinghttps://www.httpbin.org, the request connection is refused. After deleting the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration, access to bothhttp://www.httpbin.organdhttps://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service fails.
The output indicates that the egress traffic policy takes effect.
Solution 2: Use HTTPS for communication between the sidecar proxy and the egress gateway

Create an egress traffic policy.
Configure through the console interface
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the gateway name to enter the Gateway overview page and click Outbound Traffic Policy on the left. Configure parameters as shown in the following figure.
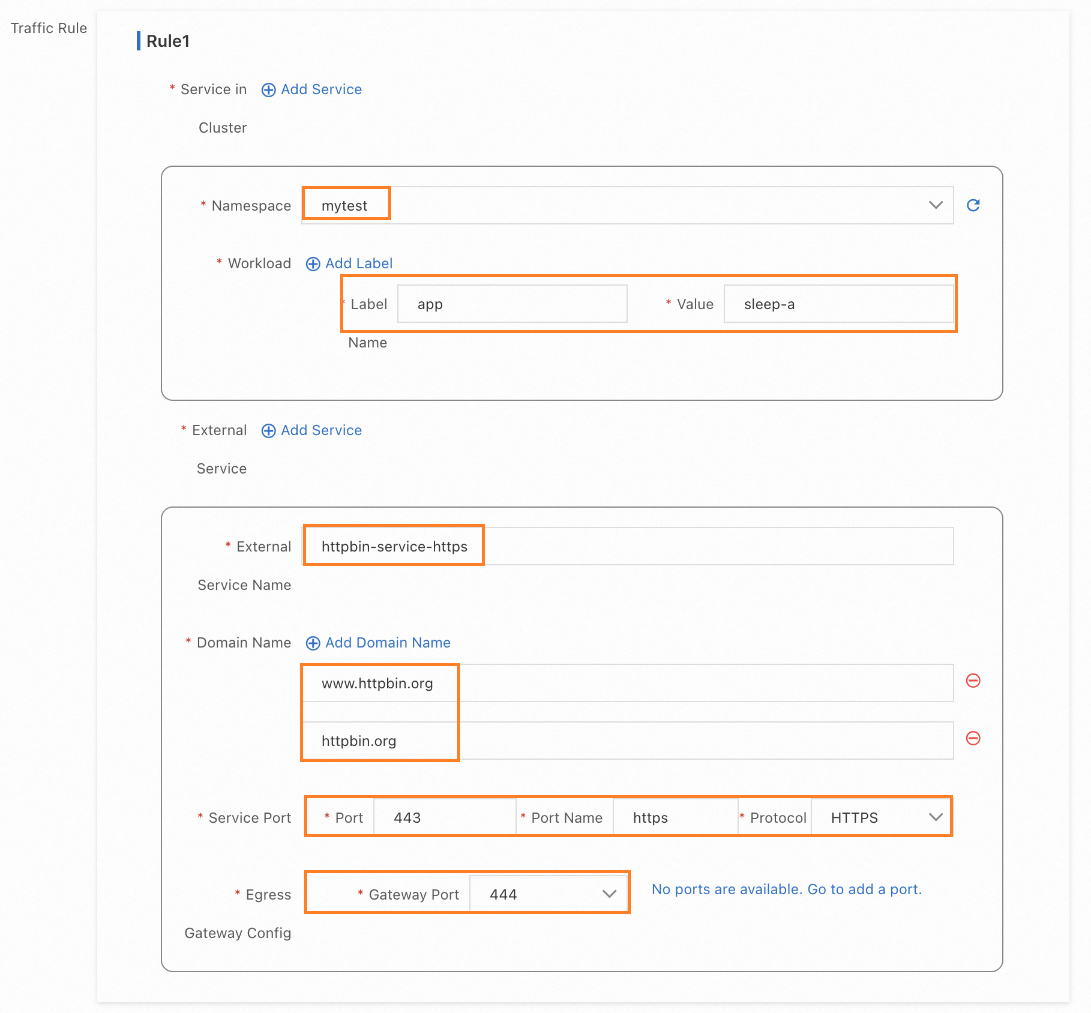
Configure through kubectl
Update the egress-by-egressgateway.yaml file with the following content:
The spec field is updated to include the httpsUpgrade field and the definition for direct access to
https://www.httpbin.org. For more information about the fields, see ASMEgressTrafficPolicy CRD description.apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: ASMEgressTrafficPolicy metadata: name: egress-by-egressgateway # The format of this value is egress-by-{Name of the egress gateway}. This value corresponds to the name of the egress gateway. namespace: istio-egress # This value is fixed to istio-egress. spec: byEgressGateway: name: egressgateway egressRules: - from: - namespace: mytest workloadSelector: app: sleep-a to: - name: httpbin-service-https hosts: - www.httpbin.org - httpbin.org port: name: https number: 443 protocol: HTTPS byEgressGateway: port: 444 # HTTPS 444 port defined in step 3 of Preparations.In the ACK cluster, run the following command to create the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy resource:
kubectl apply -f egress-by-egressgateway.yaml
Verify whether the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration takes effect.
