This glossary defines the terms used in the Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) alert management system.
How alert management works
The alert management system processes monitoring data through a pipeline:
An integration connects a monitoring product to the alert management system.
The monitoring product detects a fault (an anomaly in monitoring data) and sends an event to the system.
The system applies event deduplication, event grouping, and event silencing rules to reduce noise.
A notification policy evaluates the events and creates an alert for events that require resolution.
The system sends a notification to assigned contacts through the configured channels.
If no one acknowledges or resolves the alert within the escalation timeout, the escalation policy notifies additional contacts.
A contact can claim the alert to take ownership, or the system can automatically resolve the alert when all related events recover.
Core terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Alert | An event that requires a contact to resolve. Alerts are created only for events triggered by a notification policy and that require resolution. |
| Alert card | A card-formatted alert sent by a chatbot in a DingTalk group. Contacts can view, handle, and resolve alerts directly from the card. Configure the chatbot in the ARMS console. |
| Alert management system | The alert management feature in ARMS. |
| Automatic alert resolution | When all events related to an alert recover, the system automatically sets the alert status to Resolved. |
| Claim alert | An action where a contact takes ownership of an unresolved alert and becomes its handler. |
| Fault | An anomaly in monitoring data that can be caused by business rules. When a monitoring tool detects an anomaly, it generates an event. |
Event management terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Event | A record sent from an integrated monitoring product to the alert management system. An alert is created for each event unless the event is suppressed. |
| Event deduplication | Merges duplicate events from an integration into a single event. Only the number of occurrences is counted. |
| Event grouping | Consolidates multiple related events into a single alert. This reduces the number of alerts that contacts handle and summarizes key information to minimize notification fatigue. |
| Event silencing | Prevents alerts from being created for specific, unimportant events. |
| Automatic event recovery | Automatically resolves an event after a specified period. The default recovery period is 5 minutes. |
Notification and escalation terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Contact | An operations and maintenance (O&M) engineer who handles alerts. Contacts can view, handle, and resolve alerts through DingTalk. |
| Escalation policy | A set of rules that defines which contacts to notify, and in what order, when an alert is not acknowledged or resolved within the escalation timeout. An escalation policy can be added to a notification policy. |
| Escalation timeout | The period after which the system notifies contacts defined in the escalation policy about unacknowledged or unresolved alerts. Default: 10 minutes. Maximum: 90 minutes. |
| Integration | The process of connecting a monitoring product with the alert management system, typically through APIs. Most monitoring products can be integrated. |
| Notification | A message sent to contacts when an alert is triggered. The message contains the alert object and title. Channels: text message, email, WeChat, DingTalk group, or webhook. |
| Notification policy | A policy that determines how to consolidate events into alerts and how to notify contacts. Channels: phone call, text message, email, or DingTalk group. Contacts are notified within one minute of an alert that requires resolution or attention. |
| Repeat escalation rules | If an alert remains unresolved after the escalation policy has processed all its rules, the escalation process restarts. Default: repeats once. Maximum: 9 times. |
| User | An Alibaba Cloud account or a Resource Access Management (RAM) user. Users can create, edit, and modify notification policies, escalation policies, and integrations, and can view, handle, and resolve alerts in the ARMS console. |
Data comparison terms
ARMS alert rules support three types of data comparison. Each compares data from a recent time window against a previous time window. The compared value can be an average, sum, maximum, or minimum.
| Term | Comparison logic |
|---|---|
| Period-over-period increase/decrease (%) | Compares data from the last N minutes (β) with data from the previous N minutes (α), that is, the period from 2N to N minutes ago. 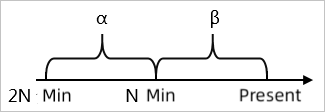 |
| Hour-over-hour increase/decrease (%) | Compares data from the last N minutes (β) with data from the same N-minute window in the previous hour (α). 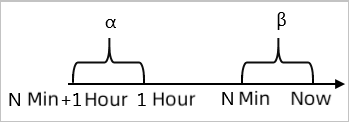 |
| Day-over-day increase/decrease (%) | Compares data from the last N minutes (β) with data from the same N-minute window on the previous day (α). 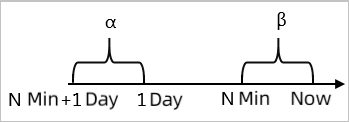 |
Alert data revision policy
When alert data is missing or cannot be calculated, ARMS applies a revision policy to fill in the gap and prevent missed alerts. This covers three types of data anomalies: missing data, uncalculable compound indicators, and uncalculable period-over-period comparisons.
Revision options
| Option | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Fill with 0 | Sets the missing or uncalculable value to 0. |
| Fill with 1 | Sets the missing or uncalculable value to 1. |
| Fill with null (default) | No value is inserted. The alert is not triggered. |
Scenarios
The following examples show when each revision option applies.
Missing data
An alert rule monitors page views using Browser Monitoring and triggers if total page views fall to 10 or below within a period (N=5). If no one visits the page, no data is reported, and the alert does not trigger. Select Fill with 0 to treat the absence of data as zero, which satisfies the alert condition.
Uncalculable compound indicator
An alert rule monitors the real-time unit price of a commodity using custom monitoring. Variable a is the current total price, and variable b is the current total number of items. The rule triggers if the minimum value of a/b falls to 10 or below within a period (N=3). If the total number of items is 0, the division cannot be calculated, and the alert does not trigger. Select Fill with 0 to treat the compound indicator value as 0, which satisfies the alert condition.
Uncalculable period-over-period comparison
An alert rule monitors CPU usage using Application Monitoring and triggers if the average CPU usage decreases by 100% period-over-period within a period (N=3). If the CPU fails in the last N minutes, no current-period data is available, and the period-over-period result cannot be calculated. Select Fill with 1 to treat the comparison result as a 100% decrease, which satisfies the alert condition.