In Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, NetworkManager and systemd-resolved are network management services that can read the /etc/resolv.conf configuration file to resolve domain names to IP addresses. By default, NetworkManager automatically manages the configuration file, and systemd-resolved reads but does not update the configuration file. If you want to configure custom settings such as DNS parameters in the /etc/resolv.conf file, you must disable NetworkManager from automatically managing the configuration file. This topic describes how the two network management services manage the configuration file and how to enable manual management for the file.
How network management services manage the /etc/resolv.conf file
The /etc/resolv.conf configuration file contains a file but not a soft link in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3. NetworkManager and systemd-resolved use the following policies to manage the configuration file:
NetworkManager
File creation policy: The first time the system starts, NetworkManager automatically creates the
/etc/resolv.conffile after the primary network interface controller starts as expected and obtains an IP address.File update policy: NetworkManager updates the
/etc/resolv.conffile when changes occur in network interface controller parameters, such as the device status, IP address, routes, DNS name, and hostname.
systemd-resolved
systemd-resolved is a consumer that can read but does not update the
/etc/resolv.conffile.
The /etc/resolv.conf configuration file may contain a file or a soft link in Linux distributions other than Alibaba Cloud Linux 3. The management policies may vary based on whether the configuration file contains a file or a soft link.
Enable manual management for the /etc/resolv.conf file
In Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, if you want to configure custom DNS settings in the /etc/resolv.conf file, disable NetworkManager from automatically managing the file. Perform the following steps:
Create and open the /etc/resolv.conf file.
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/90-dns-none.confPress the
Ikey to enter Insert mode and add the following content to the configuration file:[main] dns=nonePress the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press theEnterkey to save and close the configuration file.Reload the configuration file.
sudo systemctl reload NetworkManager
If the /etc/resolv.conf file is not automatically created on system startup, the system cannot use the DNS server defined in the configuration file to perform DNS resolution. For more information, see the What do I do if the system does not automatically create the /etc/resolv.conf file after the system starts? section of this topic.
Re-enable automatic management for the /etc/resolv.conf configuration file
After you enable manual management for the /etc/resolv.conf file, NetworkManager no longer automatically manages the file. To re-enable NetworkManager to automatically manage the file, delete or comment out the content that you added in Step 2 and perform Step 4 to reload the configuration file.
FAQ
What do I do if the system does not automatically create the /etc/resolv.conf file after the system starts?
Cause: NetworkManager fails to start. As a result, the /etc/resolv.conf file is not created.
Solution: Query the status and logs of NetworkManager and resolve the issue.
Query the NetworkManager status.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManagerThe state shown in the following figure indicates that NetworkManager runs as expected.
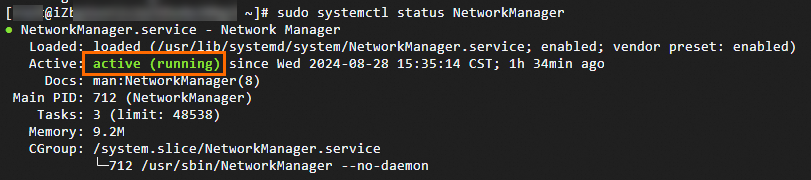
If another state appears, view NetworkManager service logs to identify the issue.
View logs about NetworkManager activation.
sudo journalctl -u NetworkManager -bAfter the issue is resolved based on the logs, run the following command to start NetworkManager:
sudo systemctl start NetworkManagerAfter NetworkManager is started, the
/etc/resolv.confconfiguration file is automatically created.