Verify the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace.
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://httpbin.orgThe output returns
200, indicating successful access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.Run the following command to request the
anythingAPI ofhttpbin.orgto verify whether the egress gateway upgrades the HTTP request to an HTTPS request:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- sh -c "curl -s http://httpbin.org/anything |grep url"Expected output:
"url": "https://httpbin.org/anything"You can see that the
urlfield information starts withhttps, indicating that the egress gateway successfully upgrades the request tohttpsand then forwards it tohttpbin.org.Run the following command to access
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace:kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
200, indicating successful access tohttps://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service.
Verify the NGINX service in the default namespace.
Run the following command to access
http://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service:kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.orgThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to access
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service:kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgThe output shows that the request connection is refused, indicating that access to
https://www.httpbin.orgthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to view the access logs of the sidecar proxy in the NGINX service workload and obtain the rejection reason:
kubectl -n default logs -f deployment/nginx -c istio-proxy --tail=1Expected output:
{"authority":"-","bytes_received":"0","bytes_sent":"0","downstream_local_address":"52.86.XX.XX:443","downstream_remote_address":"172.16.0.199:56748","duration":"0","istio_policy_status":"-","method":"-","path":"-","protocol":"-","request_id":"-","requested_server_name":"-","response_code":"0","response_flags":"UH","route_name":"-","start_time":"2023-04-11T02:00:07.409Z","trace_id":"-","upstream_cluster":"BlackHoleCluster","upstream_host":"-","upstream_local_address":"-","upstream_service_time":"-","upstream_transport_failure_reason":"-","user_agent":"-","x_forwarded_for":"-"}The expected output indicates that the request is forwarded to
BlackHoleCluster, resulting in the connection being refused.
Run the following command to delete egress-by-egressgateway, and then access
http://www.httpbin.orghttps://www.httpbin.orgkubectl -n istio-egress delete ASMEgressTrafficPolicy egress-by-egressgateway kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.httpbin.org kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.httpbin.orgWhen accessing
http://www.httpbin.org,502is returned. When accessinghttps://www.httpbin.org, the request connection is refused. After deleting the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration, access to bothhttp://www.httpbin.organdhttps://www.httpbin.orgthrough the sleep-a service fails.
The output indicates that the egress traffic policy takes effect.
Use the sleep-a service to access an external service over TCP

Create an egress traffic policy.
Configure through the console
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the gateway name to enter the Gateway overview page and click Outbound Traffic Policy on the left. Configure parameters as shown in the following figure.
