If you need to enable a specific feature in the Alibaba Cloud Linux kernel, or disable a default feature for performance or security reasons, you can build custom kernel RPM packages from the source code. This process ensures that your custom kernel remains compatible with the Alibaba Cloud Linux distribution. This guide explains how to modify and build Alibaba Cloud Linux kernel RPM packages in a container on an Alibaba Cloud Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Prerequisites
You need an ECS instance running Alibaba Cloud Linux. For more information, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
Image: Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.
Instance type: An instance type with 32 vCPUs or more is recommended.
NoteBuilding RPM packages is time-consuming. To speed up the process, use an instance with 32 vCPUs or more.
Step 1: Prepare the environment
Connect to your ECS instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following commands to download the Docker image and enter the container.
#Install Docker. sudo yum install -y docker #Pull a Docker image. sudo docker pull <image_url> #Start the Docker container. sudo docker run -itd --net host --name alinux-build <image_url> bash #Access the Docker container. sudo docker exec -it alinux-build bashReplace
<image_url>with the Docker image URL for your Alibaba Cloud Linux version.Image
Docker image URL
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2
alibaba-cloud-linux-2-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/alinux2/alinux2
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
alibaba-cloud-linux-3-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/alinux3/alinux3
This example uses the Docker image for Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.
sudo yum install -y docker sudo docker pull alibaba-cloud-linux-3-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/alinux3/alinux3 sudo docker run -itd --net host --name alinux-build alibaba-cloud-linux-3-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/alinux3/alinux3 bash sudo docker exec -it alinux-build bash
Step 2: Download the source code
Run the following commands to download and install the source RPM package.
# Download the source code package.
yum install -y wget
wget <rpm_url>/<src.rpm_name>
# Install the source code package.
rpm -ivh <src.rpm_name><rpm_url>is the URL to the RPM package repository for Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or 3.Image
RPM package URL
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/alinux/3/plus/source/SRPMS/kernels/
<src.rpm_name>is the name of the source RPM package you want to modify.
This example downloads the kernel-5.10.134-13.1.al8.src.rpm package for Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.
yum install -y wget
wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/alinux/3/plus/source/SRPMS/kernels/kernel-5.10.134-13.1.al8.src.rpm
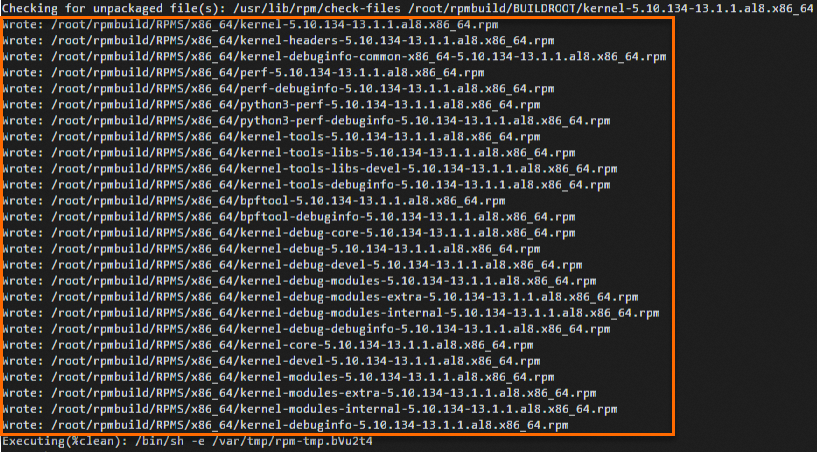
rpm -ivh kernel-5.10.134-13.1.al8.src.rpmAfter the source package is installed, the files are saved in the /root/rpmbuild directory. To view the files, run the ls /root/rpmbuild command. The output is similar to the following:
Step 3: Modify the source code
Run the following commands to install dependencies.
yum install -y rpm-build yum-utils yum-builddep -y <src.rpm_name>Replace
<src.rpm_name>with the name of your source RPM package. In this example, the package name iskernel-5.10.134-13.1.al8.src.rpm.yum install -y rpm-build yum-utils yum-builddep -y kernel-5.10.134-13.1.al8.src.rpmRun the following commands to extract the source package.
