Integrate your RDS SQL Server instance with your company's Active Directory (AD) for centralized permission management and unified identity authentication. This topic describes how to configure a self-managed domain and join your instance to it. Before you begin, ensure that your RDS instance and domain controller can communicate over the network. The domain controller can be located on an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance, on another cloud platform, or in an on-premises data center. This topic uses an ECS instance as an example to demonstrate the deployment.
Background information
Microsoft Active Directory (AD) is a directory service for Microsoft products such as Windows Standard Server, Windows Enterprise Server, and Microsoft SQL Server. A directory is a hierarchical structure that stores information about objects on a local area network. For example, AD stores user account information, such as names, passwords, and phone numbers. It allows other authorized users on the same local area network to access this information.
AD is a key component of the Windows ecosystem. Many large enterprises use domain control for centralized access management, a native method they have long relied on. When you migrate services to the cloud or use a hybrid cloud architecture, you often need AD support in the cloud for global management. For SQL Server databases, which are a vital part of the Microsoft ecosystem, AD support is a basic requirement for large enterprises that are moving to the cloud.
RDS SQL Server provides a feature that lets you join an instance to a self-managed domain to help you complete your business ecosystem.
After you enable and configure the AD domain feature, you can create accounts in your self-managed AD domain. You can then grant permissions to these accounts to log on to RDS SQL Server and perform database operations.
However, because superuser (System Admin) or host accounts have permissions that exceed the scope of RDS control, we cannot guarantee the SLA for RDS instances where these types of accounts are created using the self-managed AD domain feature.
Prerequisites
Your RDS SQL Server instance must meet the following requirements:
Instance type: General-purpose or Dedicated. Shared instances are not supported.
Billing method: Subscription or pay-as-you-go (not available for Serverless ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances)
Account: You must use an Alibaba Cloud account to perform the configuration.
You can view this information on the Basic Information page of the instance.
Preparations
Deploy a domain controller
Operating system: Requires a Windows Server operating system. The minimum version is Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2016 or later is recommended. (This topic uses the English edition of Windows Server 2016 as an example.)
DNS configuration: The domain controller must also be a DNS server. Its IP address must be the same as the DNS server address.
Permission requirements: The domain account used to join the RDS instance to the domain must be a member of the Domain Admins group because the client requires high permissions to join a domain.
Ensure network connectivity: The RDS instance and the domain controller must have bidirectional network connectivity. The domain controller can be deployed on an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance, on another cloud platform, or in an on-premises data center.
Notes
Joining or leaving an AD domain requires a restart of the Windows operating system. To avoid business interruptions, perform these operations during off-peak hours.
Limits
AD domain-joined instances do not support upgrading the major database version, upgrading the minor engine version, or migrating the zone.
Step 1: Configure the domain controller on the ECS instance
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

On the Instance page, click the ID of the target instance.
Remotely log on to the Windows Server 2016 operating system of the ECS instance.
Search for and open Server Manager.
Click Add roles and features and configure the settings as follows.
Page Name
Settings
Installation Type
Keep the default settings.
Server Selection
Keep the default settings.
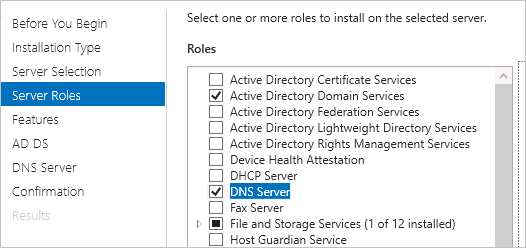
Server Roles
Select Active Directory Domain Services and click Add Features in the dialog box that appears.
Select DNS Server and click Add Features in the dialog box that appears. If a message indicates that your computer does not have a static IP address, change it to a static IP address. This prevents the DNS server from becoming unavailable due to automatic IP address changes.
Features
Keep the default settings.
AD DS
Keep the default settings.
DNS Server
Keep the default settings.
Confirmation
Click Install.
After the installation is complete, click Close.
In the navigation pane on the left, click AD DS. Then, in the upper-right corner, click More.
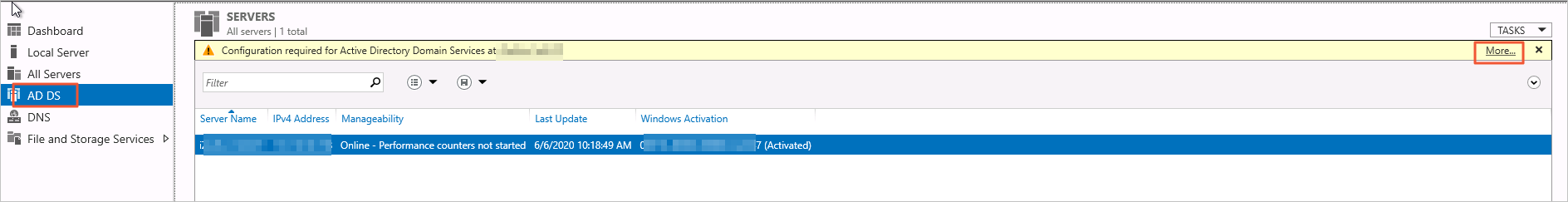
Click Promote this server to a domain... and configure the settings as follows.