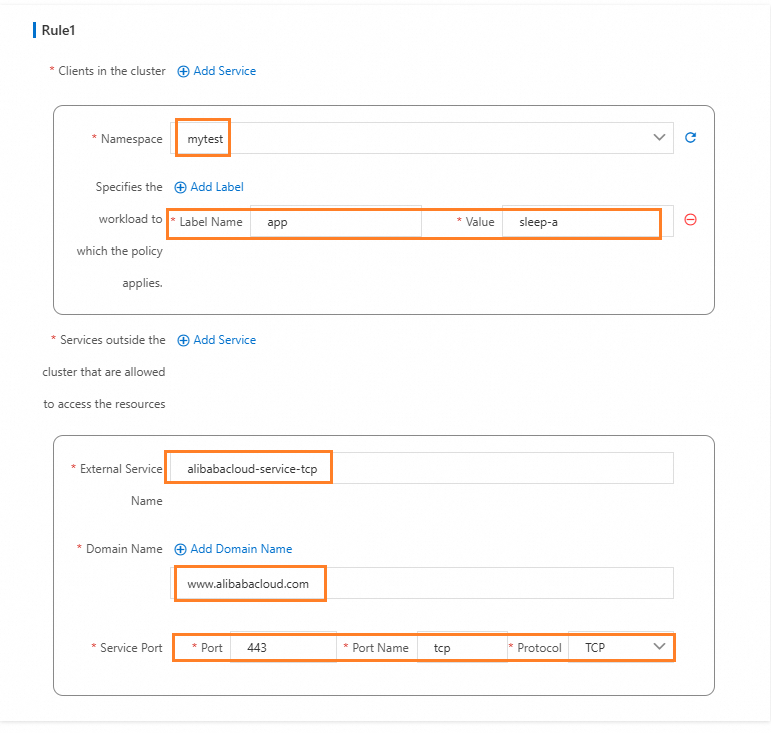
Configure through kubectl
Create the egress-by-egressgateway.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: ASMEgressTrafficPolicy metadata: name: egress-by-egressgateway namespace: istio-egress spec: byEgressGateway: name: egressgateway egressRules: - from: - namespace: mytest workloadSelector: app: sleep-a to: - byEgressGateway: {} hosts: - www.alibabacloud.com name: aliyun-service-tcp port: name: tcp number: 443 protocol: TCPIn the ACK cluster, run the following command to create the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy resource:
kubectl apply -f egress-by-egressgateway.yaml
Verify whether the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration takes effect.
Verify the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace.
Run the following command to access
www.alibabacloud.comthrough the sleep-a service.kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.alibabacloud.comThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the sleep-a service fails.Run the following command to access
https://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the sleep-a service service in the mytest namespace.kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.alibabacloud.comThe output returns
200, indicating successful access tohttps://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the sleep-a service.
Verify the NGINX service in the default namespace.
Run the following command to access
http://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the NGINX service:kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.alibabacloud.comThe output returns
502, indicating that access tohttp://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to access
https://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the NGINX service:kubectl -n default exec deployment/nginx -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.alibabacloud.comThe output shows that the request connection is refused, indicating that access to
https://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the NGINX service fails.Run the following command to view the access logs of the sidecar proxy in the NGINX service workload and obtain the rejection reason:
kubectl -n default logs -f deployment/nginx -c istio-proxy --tail=1Expected output:
{"authority":"-","bytes_received":"0","bytes_sent":"0","downstream_local_address":"52.86.XX.XX:443","downstream_remote_address":"172.16.0.199:56748","duration":"0","istio_policy_status":"-","method":"-","path":"-","protocol":"-","request_id":"-","requested_server_name":"-","response_code":"0","response_flags":"UH","route_name":"-","start_time":"2023-04-11T02:00:07.409Z","trace_id":"-","upstream_cluster":"BlackHoleCluster","upstream_host":"-","upstream_local_address":"-","upstream_service_time":"-","upstream_transport_failure_reason":"-","user_agent":"-","x_forwarded_for":"-"}The expected output indicates that the request is forwarded to
BlackHoleCluster, resulting in the connection being refused.
Run the following command to delete egress-by-egressgateway, and then access
http://www.alibabacloud.comandhttps://www.alibabacloud.comagain through the sleep-a service in the mytest namespace:kubectl -n istio-egress delete ASMEgressTrafficPolicy egress-by-egressgateway kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.alibabacloud.com kubectl -n mytest exec deployment/sleep-a -- curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" https://www.alibabacloud.comWhen accessing
http://www.alibabacloud.com,502is returned. When accessinghttps://www.alibabacloud.com, the request connection is refused. After deleting the ASMEgressTrafficPolicy configuration, access to bothhttp://www.alibabacloud.comandhttps://www.alibabacloud.comthrough the sleep-a service fails.The output indicates that the egress traffic policy takes effect.
Related operations
Reject POST requests sent from a specified namespace
By using an egress gateway and an egress traffic policy, you can flexibly control outbound traffic in a cluster. In combination with an authorization policy, you can implement more fine-grained access control. For example, you can use the following policy to reject POST requests sent from the mytest namespace:
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: sleep-a-egress-www-httpbin-org
namespace: istio-system
spec:
action: DENY
rules:
- to:
- operation:
hosts:
- www.httpbin.org
- httpbin.org
methods:
- POST
from:
- source:
namespaces: ["mytest"]
selector:
matchLabels:
istio: egressgateway-aAfter applying the above configurations, when accessing www.httpbin.org through the sleep-a service using POST requests, RBAC: access is returned. GET requests to www.httpbin.org will not be affected.