After you create an ApsaraDB for MyBase dedicated cluster, you can view, modify, and delete the dedicated cluster.
Background information
For more information about ApsaraDB for MyBase, see What is ApsaraDB for MyBase?
Modify the information of a dedicated cluster
Log on to the ApsaraDB for MyBase console.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Dedicated Clusters.
On the Dedicated Clusters page, find the dedicated cluster that you want to modify and click Edit in the Actions column.
Configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
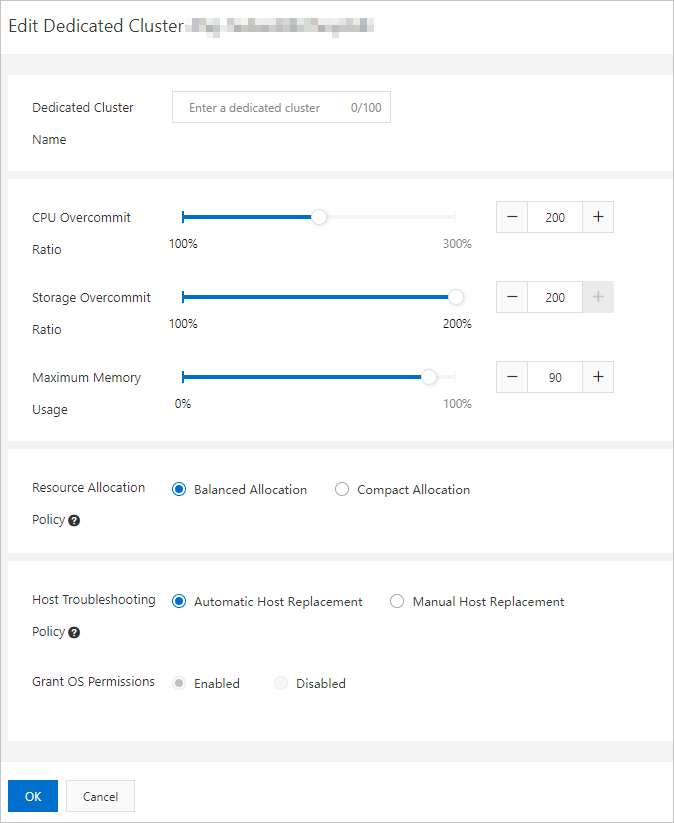
Parameter
Description
Dedicated Cluster Name
The name of the dedicated cluster. You can specify a descriptive name that makes it easy to identify.
CPU Overcommit Ratio
The CPU overcommit ratio of the dedicated cluster.
NoteThe default value and valid values of this parameter vary based on database engines. You can view the default value and valid values in the Edit Dedicated Cluster panel.
Storage Overcommit Ratio
The storage overcommit ratio of the dedicated cluster. You can change the value of this parameter only for ApsaraDB MyBase for MySQL dedicated clusters.
NoteThe default value and valid values of this parameter vary based on database engines. You can view the default value and valid values in the Edit Dedicated Cluster panel.
Maximum Memory Usage
The maximum memory usage of each host in the dedicated cluster.
NoteThe default value and valid values of this parameter vary based on database engines. You can view the default value and valid values in the Edit Dedicated Cluster panel.
Resource Allocation Policy
The default policy that is used to allocate resources in the dedicated cluster. Valid values:
- Automatic Host Replacement: The system automatically replaces the faulty hosts. Note
- If a faulty host uses ESSDs, the host is replaced after the computing resources on the host are migrated.
- If a faulty host uses local SSDs, the host is replaced only after all instances are removed from the host.
- Manual Host Replacement: You must manually replace the faulty hosts.
Host Troubleshooting Policy
The policy that is used to handle host failures. Valid values:
- Balanced Allocation: New database instances are preferentially created on hosts that have the most available resources to maximize cluster stability.
- Compact Allocation: New database instances are preferentially created on hosts that have been created earlier and have more resources allocated. This maximizes resource usage.
Grant OS Permissions
If you grant the host OS permissions for a dedicated cluster that runs the MySQL, SQL Server, or PostgreSQL database engine, you can log on to the hosts in the dedicated cluster to upload files, download files, and install software.
ImportantAfter you grant the host OS permissions for a dedicated cluster, you cannot revoke the permissions.
- Automatic Host Replacement: The system automatically replaces the faulty hosts.
Click OK.
Delete a dedicated cluster
Log on to the ApsaraDB for MyBase console.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Dedicated Clusters.
On the Dedicated Clusters page, find the dedicated cluster that you want to delete and click Delete in the Actions column.

In the message that appears, click OK.