Dead-letter exchanges in ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ process messages that are negatively acknowledged by consumers or that fail all retry attempts. This topic describes the core concepts, routing process, configuration methods, and usage notes for dead-letter exchanges. It also provides links to related topics.
Core concepts
Dead-letter exchange
A dead-letter exchange routes dead-letter messages to a dead-letter queue based on binding keys, dead-letter routing keys, and header attributes. Any standard exchange type, such as a direct exchange, can be configured as a dead-letter exchange.
Dead-letter routing key
A routing key that determines how a dead-letter message is routed. If you do not specify a dead-letter routing key, the original routing key of the message is used.
Dead-letter message
A message that is sent to a dead-letter exchange. A message may be sent to a dead-letter exchange in the following scenarios:
The requeue parameter is set to false, and the consumer uses
basic.rejectorbasic.nackto send negative acknowledgments (NACKs) for messages.The message fails to be consumed after being re-sent 16 times. For more information, see Consumption retry policies.
The message expires. The time for which the message is stored in the queue exceeds the specified message TTL. For more information, see Message TTL.
Dead-letter queue
A queue that is bound to a dead-letter exchange to store dead-letter messages.
Routing process
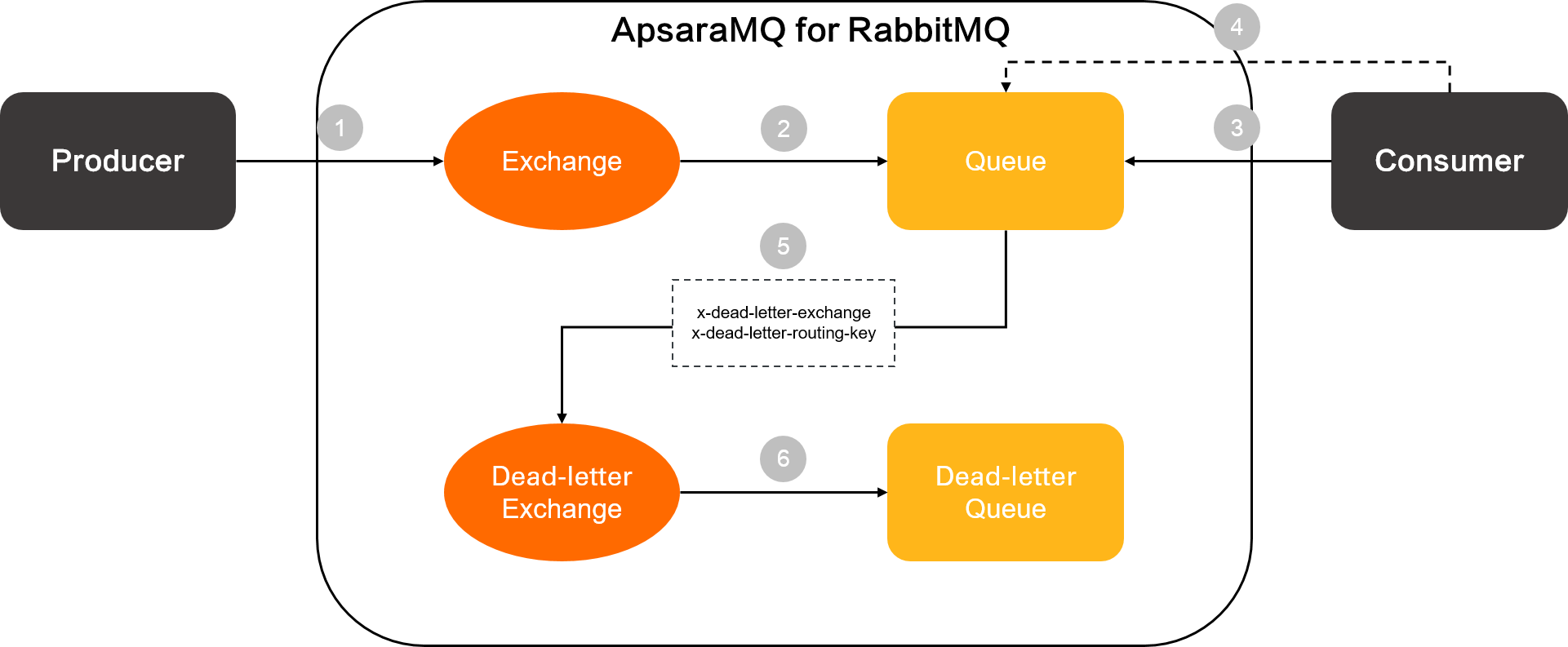
The following steps describe the routing process for a dead-letter message:
A producer sends a message to an exchange.
The exchange routes the message to a queue.
A consumer pulls the message from the queue.
The message becomes a dead-letter message if a consumer negatively acknowledges it, or if consumption fails after 16 retries.
The queue sends the dead-letter message to a dead-letter exchange based on the x-dead-letter-exchange parameter and specifies a dead-letter routing key for the message based on the x-dead-letter-routing-key parameter.
The dead-letter exchange routes the message to a dead-letter queue.
Usage notes
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ does not allow you to route dead-letter messages across vhosts. You must ensure that the dead-letter exchange and its corresponding queue reside in the same vhost.
You cannot modify the dead-letter exchange of an existing queue in ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ. To change the dead-letter exchange, you must delete the queue and create a new one with the updated configuration.
Configuration methods
You can configure a dead-letter exchange using one of the following methods in ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ:
Console
You can configure a dead-letter exchange for a queue when you create the queue in the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ console.
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ console.
On the Overview page, in the Resource Distribution section, select a region.
On the Instances page, click the name of the instance that you want to manage.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Queues.
On the Queues page, next to vhost, select a vhost from the Change drop-down list and click Create Queue.
In the Create Queue panel, enter a queue name in the Queue Name field and configure the Auto Delete parameter. Click Advanced Settings and configure the queue parameters that are displayed. Then, click OK.
Table 1. Parameters
Parameter
Description
Usage notes
Queue Name
The queue name.
The name can contain letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), periods (.), number signs (#), forward slashes (/), and at signs (@).
The name must be 1 to 255 characters in length.
After a queue is created, you cannot change its name. If you want to change the name of a queue, delete the queue and create another queue.
amq. is a reserved field and cannot be used as the prefix of an exchange name. For example, you cannot use amq.test as the name of an exchange.
Auto Delete
Specifies whether the queue is automatically deleted after the last subscription from consumers to the queue is canceled.
true: The queue is automatically deleted after the last subscription from consumers to this queue is canceled.
false: The queue is not automatically deleted after the last subscription from consumers to this queue is canceled.
Advanced Settings
Other parameters for the queue, such as the dead-letter exchange, dead-letter routing key, and message time-to-live (TTL).
DeadLetterExchange: the exchange to which dead-letter messages are delivered.
DeadLetterRoutingKey: the routing key of dead-letter messages. A dead-letter exchange sends dead-letter messages to the queue whose routing key matches the routing key of the dead-letter messages.
MessageTTL: the message TTL, in milliseconds. A message that is not consumed within the specified message TTL is a dead-letter message and is sent to a dead-letter exchange. For more information, see Message TTL.
API
You can configure a dead-letter exchange for a queue when you call the CreateQueue API operation to create the queue. For more information, see CreateQueue.
Client
You can also configure a dead-letter exchange for a queue when you declare the queue on an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ client.
Use the x-dead-letter-exchange parameter to specify a dead-letter exchange and the x-dead-letter-routing-key parameter to specify a dead-letter routing key.
For example, to declare a direct exchange named some.exchange.name, use the x-dead-letter-exchange parameter to specify the dead-letter exchange and the x-dead-letter-routing-key parameter to specify demo-routing-key as the dead-letter routing key.
Sample code in Java:
channel.exchangeDeclare("some.exchange.name", "direct");
Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<String, Object>();
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", "some.exchange.name");
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "demo-routing-key");
channel.queueDeclare("MyQueue", false, false, false, arguments);Dead-letter header
The dead-letter message header includes the following information:
Header | Description |
x-first-death-exchange | The exchange to which the message belongs when the message first becomes a dead-letter message. |
x-first-death-queue | The queue to which the message belongs when the message first becomes a dead-letter message. |
x-first-death-reason | The reason why the message first becomes a dead-letter message. |
x-death-total | The number of times that the message becomes a dead-letter message. |
x-death | The array that contains more detailed information about the dead-letter message.
|
The possible reasons include the following:
expired: The message TTL expired.
nack: The message was negatively acknowledged (NACKed) with the `requeue` parameter set to `false`.
reject: The message was rejected with the `requeue` parameter set to `false`.
Consumption limit exceeded
Enable the TTL feature for a dead-letter queue
By default, the time-to-live (TTL) feature is disabled for messages in a dead-letter queue. This means that even if a TTL is set on the dead-letter queue, messages in it will not expire and be routed to another dead-letter queue. You can enable this feature for an instance in the console. When enabled, dead-letter messages adhere to the TTL settings of the dead-letter queue they are in. If a message's TTL expires in the dead-letter queue, it is forwarded to the next configured dead-letter exchange.
Instance limits
The TTL feature for dead-letter queues is available for Serverless, Enterprise Edition (Subscription), and Platinum Edition (Subscription) instances.
Procedure
On the Instances page of the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ console, click the name of the target instance.
On the Instance Details page, click the Limits tab.
Click Activate next to TTL Feature Supported to enable the TTL feature for dead-letter queues.
When you configure dead-letter queues, be careful not to create a message loop. For example, if you set Queue B as the dead-letter queue for Queue A and set Queue A as the dead-letter queue for Queue B, this creates a dead-letter routing loop. If a loop is detected and no message rejection event occurs within the loop, the TTL feature is automatically disabled for the affected messages to prevent infinite routing.
A dead-letter message can be routed between queues a maximum of 16 times. After this limit is reached, the TTL feature is disabled for the affected dead-letter messages.
More information
For more information about how to delete a dead-letter exchange or bind a dead-letter queue to a dead-letter exchange, see Manage exchanges.