This topic describes how to troubleshoot failures in connecting to an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance from an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
When you set up a test environment to debug your business, you may fail to connect to your RDS instance from your ECS instance. The connection failures may occur due to various reasons. For example, the network type of your RDS instance is different from the network type of your ECS instance, or the IP address of your ECS instance is not added to an IP address whitelist of your RDS instance. This topic describes the most common causes of connection failures and the methods that you can use to troubleshoot the connection failures.
Different network types
The ECS instance resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC), and the RDS instance resides in the classic network.
Method 1: Migrate the RDS instance to the VPC in which the ECS instance resides. For more information, see Change the network type of an ApsaraDB RDS instance. This is the recommended method.
NoteIf the ECS instance and the RDS instance both reside in VPCs, they must reside in the same VPC to communicate with each other over an internal network.
Method 2: Purchase an ECS instance that resides in the classic network, and connect to the RDS instance from the ECS instance. ECS instances cannot be migrated from VPCs to the classic network. A VPC provides higher security than the classic network. We recommend that you use the VPC network type.
Method 3: Connect to the RDS instance from the ECS instance by using the public endpoint of the RDS instance. This method cannot ensure optimal performance, security, or stability.
The ECS instance resides in the classic network, and the RDS instance resides in a VPC.
Method 1: Migrate the ECS instance to the VPC to which the RDS instance belongs. This is the recommended method.
NoteIf the ECS instance and the RDS instance both reside in VPCs, they must reside in the same VPC to communicate with each other over an internal network.
Method 2: Migrate the RDS instance to the classic network. A VPC provides higher security than the classic network. We recommend that you use the VPC network type.
Method 3: Use the ClassicLink feature to establish an internal network connection between the ECS instance and the RDS instance. For more information, see Overview of ClassicLink.
Method 4: Connect to the RDS instance from the ECS instance by using the public endpoint of the RDS instance. This method cannot ensure optimal performance, security, or stability.
Different VPCs
A VPC is an isolated network environment that is built on Alibaba Cloud. VPCs are logically isolated from each other. If the ECS instance and the RDS instance both reside VPCs, they must reside in the same VPC to communicate with each other over an internal network.
Method 1: Change the VPC for the RDS instance and the ECS instance to reside in the same VPC. We recommend that you use this method.
You can change the VPC of the RDS instance or the VPC of the ECS instance.
Method 2: Create a Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance to establish a private connection between the VPCs of the ECS instance and the RDS instance. For more information, see Use CEN to enable intra-region network communication.
Method 3: Connect to the RDS instance from the ECS instance over the Internet. This method cannot ensure optimal performance, security, or stability.
Different regions
Internet-based connection: You can use the public endpoint of the RDS instance to establish a cross-region or cross-account Internet-based connection to the RDS instance. You are not charged for the inbound and outbound Internet traffic generated on the RDS instance.
Internal network-based connection: If the ECS instance and the RDS instance reside in different regions or within different Alibaba Cloud accounts, you cannot connect the instances over an internal network. VPCs are isolated from each other. However, you can use VPC peering connections or a Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance to connect two different VPCs. This way, the ECS instance can connect to the RDS instance across regions or Alibaba Cloud accounts.
VPC peering connection: enables communication between VPCs across regions or Alibaba Cloud accounts at low costs. However, a VPC peering connection is relatively complex to configure. This method is suitable for simple scenarios in which a small number of VPCs need to be connected.
CEN instance: enables communication between VPCs across regions or Alibaba Cloud accounts at high costs. However, a CEN instance is simple to configure. This method is suitable for complex scenarios in which a large number of VPCs need to be connected.
Incorrect IP address whitelist settings
The IP address whitelist labeled default contains only the IP address 127.0.0.1. This IP address indicates that no devices are allowed to access the RDS instance. Therefore, you must add IP addresses to the whitelist. For more information, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
The 0.0.0.0 entry is added to an IP address whitelist of the RDS instance.
ImportantIf you add the 0.0.0.0/0 entry to an IP address whitelist of the RDS instance, all devices are allowed to access the RDS instance. Proceed with caution.
The enhanced whitelist mode is enabled for the RDS instance. In this case, take note of the following limits:
If the RDS instance resides in a VPC and is connected by using its internal endpoint, the private IP address of the ECS instance must be added to the IP address whitelist of the VPC type.
If the RDS instance resides in the classic network and is connected by using its internal endpoint, the private IP address of the ECS instance must be added to the IP address whitelist of the classic network type.
If the RDS instance resides in the classic network and is connected over the Internet, the public IP address of the ECS instance must be added to the IP address whitelist of the classic network type.
The public IP address that you add to an IP address whitelist is invalid Possible causes:
The public IP address dynamically changes.
The tool or website that is used to query public IP addresses returns inaccurate results.
For more information, see the following topics:
Domain name resolution failures or errors
If the Domain Name System (DNS) servers are faulty or the configurations of the network interface controller (NIC) are modified, domain names may fail to be resolved or may be resolved into incorrect IP addresses. In this case, you can run the ping command or the telnet command to check the connectivity to the RDS instance.
ping <Domain name>
telnet <Domain name> <Port number>
Example
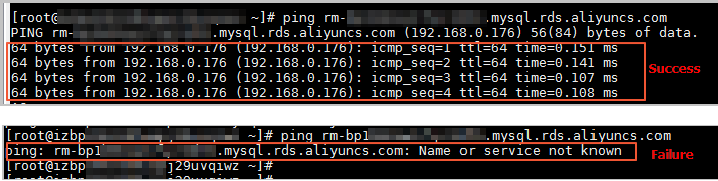
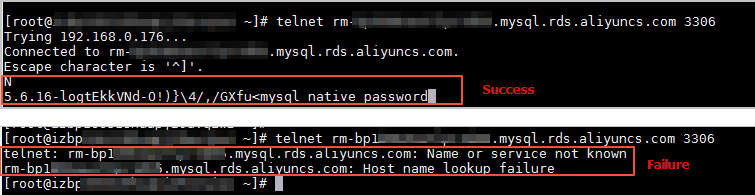
If the RDS instance fails the connectivity test, perform the following operations to modify the configuration file of the network interface controller (NIC):
Open the configuration file in edit mode.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/<The name of the configuration file of the NIC>NoteThe NIC in the command refers to the NIC of the ECS instance. You can run the
ifconfigcommand to check the file name extension of the configuration file. The default file name extension is ifcfg-eth0.Add the following settings to the end of the configuration file.
DNS1=100.100.XX.XX DNS2=100.100.XX.XXNoteIf the DNS1 and DNS2 configuration items exist in the configuration file, you must change the values of these configuration items to the values that are shown in the settings.
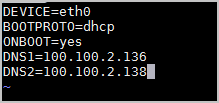
Run the following command to restart the network service:
sudo systemctl restart networkRun the following command to check whether the modification is successful:
cat /etc/resolv.conf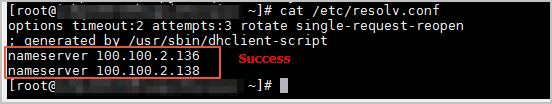
RDS instance in the Creating Network Connection state
Go to the Tasks page in the ApsaraDB RDS console, find the task in the Creating Network Connection state, and then click Retry or Modify switching time. For more information, see Use Task Center.