# Enter the source code directory. cd /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES # Decompress the source code package. tar xf <Name of the compressed source code package>In this example,
<source_archive_name>islinux-5.10.134-13.1.al8.tar.xz.cd /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES tar xf linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8.tar.xzRun the following command to go to the extracted directory.
cd <Name of the decompressed source code package>In this example,
<extracted_source_directory_name>islinux-5.10.134-13.1.al8.cd linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8(Optional) Modify the configuration files.
Modify the source code or a
configfile as needed. This section covers how to modify aconfigfile.Run the following command to view and select the configuration file you want to modify.
ls /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES
There are four
configfiles in the/root/rpmbuild/SOURCESdirectory.config file
Description
kernel-5.10.134-aarch64.config
The configuration file of the Arm architecture and the release version.
kernel-5.10.134-aarch64-debug.config
The configuration file of the Arm architecture and the debug version, which can be used only for testing.
kernel-5.10.134-x86_64.config
The configuration file of the x86 architecture and the release version.
kernel-5.10.134-x86_64-debug.config
The configuration file of the x86 architecture and the debug version, which is used only for testing.
Choose the file that matches your platform's architecture. You can also modify the configurations for both platforms.
Run the following command to modify the configuration file.
This example uses the
kernel-5.10.134-x86_64.configfile for the x86 architecture.Copy the configuration file to the source directory.
cd /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES cp kernel-5.10.134-x86_64.config linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8/.configGo to the source directory.
cd linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8Apply default values for any new configuration options.
make olddefconfigTo make changes, use
make menuconfig. This command ensures that all configuration dependencies are handled correctly.make menuconfigThe
menuconfiginterface opens. To search for the item you want to modify, press the/key, and then make changes as needed.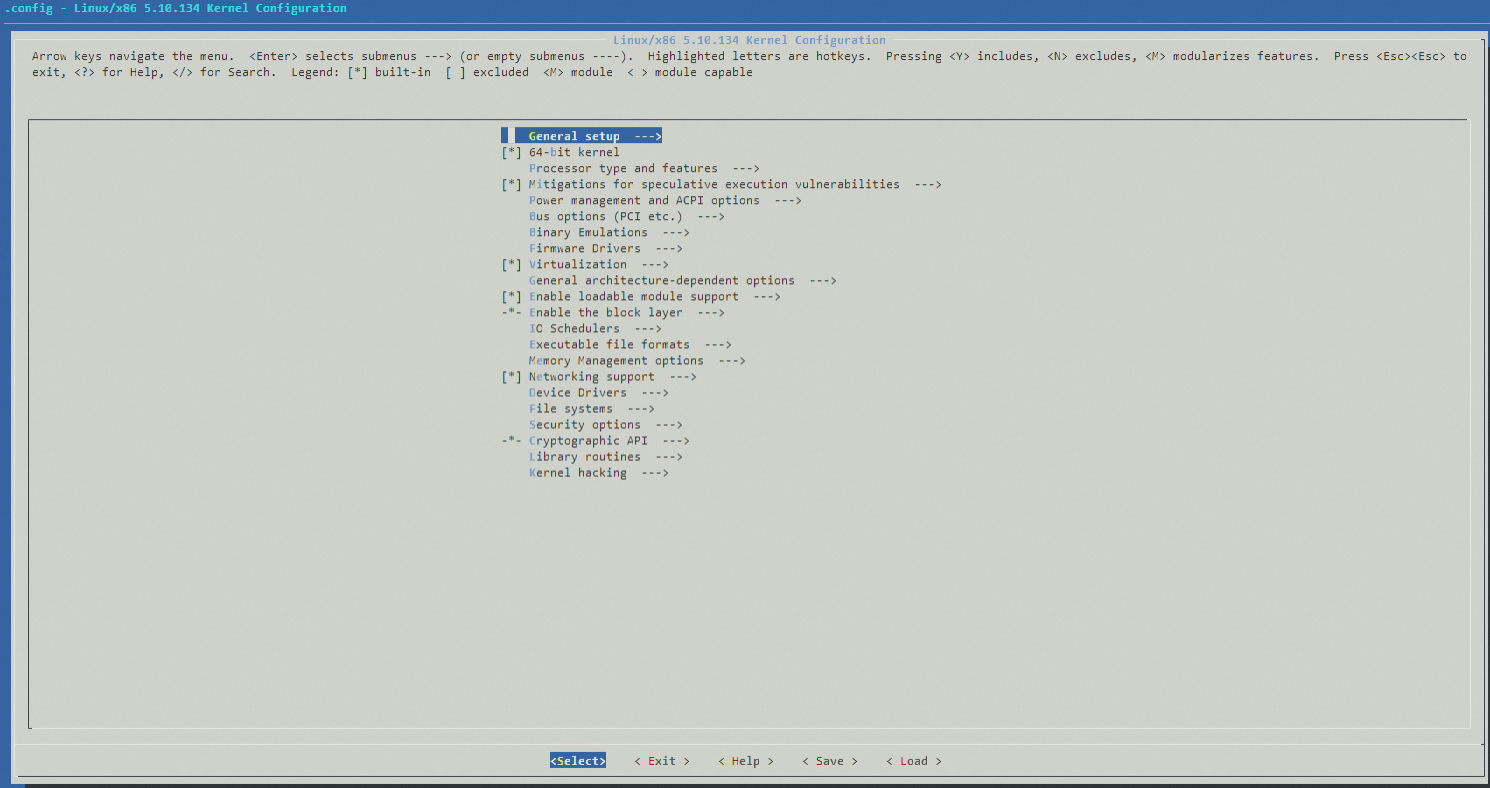
To overwrite the original file, copy the modified configuration file.