Page Name
Settings
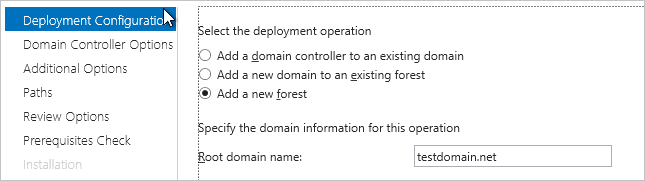
Deployment Configuration
Select Add a new forest and set the domain name.
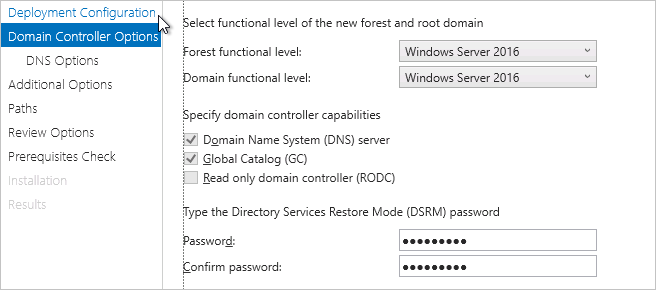
Domain Controller Options
Set the recovery model password.
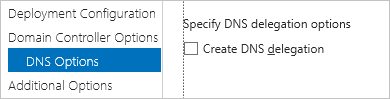
DNS Options
Deselect the Create DNS delegation option's √.
Additional Options
Keep the default settings.
Paths
Keep the default settings.
Review Options
Keep the default settings.
Prerequisites Check
Click Install.
NoteThe system restarts after the installation is complete.
Wait for the system to restart. Then, search for and open Server Manager again.
In the navigation pane on the left, click AD DS. Then, right-click the target domain controller on the right and select Active Directory Users and Computers to open the AD user management module.
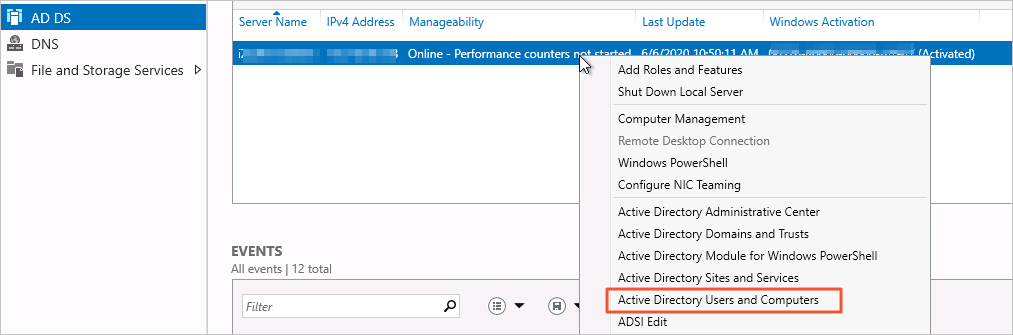
Right-click and choose .
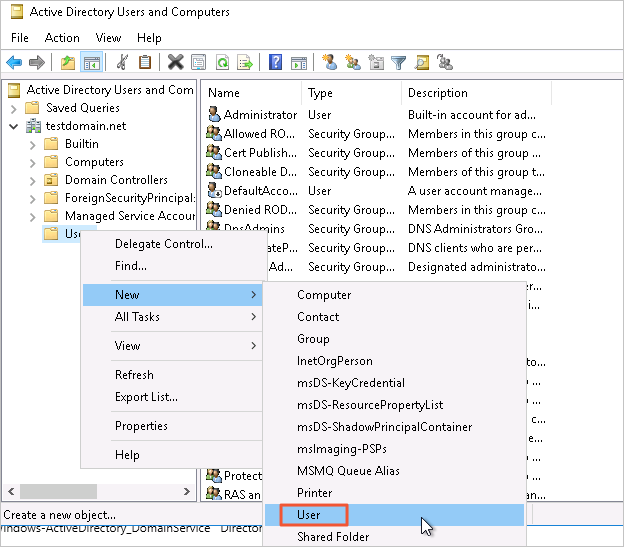
Set the user logon name and click Next.
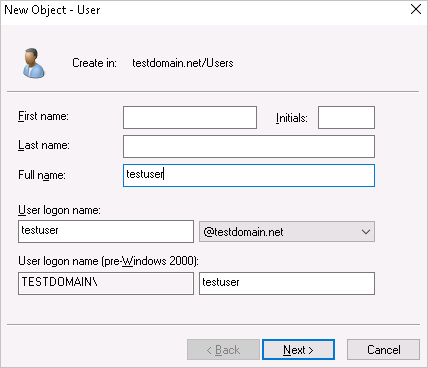
Set the logon password, select the option for the password to never expire, and then click Next and Finish to complete the creation.
