A certification authority (CA) certificate is used to issue device certificates, server certificates, and validation certificates. When MQTT clients authenticate with device certificates, the broker must verify each certificate against the signing CA. Register your CA certificate with ApsaraMQ for MQTT so the broker can validate device certificates it has signed.
This topic covers how to create a self-signed CA certificate, register it with your instance, and manage its lifecycle.
How it works
To register a CA certificate, upload both the CA certificate and a validation certificate that proves you own the CA's private key. After registration, the CA certificate is Active by default, and all device certificates it has signed can authenticate with the broker.
Instance and CA certificate relationships:
An instance can have multiple CA certificates.
A CA certificate can be registered with only one instance per region.
Limits
| Constraint | Details |
|---|---|
| Supported editions | Platinum and Professional Edition only |
| Serial number (SN) | Must be unique; cannot exceed 128 bytes |
| Supported algorithms | RSA and ECC |
Create a self-signed CA certificate
Purchase a CA certificate from a trusted CA, or generate a self-signed one with OpenSSL.
Before you begin, install OpenSSL v1.1.1i or later.
On Windows, add the bin subdirectory of the OpenSSL installation folder to your system PATH environment variable after installation.
Select the procedure for your preferred algorithm.
RSA
Generate a 2048-bit RSA private key.
openssl genrsa -out CA.key 2048Create a certificate signing request (CSR).
openssl req -new -key CA.key -out CA.csrEnter the following fields when prompted:
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]: State or Province Name (full name) []: Locality Name (for example, city) []: Organization Name (for example, company) []: Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []: Email Address []:Generate the self-signed CA certificate (
CA.crt). The path toopenssl.cnfvaries by operating system.macOS
openssl x509 -req -extfile /System/Library/OpenSSL/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650CentOS
openssl x509 -req -extfile /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650Windows
openssl x509 -req -extfile C:\Progra~1\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\cnf\openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
Verify the generated certificate.
openssl x509 -in CA.crt -text
ECC
Generate an ECC private key using the
prime256v1curve.openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out CA.keyGenerate the self-signed ECC CA certificate (
CA.crt). The path toopenssl.cnfvaries by operating system.macOS
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -config /System/Library/OpenSSL/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -key CA.key -out CA.crtCentOS
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -key CA.key -out CA.crtWindows
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -config C:\Progra~1\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\cnf\openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -key CA.key -out CA.crtNoteIf this step fails, verify that the
openssl.cnfpath in the command is correct for your system.
Enter the following fields when prompted:
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]: State or Province Name (full name) []: Locality Name (for example, city) []: Organization Name (for example, company) []: Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []: Email Address []:Verify the generated certificate.
openssl x509 -in CA.crt -text
Register a CA certificate
Registration proves that you own the CA certificate's private key. The process has three steps: get a registration code from the console, create a validation certificate signed by your CA, and upload both certificates.
After registration, the CA certificate is Active by default.
Step 1: Get the registration code
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for MQTT console and click Instances in the left-side navigation pane.
In the top menu bar, select the target region. In the instance list, click the target instance name to open the Instance Details page. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the CA Certificate page, click Register Certificate. Copy the registration code from the panel that appears.
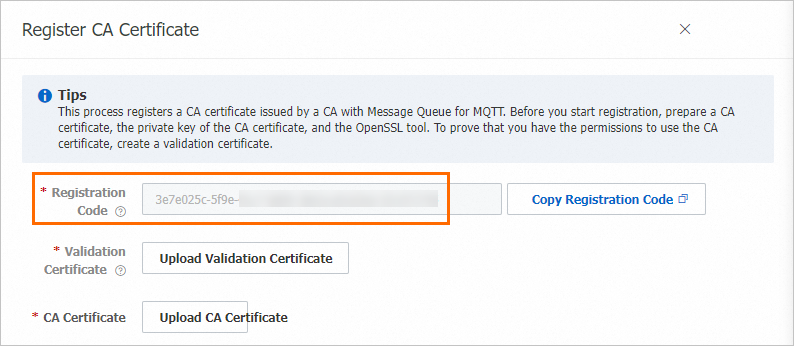
Step 2: Create a validation certificate
The validation certificate proves you own the CA's private key. The CommonName field in the CSR must be set to the registration code from Step 1. Select the procedure that matches the algorithm of your CA certificate.
RSA
Generate a private key for the validation certificate.
openssl genrsa -out verificationCert.key 2048Create a CSR and set the
Common Namefield to the registration code from Step 1. Other fields are optional.openssl req -new -key verificationCert.key -out verificationCert.csrCountry Name (2 letter code) [AU]: State or Province Name (full name) []: Locality Name (for example, city) []: Organization Name (for example, company) []: Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:i29adsjfp29jfj92jlajsdf****** Email Address []:ImportantThe
CommonNamefield is required and must match the registration code from Step 1.Sign the validation certificate with your CA certificate.
openssl x509 -req -in verificationCert.csr -CA CA.crt -CAkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -out verificationCert.crt -days 300 -sha512NoteIf your CA certificate is not self-signed, submit the CSR to your CA to have the validation certificate generated.
ECC
Generate a private key for the validation certificate.
openssl ecparam -out verificationCert.key -name prime256v1 -genkeyCreate a CSR and set the
Common Namefield to the registration code from Step 1. Other fields are optional.openssl req -new -key verificationCert.key -out verificationCert.csrCountry Name (2 letter code) [AU]: State or Province Name (full name) []: Locality Name (for example, city) []: Organization Name (for example, company) []: Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:i29adsjfp29jfj92jlajsdf****** Email Address []:ImportantThe
CommonNamefield is required and must match the registration code from Step 1.Sign the validation certificate with your CA certificate.
openssl x509 -req -in verificationCert.csr -CA CA.crt -CAkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -out verificationCert.crt -days 300 -sha512NoteIf your CA certificate is not self-signed, submit the CSR to your CA to have the validation certificate generated.
Step 3: Upload certificates
On the CA Certificate page, click Register Certificate.
In the Register CA Certificate panel, click Upload Validation Certificate and Upload CA Certificate. Upload the
verificationCert.crtandCA.crtfiles, then click OK.
Manage CA certificates
Download a CA certificate
Download a CA certificate to your local machine for backup or to inspect its details.
In the CA certificate list, find the target certificate and click Actions > Download.
Search for a CA certificate
On the CA Certificate page, the certificate list displays all registered CA certificates. To find a specific certificate, enter its SN in the search box and click Search.
View device certificates issued by a CA certificate
In the CA certificate list, find the target CA certificate and click Actions > Device Certificate. The Device Certificate page lists all registered device certificates issued by that CA certificate.
Activate or unregister a CA certificate
CA certificates have two statuses: Active and Inactive. After registration, a certificate is Active by default.
| Action | When to use | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Unregister | Temporarily disable the certificate | Status changes to Inactive. The certificate and all device certificates it issued become unavailable for authentication. |
| Activate | Restore a disabled certificate | Status changes to Active. The certificate and all associated device certificates become available again. |
In the CA certificate list, find the target CA certificate and click Actions > Unregister or Activate.
Delete a CA certificate
Deleting a CA certificate permanently removes all records of that certificate and its associated device certificates from the server. The certificate files on your local machine are not affected. After deletion, neither the CA certificate nor its associated device certificates can be used for authentication unless registered again.
In the CA certificate list, find the target CA certificate and click Actions > Delete.
In the confirmation dialog box, click OK.