cp .config ../kernel-5.10.134-x86_64.configReturn to the parent directory.
cd ..
NoteYou can use the same method to modify the configuration file for the Arm architecture.
Run the following commands to update the version number.
cd /root/rpmbuild/SPECS vi kernel.specPress
Ito enter Insert mode. When you are finished, pressEsc, type:wq, and pressEnterto save and exit.Versioning recommendations: To distinguish your build from an official version, update the version number. For example:
Change a major version like
5.10.134-12to5.10.134-12.0.1.Change a minor version like
5.10.134-13.1to5.10.134-13.1.1.
This example updates the version number from
5.10.134-13.1to5.10.134-13.1.1.In the file, find the
%define pkgrelease %{?KREL:%{KREL}}%{?!KREL:13.1}line and update it to%define pkgrelease %{?KREL:%{KREL}}%{?!KREL:13.1.1}.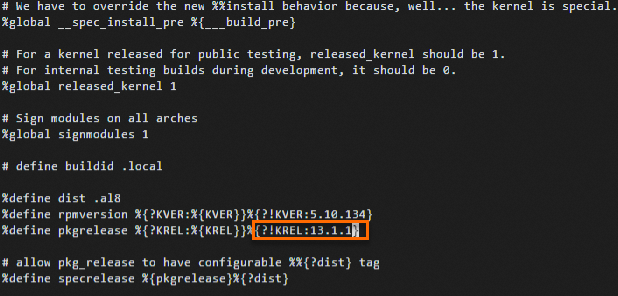
You can also describe your changes in the changelog section of the
kernel.specfile.
Step 4: Rebuild the RPM packages
Run the following commands to recompress the modified source code.
In this example, the source directory name is
linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8.Go to the
SOURCESdirectory.cd /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES/Rename the source directory.
In the previous step, the version number was updated from
5.10.134-13.1to5.10.134-13.1.1. Therefore, rename the source directory tolinux-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8.mv linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8 linux-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8Recompress the directory into a tarball.
tar cJf linux-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8.tar.xz linux-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8Remove the original source directory and the old tarball.
rm -rf linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8 rm -f linux-5.10.134-13.1.al8.tar.xz
Run the following command to rebuild the source RPM package.
cd /root rpmbuild -bs rpmbuild/SPECS/kernel.specWhen the command finishes, the output shows the new source RPM package's location:
/root/rpmbuild/SRPMS/kernel-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8.src.rpm.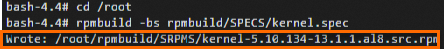
(Optional) Run the following command to downgrade the
dwarvespackage.If your installed source RPM kernel version is
5.10.134-13.1.al8or earlier, the build requiresdwarves-1.22-1.al8to prevent errors.yum downgrade dwarves-1.22-1.al8 -yRun the following command to rebuild the RPM packages.
rpmbuild --rebuild /root/rpmbuild/SRPMS/<src.rpm_name>Replace
<src.rpm_name>with the name of your modified source RPM package. In this example, the package name iskernel-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8.src.rpm.rpmbuild --rebuild /root/rpmbuild/SRPMS/kernel-5.10.134-13.1.1.al8.src.rpmThe build process is time-consuming. When the following message appears, the RPM packages have been built successfully.