NetworkManager is a tool that is used to manage network interface controller (NIC) configurations and the connection status. NetworkManager can automatically detect available networks and switch between networks based on your business requirements. NetworkManager also allows you to configure network settings such as IP addresses, gateways, and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. This topic describes the configuration files and common settings of NetworkManager in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3. You can modify the configurations based on your business requirements.
NetworkManager configuration files
NetworkManager manages the following configuration files that are loaded in sequence and prioritized in ascending order: configuration files in the /usr/lib/NetworkManager/conf.d directory, configuration files in the /run/NetworkManager/conf.d/ directory, /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf, and configuration files in the /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d directory.
/usr/lib/NetworkManager/conf.d: mainly stores the default settings of software. Custom settings must be saved in configuration files that have a higher priority, such as files in the/etc/NetworkManager/conf.ddirectory, to prevent the custom settings from being overwritten when the software package is updated./run/NetworkManager/conf.d/: stores temporary running configurations. Files in this directory are created by system services or by using startup scripts on system startup. We recommend that you do not store custom settings in this directory because the configurations are lost when the system is restarted./etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf: is the primary configuration file of NetworkManager and is updated when the software package is removed or updated. To prevent custom settings from being overwritten, we recommend that you do not modify theNetworkManager.conffile./etc/NetworkManager/conf.d: stores.conffiles that you create to modify the default settings of NetworkManager.This ensures that custom settings are retained when the software package is updated. Take note that files in this directory are read based on the lexicographic order of the file name.
Common settings of NetworkManager
NetworkManager log settings
In the following example, level is set to TRACE and domains is set to ALL to record all operation logs.
Run the following command to create and open the
set-log.conffile:sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/set-log.confPress the
Ikey to enter Insert mode and copy the following content to theset-log.conffile:[logging] level=TRACE domains=ALLDescription of the level parameter
Value
Description
OFF
Disables logs. No logs are output.
ERR
Outputs logs at the error level.
WARN
Outputs logs at the warning level and higher levels.
INFO
Outputs logs at the information level.
DEBUG
Outputs logs at the debug level.
TRACE
Outputs detailed logs at the trace level.
Description of the domains parameter
Value
Description
NONE
Does not record logs in domains.
ALL
Records logs of all available domains.
DEFAULT
Records logs of default domains.
DHCP
Records logs related to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) clients.
IP
Records logs related to IP management.
Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press theEnterkey to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManagerRun the following command to view NetworkManager logs:
journalctl -u NetworkManager
NetworkManager does not take over NIC configurations
To configure NetworkManager not to take over NIC configurations, specify the unmanaged-devices key in the keyfile section. In the following example, NetworkManager is configured not to take over secondary NICs such as eth1.
Run the following command to check the status of NICs:
nmcli device statusThe command output shown in the following figure indicates that
NetworkManagertakes overeth0andeth1, but notlo.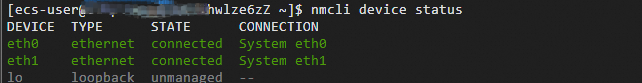
Run the following command to create and open the
unmanaged.conffile:sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/unmanaged.confPress the
Ikey to enter Insert mode and copy the following content to theunmanaged.conffile:[keyfile] unmanaged-devices=interface-name:eth1Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press theEnterkey to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManagerRun the following command to check whether the changes in the configuration file take effect:
nmcli device status
NetworkManager plug-in configurations
NetworkManager uses the ifcfg-rh/keyfile plug-ins to read and write network settings. By default, the ifcfg-rh plug-in is used to manage the primary NIC, for example, eth0, and the keyfile plug-in is used to manage secondary NICs, for example, eth1.
The
ifcfg-rhplug-in is used to read configurations from and write configurations to/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-*files.The
keyfileplug-in is a generic plug-in for NetworkManager. Each connection has a corresponding.nmconnectionconfiguration file.
Run the following command to open the NetworkManager.conf file:
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.confPress the
Ikey to enter Insert mode and add or change the values of thepluginsparameter.NoteThe
pluginsare sorted based on the declaration order. The leftmost plug-in has the highest priority.[main] plugins = ifcfg-rh, keyfilePress the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press theEnterkey to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManagerRun the following command to check whether the changes in the configuration file take effect:
sudo journalctl -u NetworkManager | grep -i "settings plugin"