Service Mesh (ASM) supports the direct migration of Kubernetes clusters that have the open source Istio installed to ASM. This topic describes how to migrate clusters that have the open source Istio installed to ASM.
Process
Perform the following steps in four phases.

During the Migrating phase, the Kubernetes cluster is injected as per the configured injection rules for Istio, and is injected in Istio Sidecar by default. In namespaces where the automatic sidecar injection is enabled, you can modify the Pod label to explicitly declare the injection of the ASM mesh proxy for the workload.

Prerequisites
To be eligible for migration, Kubernetes clusters must meet the following requirements:
The cluster version must be 1.21 or later. If your cluster is earlier than 1.21 and is hosted on Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK), refer to Manually update ACK clusters for upgrade instructions.
The Istio installed in the cluster must be V1.10 or later.
Create a new ASM instance of version 1.24 or later for the migration. For more information, see Create an ASM instance.
Procedure
Step 1: Add the cluster to be migrated to ASM
To add an ACK cluster with Istio installed or a self-built cluster registered to Alibaba Cloud Container Service to ASM, refer to Add a cluster to an ASM instance. During this process, select the "Ignore istio-system namespace check" option. If the Kubernetes cluster is not yet registered with Alibaba Cloud Container Service, register the cluster with an ACK instance based on the registered cluster feature of ACK One, and then add the cluster to ASM in the ASM console.
Once the cluster is added to ASM, the ASM instance will automatically create an ASMMigrateFromIstio resource to control the migration process. You can run the following command to view the resource.
kubectl --kubeconfig=${ASM_KUBECONFIG} get asmmigratefromistioExpected output:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: ASMMigrateFromIstio
metadata:
name: default
spec:
desiredState: Init
retryCounter: 0
advancedOptions:
stopIstioSystemInjectionDisabling: false
status:
message: ""
retryCounter: 0
state: InitThe configuration items for this resource are described as follows.
Field name | Type | Description | Value |
spec.desiredState | string | Specifies the migration status of the cluster to be migrated. You can modify this value to enter the specified migration status. Important This value can only change in a fixed order: Init -> SetupIstioForMigrate -> Migrating -> Finished. |
|
spec.retryCounter | int32 | The control plane of ASM may perform some necessary checks when switching states to ensure that the standards that are specified in new state are met. After you modify the desiredState parameter, this check is automatically triggered. If the check fails, adjust the state based on the on-screen instructions before modifying this value to trigger a recheck. | 0~2147483647 |
spec.advancedOptions | object | Indicates advanced options. | |
spec.advancedOptions.stopIstioSystemInjectionDisabling | bool | Specifies whether to disable the synchronization of labels in the istio-system namespace by ASM. When an east-west gateway is configured in the cluster to be migrated, set the value to |
|
status.retryCounter | int32 | Describes whether retryCounter is correctly reconciled. If the last modification is successfully reconciled, this value equals to spec.retryCounter. | Read-only |
status.state | string | Indicates the current state. After switching states, if the state successfully switches to the state specified by spec.desiredState, the value of status.state equals to that of spec.desiredState. | Read-only |
status.message | string | Indicates the reason for the failure when the state switch fails. If this field is not empty, users need to make adjustment as prompted before modifying spec.retryCounter to trigger a retry. | Read-only |
State switching for ASMMigrateFromIstio
To progress to the next phase, you must manually change the state of the ASMMigrateFromIstio resource. In this example, the current state is Init, and the state SetupIstioForMigrate indicates that it is advanced to the next phase.
The following sample code provides an example on how to switch state:
SetupIstioForMigratekubectl --kubeconfig=${ASM_KUBECONFIG} patch asmmigratefromistio default --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"desiredState":"SetupIstioForMigrate"}}'Migratingkubectl --kubeconfig=${ASM_KUBECONFIG} patch asmmigratefromistio default --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"desiredState":"Migrating"}}'Finishedkubectl --kubeconfig=${ASM_KUBECONFIG} patch asmmigratefromistio default --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"desiredState":"Finished"}}'
Assuming the state in next phase is SetupIstioForMigrate, you can run the following command to verify a successful switch:
kubectl get asmigratefromistio default -o yamlExpected output:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: ASMMigrateFromIstio
metadata:
name: default
spec:
desiredState: SetupIstioForMigrate
retryCounter: 0
status:
message: ""
retryCounter: 0
state: SetupIstioForMigrateIf the status.state value is SetupIstioForMigrate, the state has switched successfully.
If the value of status.state does not change as expected, modify it as status.message prompted. After the modification, increment spec.retryCounter by 1 before you try again.
Additional settings required for clusters with Istio east-west gateways enabled
By default, automatic sidecar injection is disabled for the istio-system namespace in ASM. However, the cached image of the Istio east-west gateway pod needs to be manually modified by MutatingWebhook, which requires the sidecar injection is enabled for the istio-system namespace. If the east-west gateway is enabled in your cluster, run the following command to prevent ASM from disabling the automatic sidecar injection in the istio-system namespace.
kubectl --kubeconfig=${ASM_KUBECONFIG} patch asmmigratefromistio default --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"advancedOptions":{"disableIstioSystemLabelReconciliation": true}}}' Next, manually remove the labels that has synchronized from ASM to the istio-system:
Edit the configuration of Istio-system namespace.
kubectl --kubeconfig=${The path of the kubeconfig file of the ACK instance} edit ns istio-systemRemove the label
istio-injection: disable, then save and exit.
Step 2: Configure Istio for preparation
Change the state to SetupIstioForMigrate.
ImportantAfter you run the preceding command, the Istiod needs to be reconfigured in ASM. In this case, you can restart Istiod in rolling mode for subsequent migration.
In this phase, ASM add the following configuration to Istio to enable mTLS communication between Istio Sidecar and ASM Sidecar during migration.
defaultConfig: proxyMetadata: PROXY_CONFIG_XDS_AGENT: "true"After entering this phase, To apply this configuration to all workloads, you need to restart all workloads with Istio Sidecar enabled. You can run the following command to confirm whether a Pod is qualified:
kubectl get pod ${POD name} -o yaml|grep PROXY_CONFIG_XDS_AGENTA non-empty output indicates that the workload is configured correctly. Once all workloads with Istio Sidecar enabled are configured, proceed to the Migrating phase.
Step 3: Migration
During the Migrating phase, you can inject either Istio Sidecar or ASM mesh proxy in workloads until all Istio Sidecars are replaced by ASM mesh proxies.
Switch the state to Migrating. In this phase, connect all Istio APIs to ASM, and then migrate the components of Istio Sidecar including ingress gateway, egress gateway, and east-west gateway to ASM as outlined in the following steps.
(Optional) Deploy an ASM cross-cluster gateway.
Within ASM, workloads with mesh proxies enabled automatically utilize the ASM cross-cluster gateway for cross-cluster communication, akin to Istio's east-west gateway. In this case, if the east-west gateway is enabled, it is essential to deploy the ASM cross-cluster gateway prior to integrating any workload with the ASM mesh proxy to maintain seamless cross-cluster communication after transitioning from Istio Sidecar to ASM mesh proxy.
Configure networks for the clusters in the ASM console. The networks must be the same as the networks configured for the clusters in Istio. In addition, you need to enable the Enable Access Through Cross-cluster Mesh Proxy for clusters with the Istio east-west gateway enabled. For more information, see Configure network settings for the clusters and enable cross-cluster mesh proxies.
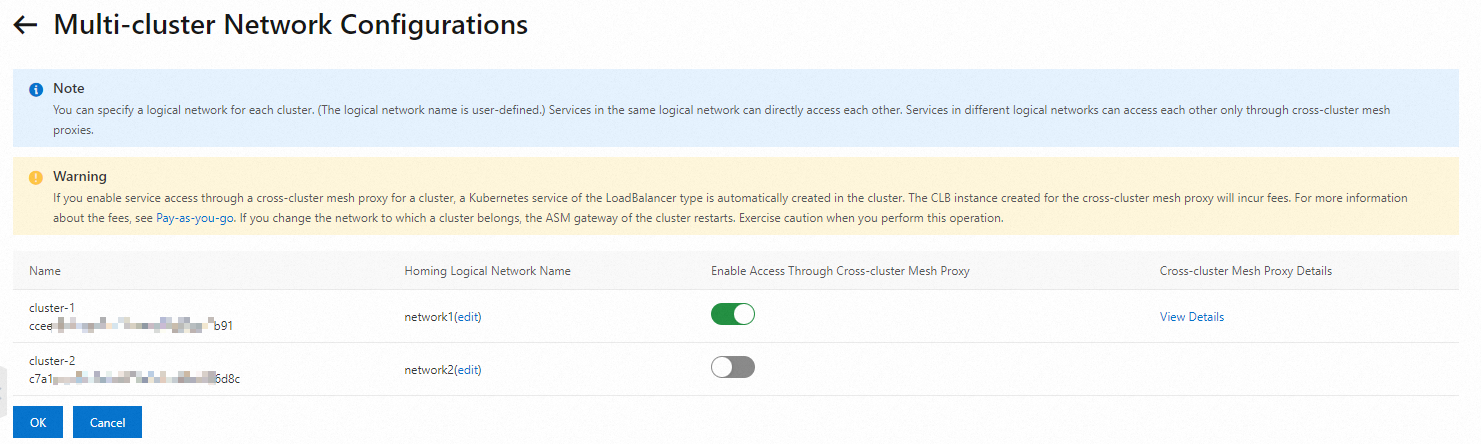 Note
NoteEnsure the network configuration in ASM aligns with that in Istio. In this example, you must configure network-1 for cluster a and network-2 for cluster b in ASM to ensure consistency.
Migrate Istio Sidecar to ASM mesh proxy.
$ kubectl --kubeconfig=${The path of the kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster} -n ${namespace} patch ${Deployment name} --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"template":{"metadata":{"labels":{"sidecar.asm.aliyun.com/inject":"true"}}}}}'ImportantThis operation may trigger a rolling restart on the workload. Traffic loss depends on whether the application supports graceful shutdown, whether graceful shutdown is configured for Istio Sidecar, and whether the application meets the requirement of graceful shutdown. The requirement is that all requests to the application must be returned within the specified timeout period. We recommend that you perform this step during off-peak hours.
Migrate Istio ingress gateway to ASM ingress gateway.
Migrate Istio ingress gateway to ASM ingress gateway. For more information, see How to migrate self-built Istio IngressGateway to ASM gateway.
Migrate Istio egress gateway to ASM egress gateway. Follow the following steps if the egress gateway is enabled in the cluster to be migrated.
Create an egress gateway in ASM. For more information, see Create an egress gateway. Create the necessary resources, such as ServiceEntry to register with external services, gateway rules to enable port forwarding for the egress gateway, and virtual services to route traffic to the egress gateway. For more information, see Traffic management for accessing external services on ASM.
Adjust the virtual service for the external service to direct traffic to the ASM egress gateway and set the desired weight.
The following sample code provides an example on how to configure virtual service. For complete sample code, see Egress gateway for HTTP traffic.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: direct-cnn-through-egress-gateway spec: hosts: - edition.cnn.com gateways: - istio-egressgateway - mesh http: - match: - gateways: - mesh port: 80 route: - destination: host: istio-egressgateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local port: number: 80 weight: 99 - destination: # Add a new destination pointing to the Egress gateway and adjust its weight as needed host: asm-egressgateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local # Assume your ASM egress gateway is called asm-egressgateway port: number: 80 weight: 1In this YAML file, traffic to edition.cnn.com is routed to Istio Ingressgateway and ASM Egressgateway at a 99:1 ratio. Adjust the ratio as needed until all traffic is routed to the ASM Egress gateway. You can monitor the access log of Istio Egress gateway to track traffic flow.
Step 4: Completion
Before moving to the next phase, ensure all operations below are completed:
All Istio Sidecars are removed.
No traffic is passing through Istio east-west gateways, ingress gateways, or egress gateways.
All Istio API configurations are imported into ASM.
Workloads that have injected with ASM mesh proxy function as expected.
After the above operations complete, you can uninstall Istio installed in the cluster using the version-specific istioctl command:
Use the istioctl tool that matches the installed version to avoid issues such as accidental removal or omission.
$ istioctl --kubeconfig=${The path of the kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster} uninstall --purgeAfter the istioctl tool is uninstalled, switch the state to Finished. If state switch fails, clear remaining Istio resources as status.message prompted, and increment spec.retryCounter by 1 before you try again. The migration is completed until the value of status.state is changed to Finished.