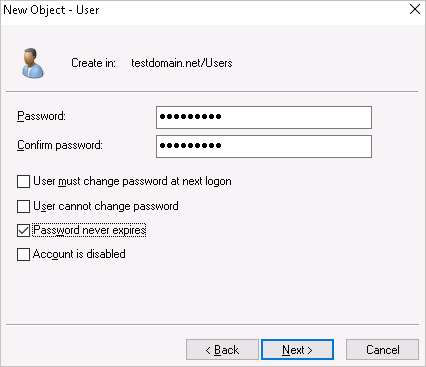
Double-click the newly created user and add the user to the Domain Admins group.
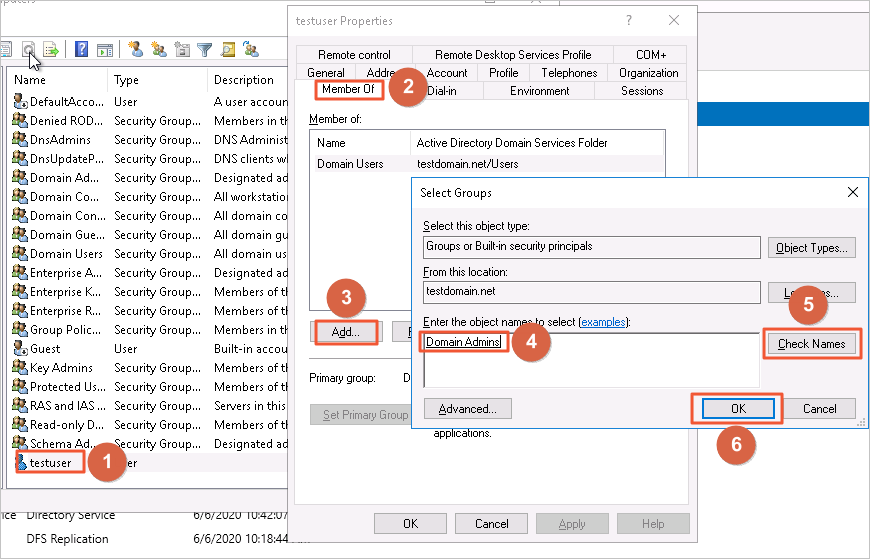
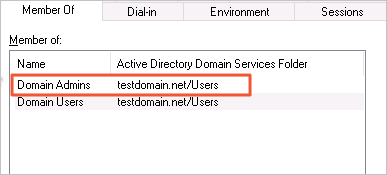
Step 2: Configure the ECS instance security group
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

On the Instance page, click the ID of the target instance.
On the top navigation bar, select Security Groups. Then, in the Operation column of the security group, click Manage Rules.
On the Inbound tab, click Add Rule to allow access to the ECS instance on the following ports.
Protocol Type
Port Range
Description
TCP
88
Kerberos authentication protocol port.
TCP
135
Remote procedure call (RPC) protocol port.
TCP/UDP
389
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) port.
TCP
445
Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol port.
TCP
3268
Global Catalog port.
TCP/UDP
53
DNS port.
TCP
49152~65535
Default dynamic port range for connections. Enter the range in the format: 49152/65535.
Step 3: Configure the AD domain service for the RDS instance
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Accounts.
Click the AD Domain Services tab, and then click Configure AD Domain Services.
In the Configure AD Domain Services dialog box, set the following parameters and select I have read and understand the impact of AD Domain Services on the RDS Service Level Agreement.
WarningAfter you enable and configure the AD domain feature, you can create accounts in your self-managed AD domain. You can then grant permissions to these accounts to log on to RDS SQL Server and perform database operations.
However, because superuser (System Admin) or host accounts have permissions that exceed the scope of RDS control, we cannot guarantee the SLA for RDS instances where these types of accounts are created using the self-managed AD domain feature.
Parameter
Description
Domain Name
The domain name specified when you created the Active Directory (on the Deployment Configuration page). For example, this topic uses testdomian.net.
Directory IP Address
The IP address of the ECS instance where the domain controller is located. You can obtain it by running the
ipconfigcommand on the ECS instance or view it in the Alibaba Cloud ECS console.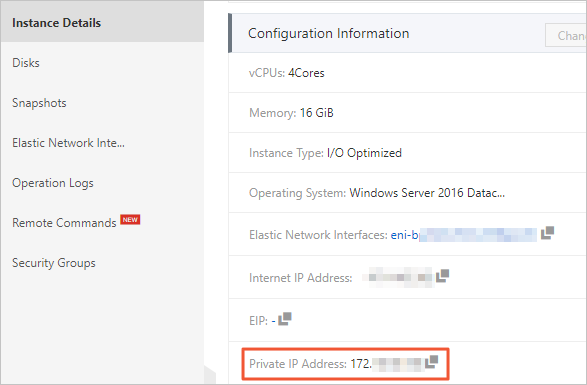
Domain Account
The username you created earlier.
Domain Password
The password for the username.
Click OK and wait for the AD domain configuration to complete.
Related operations
To view or modify AD domain association information or to leave an AD domain using an API, see the following topics: