This topic describes how to apply a partitioning plan in OceanBase Developer Center (ODC) for automatic partition management, including partition creation and deletion.
Background
The partitioning plan feature is an extension of RANGE partitioning. ODC can automatically manage RANGE-partitioned tables based on the specified partitioning strategies, and you do not need to manually create partitions. This facilitates maintenance of the RANGE-partitioned tables.
RANGE partitioning: It is the most common partitioning type and is generally used in combination with dates. In RANGE partitioning, the database maps rows to partitions based on ranges of partitioning key values. For more information, see Set partitioning rules and Partitioning types.
Partitioning plan: The partitioning plan feature is an extension of RANGE partitioning. ODC can automatically manage RANGE-partitioned tables based on the specified partitioning strategies, and you do not need to manually create partitions. This facilitates maintenance of the RANGE-partitioned tables.
Creation strategy: ODC supports automatic table partitioning based on specified partitioning rules. Two partition creation methods are supported:
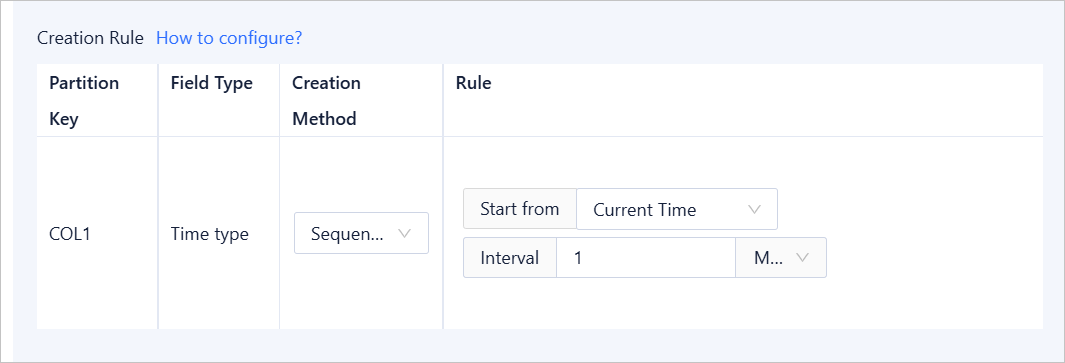
Sequential Increment: This method applies only to fields of a time, number, or character type.
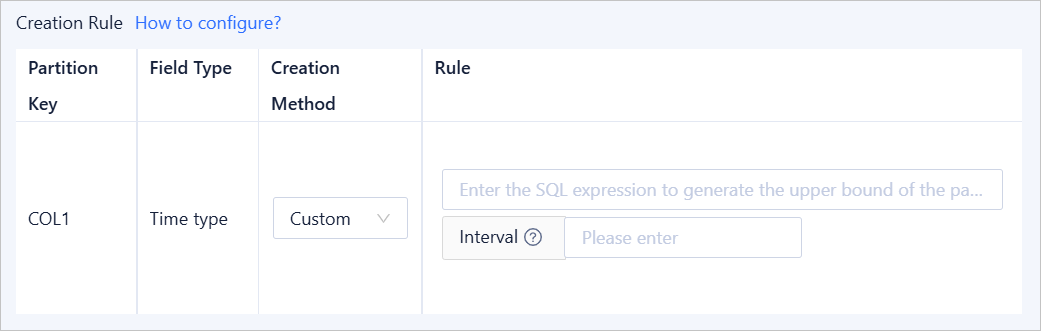
Custom: You can define a custom SQL expression for partitioning for any field type.
Deletion strategy: Based on the specified number of partitions allowed, the latest partitions are retained and redundant partitions are deleted.
Partitioning plan execution process
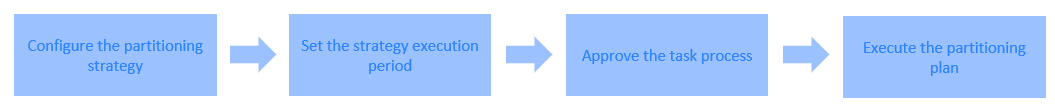
Set a partition creation strategy and a partition deletion strategy for a table.
Set a strategy execution cycle.
Approve the task process.
Execute the partitioning plan.
Considerations
Only OceanBase MySQL-compatible and OceanBase Oracle-compatible data sources are supported.
Only RANGE-partitioned tables are supported.
When the upper bound of the last partition in a RANGE-partitioned table reaches the value specified by MAXVALUE, no partition can be created. In this case, you cannot configure partitioning strategies in the Create Partitioning Plan panel.
By default, a partitioning plan is executed on the hour.
If a database already has a partitioning plan, the new partitioning plan will overwrite the existing one once it is approved.
Creating partitions for a table within a table group can fail or break the load balancing status. Proceed with caution when you decide to configure a partition creation strategy for such a table.
Creating partitions for a table within a table group can invalidate the table group, because tables in the same table group must have the same number of partitions.
Deleting partitions from a table that contains a global index will invalidate the global index. Proceed with caution. Choosing to rebuild the global index may cause business issues due to the time-consuming process or online issues resulting from rebuilding failures.
The option of rebuilding global indexes is provided only in Oracle-compatible mode. In MySQL-compatible mode, global indexes will be rebuilt by default.
Create a partitioning plan
Example: Create a partition for the order table in the test_data database of the mysql4253 data source at a time interval of 1 month.
Parameter | Example value |
Project name | odc_test |
Data source | mysql4253 |
Database name | test_data |
Table name | order |
In the SQL window, write an SQL statement to create a table named order.
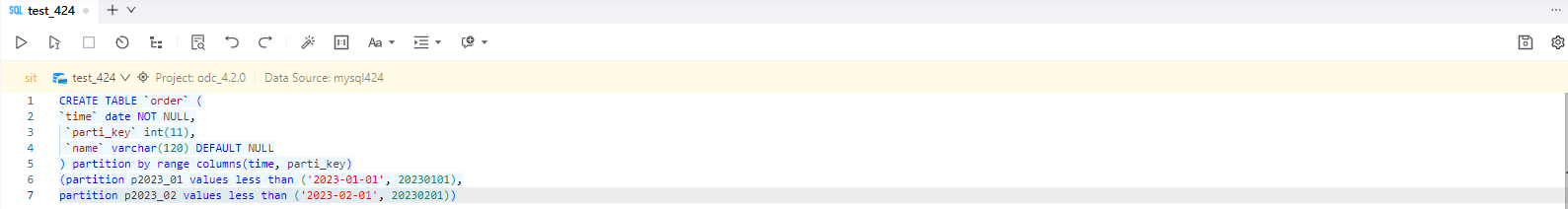
CREATE TABLE `order` ( `time` date NOT NULL, `parti_key` int(11), `name` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL ) partition by range columns(time, parti_key) (partition p2023_01 values less than ('2023-01-01', 20230101), partition p2023_02 values less than ('2023-02-01', 20230201))On the Tickets tab of the SQL window, choose Partitioning Plan > Create New.
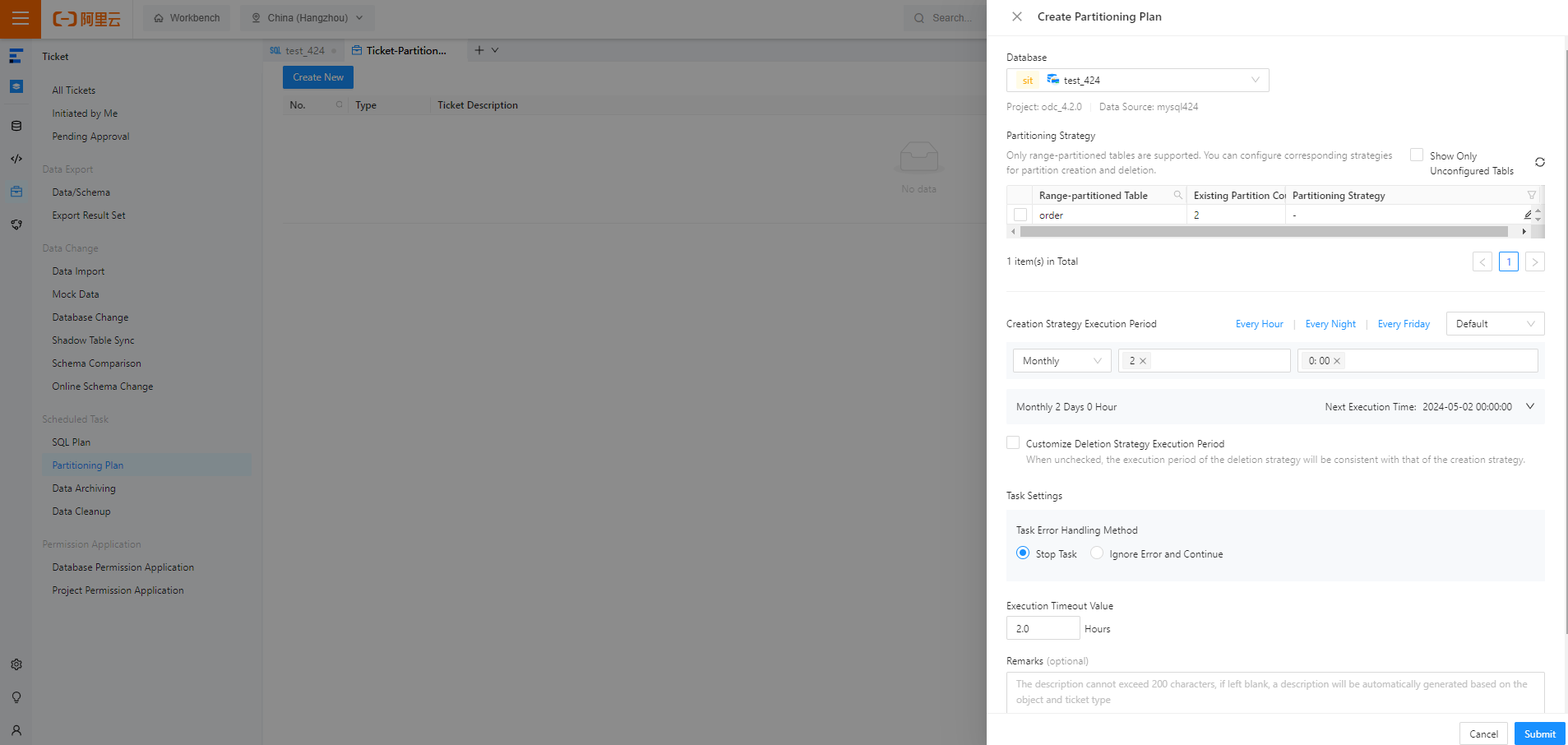
In the Create Partitioning Plan panel, configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Database
Select the database for which the partitioning plan is created.
Partitioning Strategy
Select the target RANGE-partitioned table in the specified database and click
 to set partitioning strategies. For more information, see Set partitioning strategies and Examples. Note
to set partitioning strategies. For more information, see Set partitioning strategies and Examples. NoteYou can select Show Only Unconfigured Tables next to Partition Strategy to display only tables with no partitioning strategies.
You can also select multiple RANGE-partitioned tables and configure partitioning strategies for them at a time.
Strategy Execution Cycles
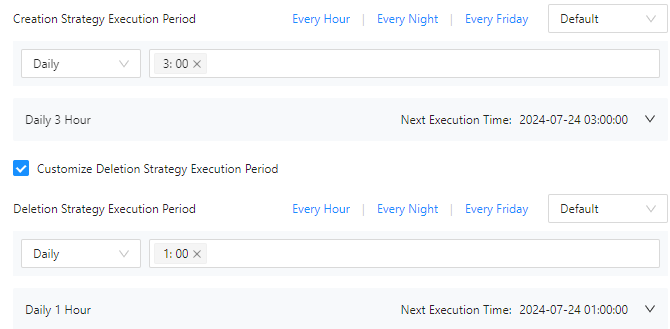
Creation Strategy Execution Period: Set an execution cycle for all partition creation strategies, for example, at 2:00 a.m. every day.
Customize Deletion Strategy Execution Period: Select this option and set an execution cycle for all partition deletion strategies. If you do not select this option, the partition deletion strategies will be scheduled together with partition creation strategies.
Example: Set the execution cycle to 3:00 a.m. every day for partition creation strategies, and to 1:00 a.m. every day for partition deletion strategies. The system will execute all partition creation strategies at 3:00 a.m. every day and all partition deletion strategies at 1:00 a.m. every day.
Task Settings
Select a method for handling task errors. Valid values:
Stop Task: This is the default option. When you select this option, the task is aborted if an error occurs when you run the script.
Ignore Error and Continue: When you select this option, the system skips the statement where an error occurs and continues to execute other statements in the script.
Execution Timeout Value
The default value is 2 hours.
Remarks
The business background of the project, such as the change purpose and expected goal.
After you specify the preceding information, click Submit in the lower-right corner of the panel.
After the task is generated, you are redirected to the Task Center panel. You can view the task approval status and task information here.

View a partitioning plan task
Task information
In the partitioning plan task list on the Tickets tab, click View in the Actions column of a partitioning plan task.
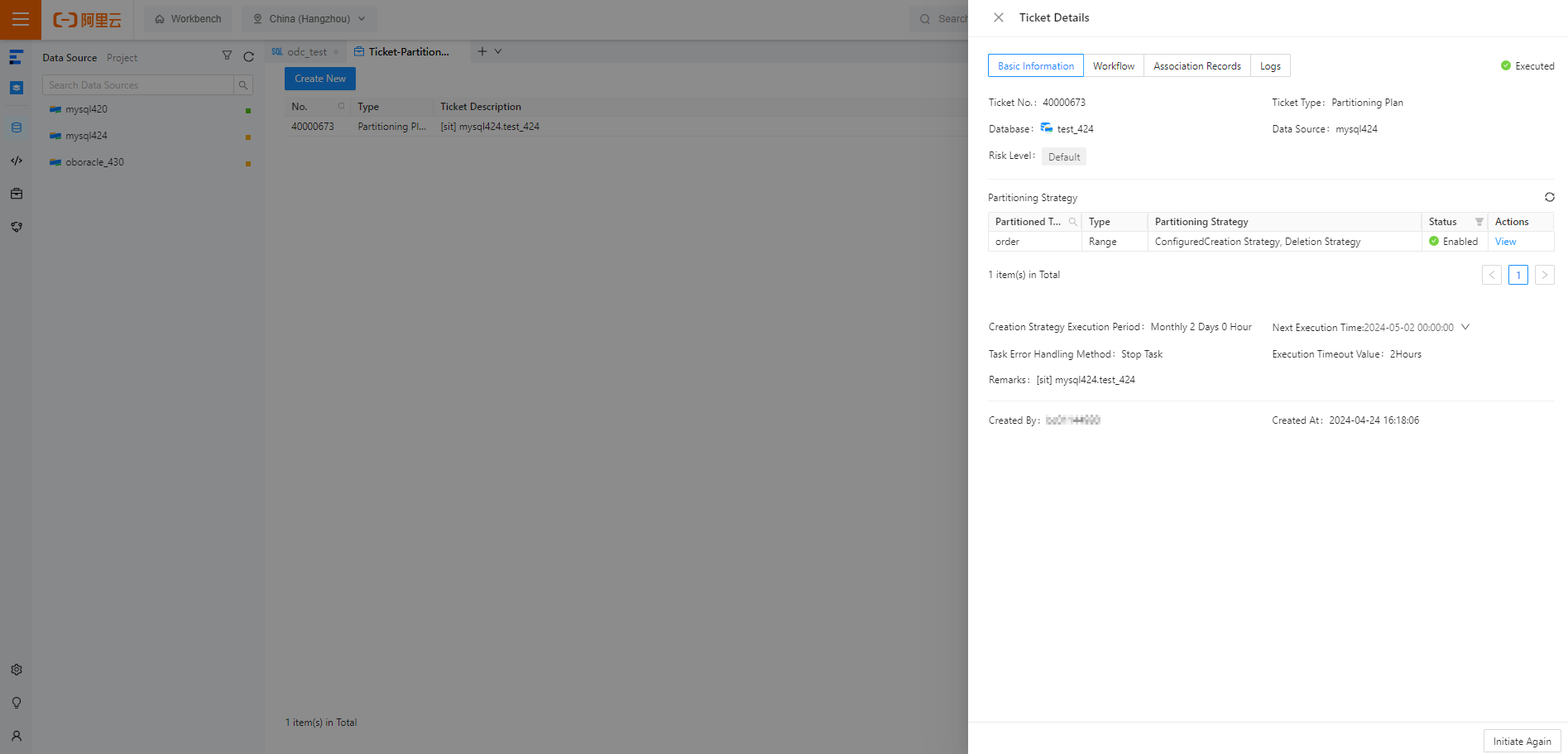
In the Ticket Details panel, click the Basic Information tab and view the basic task information and task settings.
Parameter
Description
Basic task information
The status, ID, type, data source, risk level, remarks, creator, and creation time of the task are displayed.
Task settings
You can view the partitioning strategies of the RANGE-partitioned table selected when you created the partitioning plan task.
You can click Initiate Again in the lower-right corner of the panel to initiate the task again.
Task process
In the Ticket Details panel, click the Workflow tab and view the initiation status, approval status, execution status, and execution result of the task.
You can click Initiate Again in the lower-right corner of the panel to initiate the task again.
Association records
In the Ticket Details panel, click the Association Records tab and view the ID, database, creation time, and status of the task. You can also click View in the Actions column of a record.
You can click Initiate Again in the lower-right corner of the panel to initiate the task again.
Task logs
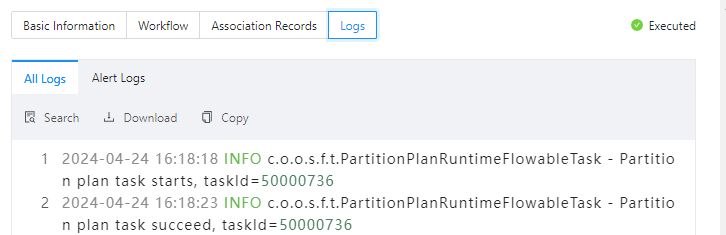
In the Ticket Details panel, click the Logs tab to view all logs and alert logs of the task.
Tab
Description
All Logs
Displays the complete information of all task logs, including INFO, ERROR, and WARN logs. You can click Search, Download, or Copy to search for, download, or copy all logs.
Alert Logs
Alert logs include the ERROR and WARN logs of the task. When a task fails, you can view the error message in the alert logs. You can click Search, Download, or Copy to search for, download, or copy alert logs.
You can click Initiate Again to initiate the task again.
Import partitioning plan tasks
You can migrate instances as well as their partitioning plan tasks from ApsaraDB for OceanBase to OceanBase Cloud.
Step 1: Export partitioning plan tasks from ApsaraDB for OceanBase
Log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console. Click Data Development in the left-side navigation pane.
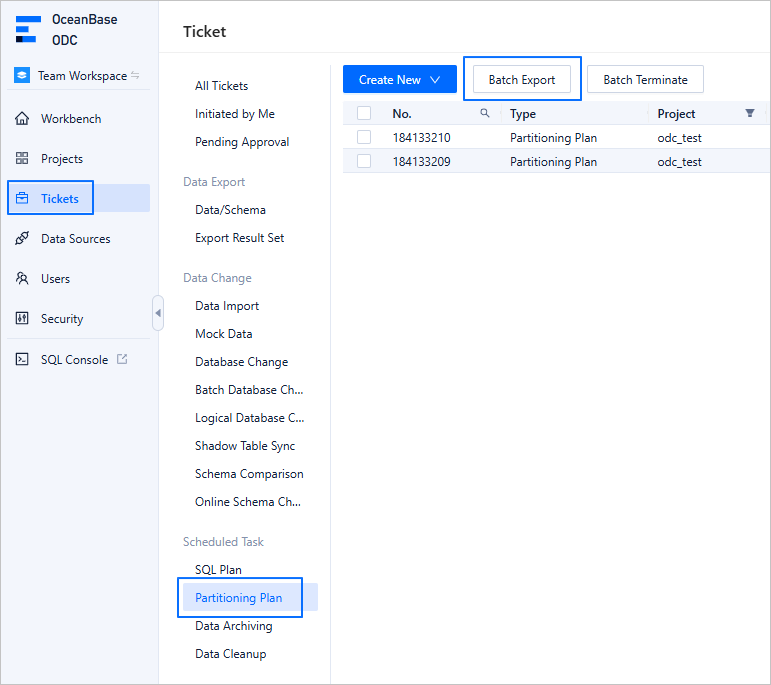
Choose Tickets > Partitioning Plan. On the partitioning plan page, select the target tickets and click Batch Export.
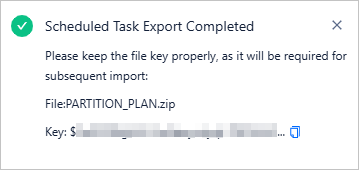
On the scheduled task export page, select the target tasks and click Export All.
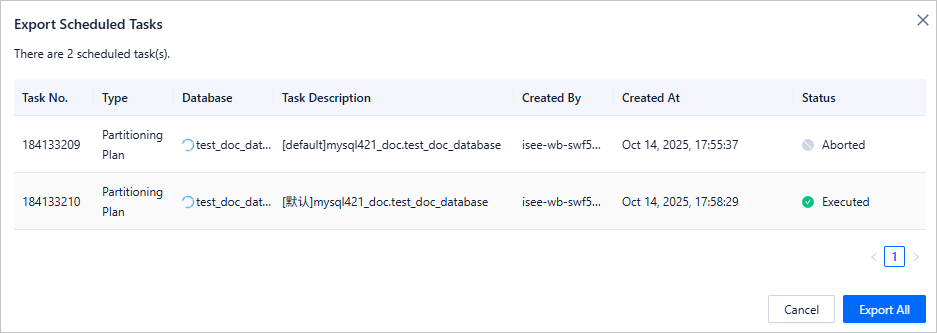
After the export, copy the key in the pop-up window and keep it properly. This key is required when you import the partitioning plans later.
Step 2: Import partitioning plan tasks to OceanBase Cloud
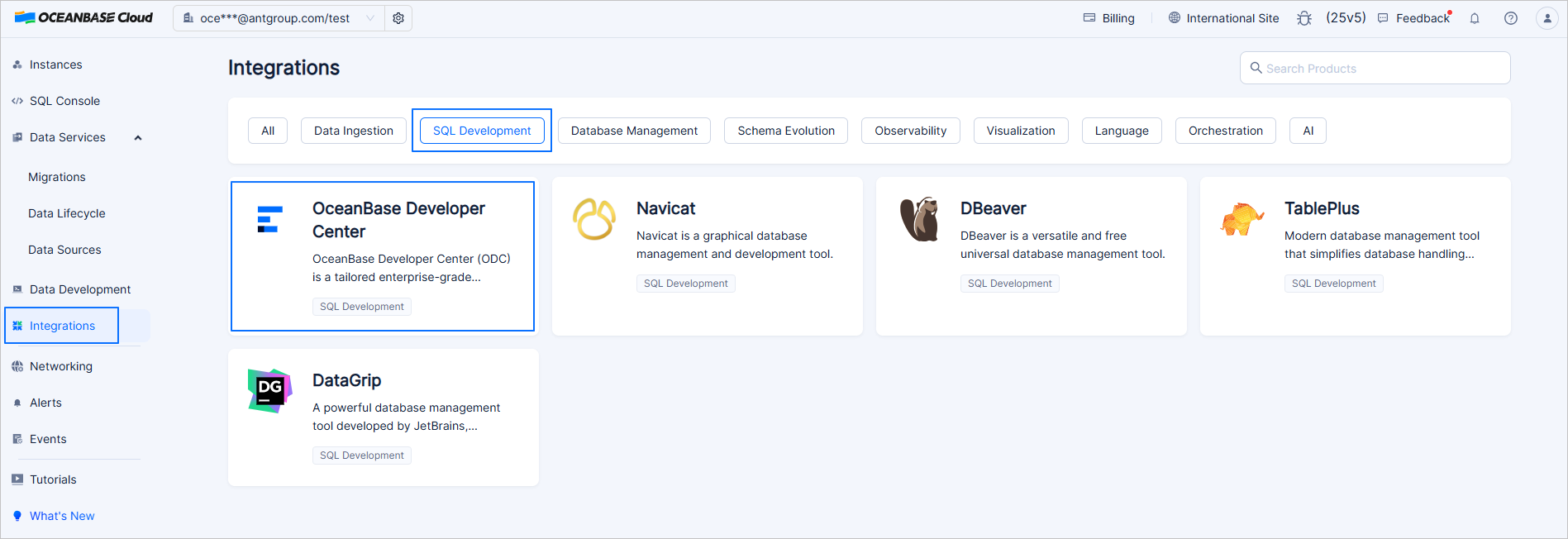
In the left-side navigation pane of the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console, click Integrations and then choose SQL Development > OceanBase Developer Center (ODC).
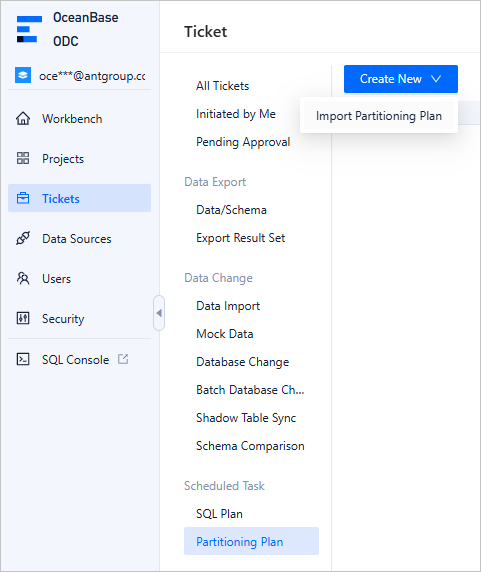
In ODC, choose Tickets > Partitioning Plan. On the partitioning plan page, select the target tickets and click Import Partitioning Plan.
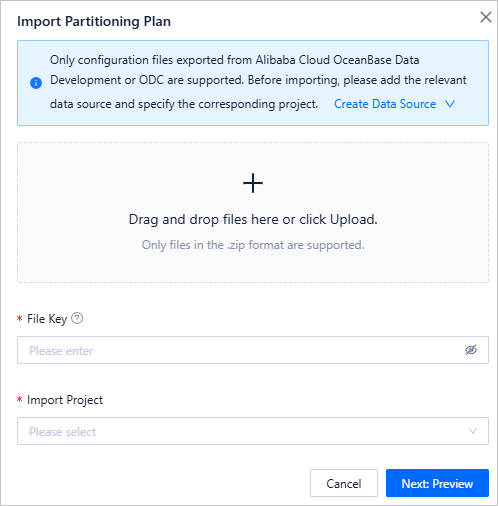
On the partitioning plan import page, add the .zip file exported in Step 1, enter the file key in File Key, select the target project, and click Next: Preview.
On the preview page, select the new target database, select I confirm the consistency of database objects between the old and new databases in the import ticket, and click Import.
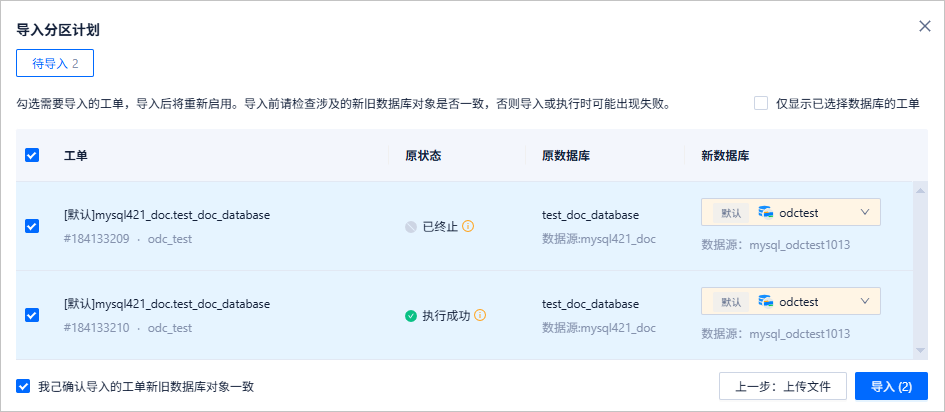
After the import, you can view the imported partitioning plans in the partitioning plan list.