This topic describes the frequently asked questions (FAQ) about the end-to-end tracing capability of the Real User Monitoring (RUM) sub-service of Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS).
What do I do if tracing is unavailable on the API Request tab of the application details page?
Generally, tracing is unavailable because tracing was not properly enabled. Perform the following operations to troubleshoot the problem:
Web application: Check whether the API requests are across domains. By default, web applications use simple mode, which takes effect only for primary domain names when tracing is enabled. To make tracing available for all domain names, you need to use full mode instead and manually configure domain names and the propagation protocol. For more information, see Enable end-to-end tracing for a web application or mini program.
Mini program: Unlike web applications, mini programs do not have primary domain names. You need to check whether the propagation protocol is properly configured for the domain names. For more information, see Enable end-to-end tracing for a web application or mini program.
iOS or Android app: Check whether the domain names corresponding to the API requests have been added to the Request Management sub-tab of the Application Settings tab on the application details page. For more information, see Enable end-to-end tracing for an app.
What do I do if some trace data is missing?
Check whether the trace details include the RUM entry span data.
No: In this case, tracing was not properly enabled for RUM. Refer to the documentation to check whether the tracing configurations are valid and whether requests sent from the app carry valid protocol headers. For more information, see Enable end-to-end tracing for a web application or mini program and Enable end-to-end tracing for an app.
Yes: Backend service trace data may be missing for the following reasons:
The application is using Web Application Firewall (WAF) and the ARMS agent is integrated into the backend.
Adjust the priority of the backend propagation protocols because WAF injects the old EagleEye protocol header (eagleeye-traceid) by default. eagleeye-traceid has a higher priority in the ARMS agent than the OpenTelemetry and SkyWalking protocol headers propagated by RUM. Then, the RUM protocol headers become ineffective.
Solution:
In the left-side navigation pane of the ARMS console, choose . On the page that appears, click the name of the application. On the Configuration tab, change the value of the Pass-through protocol parameter to the protocol used by RUM, set the Pass-through mode parameter to Priority, and then click Save.
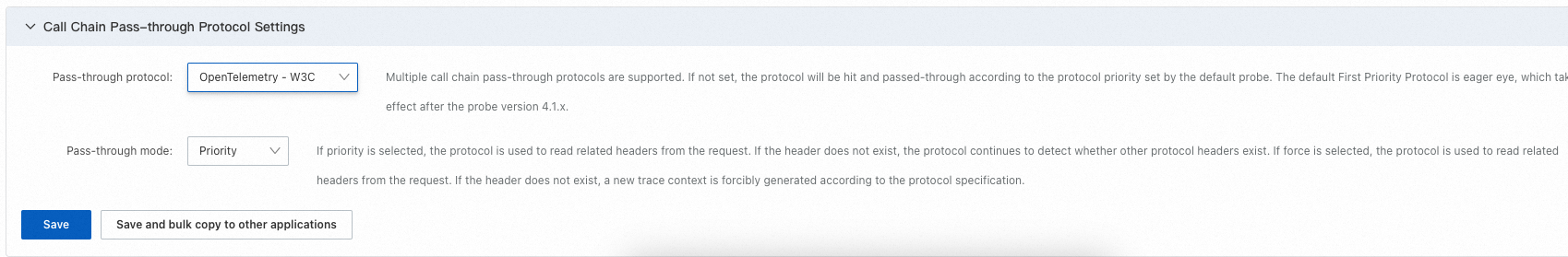 Note
NoteThe ARMS agent used by the backend must be V4.1.x or later. For information about how to upgrade the ARMS agent, see Upgrade the ARMS agent.
If the preceding change does not take effect after application startup, it indicates that the ARMS agent failed to pull the configuration. Submit a ticket.
If the application is not using WAF, check whether a gateway such as a NGINX gateway is used. Make sure that the gateway properly propagates the RUM-injected headers to maintain end-to-end tracing. For information about the protocol headers, see Enable end-to-end tracing for a web application or mini program. In the following example, NGINX forwards the W3C protocol header.
server { listen 80; location / { proxy_pass http://backend_server; # Enter the IP address of the backend server. # Forward the W3C header. proxy_set_header traceparent $http_traceparent; proxy_set_header tracestate $http_tracestate; # Configure more headers based on your needs. # proxy_set_header Host $host; # proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; # proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } }