By default, content distributed by CDN is publicly accessible to anyone with the URL. To prevent malicious downloads and unauthorized use of your site resources, you can enable URL signing. This feature offers stronger protection than hotlink protection or IP blacklists and whitelists. URL signing protects your origin resources by validating an encrypted string and a timestamp included in the request URL.
How it works
The URL signing feature uses Alibaba Cloud CDN points of presence (POPs) and your origin server to create a secure method for preventing resource hotlinking. The process involves the following components:
Origin application server: Generates signed URLs for clients based on signing rules, which include the algorithm and key.
Client: Initiates a resource request and sends the signed URL to a CDN POP for validation.
CDN POP: Validates the information in the signed URL, such as the signed string and timestamp.

The customer configures the signed URL generation rules on the origin server. These rules include the signing algorithm and key.
For example, a signed URL is
http://DomainName/timestamp/md5hash/FileName.When a client accesses a page on the server, the server generates a signed URL based on the rules. The server then returns the signed URL to the client within the page content (Steps 2 and 3 in the diagram).
The client uses the signed URL to request the resource from a POP (Step 4 in the diagram).
The POP validates the information in the signed URL, such as the signed string and timestamp, to check if the request is valid.
If authentication fails, the access request is denied.
If authentication succeeds, the request is processed.
NoteIf a resource is not cached on a POP, the POP removes the authentication parameters from the signed URL, reverts it to the original URL (for example,
http://DomainName/FileName), and then uses the original URL to generate a cache key or initiate an origin request.After your request URL is authenticated by CDN, special characters in the URL, such as Chinese characters or other non-ASCII characters, are encoded.
Log behavior
Requests that fail authentication can still reach POPs. However, the POPs will deny these requests and return a 403 status code. The failed authentication attempts are still recorded in CDN logs.
Billing
Because URL signing validates custom encrypted strings and timestamps, you incur a small amount of traffic fees when POPs block malicious requests. If the client uses the HTTPS protocol, you also incur HTTPS request fees. This is because blocking malicious requests consumes processing resources on the POPs.
Configure and enable URL signing
Make sure you have configured the generation rules for signed URLs on your origin application server. These rules include the signing algorithm and key.
The URL signing logic configured in CDN must be consistent with the URL signing logic on your origin application server.
Log on to the CDN console.
In the left navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the target domain name and click Manage in the Actions column.
In the domain's navigation pane, click Access Control.
Click the URL Signing tab.
In the URL Signing area, click Modify.
Turn on the Set URL Signing switch and configure the URL signing information.
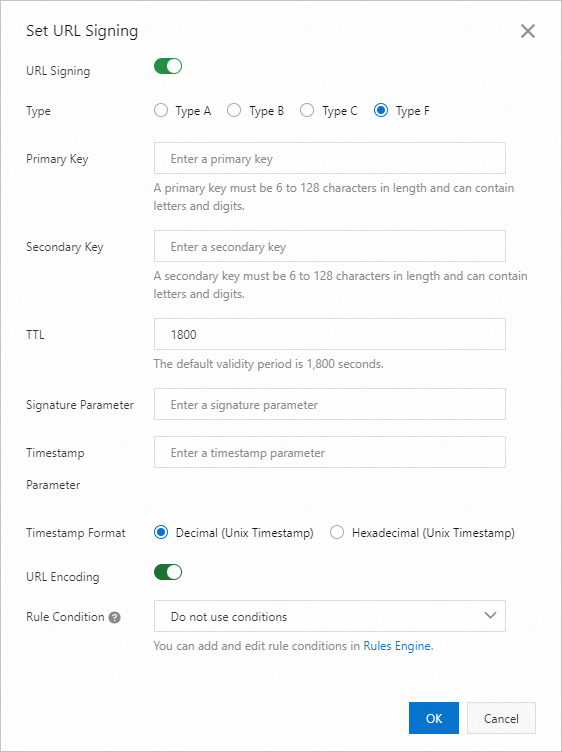
Parameter
Description
Type
Alibaba Cloud CDN provides four methods for signature calculation. Select a signing method based on the format of your encrypted access URL to protect your origin resources. The URL signing types are as follows:
NoteURL signing errors return a 403 error.
MD5 calculation errors
Example:
X-Tengine-Error:denied by req auth: invalid md5hash=de7bfdc915ced05e17380a149bd760beTime-related errors
Example:
X-Tengine-Error:denied by req auth: expired timestamp=1439469547
Primary Key
Enter the primary password for the authentication method. The password must be between 6 and 128 characters long and can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers.
Secondary Key
Enter the secondary key for the signing method. The key must be 6 to 128 characters in length and can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and digits. You must specify at least one key, either primary or secondary.
Signed URL Validity Period
The validity period of the signed URL configured in CDN. Users can access CDN within the time range of (timestamp + validity period). After this period, the authentication expires.
Unit: seconds
Value range: 1 to 31536000
Default value: 1800 (30 minutes)
Example: If the signing server generates a signed URL at 15:00:00 on August 15, 2020 (UTC+8) and the validity period is 1800 seconds, the signed URL expires at 15:30:00 on August 15, 2020 (UTC+8).
Signature Parameter
Lets you customize the name of the signature parameter. This is valid only when **Signing Type** is set to **Type F**.
Timestamp Parameter
Lets you customize the name of the timestamp parameter. This is valid only when **Signing Type** is set to **Type F**.
Timestamp Format
Set the timestamp format. Both decimal (Unix timestamp) and hexadecimal (Unix timestamp) are supported. This is valid only when **Signing Type** is set to **Type F**.
URL Encoding
The URL encoding switch. It is disabled by default. If enabled, user request URLs are URL-encoded. This is valid only when **Signing Type** is set to **Type F**.
Rule Condition
Rule conditions identify various parameters in a user request to determine whether a configuration applies to the request.
Do not use: Do not use rule conditions.
To add or edit rule conditions, manage them in the Rules Engine.
Click OK.
Verify the correctness of the signed URL
After you configure the signed URL, we recommend that you generate a corresponding signed URL in the CDN console to ensure that your server has correctly implemented the authentication logic.
In the Generate Signed URL area, configure the Original URL and signing information.
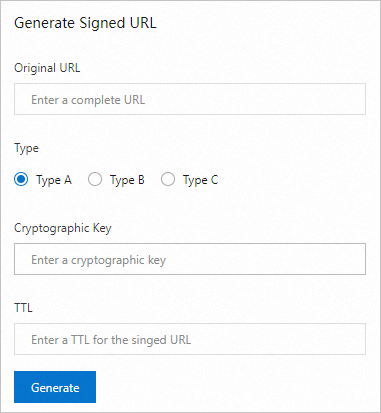
Parameter
Description
Original URL
Enter the complete original URL. For example:
https://www.aliyun.com.Type
Select the URL signing type based on your configuration in Configure and enable URL signing.
Cryptographic Key
Enter the Primary Key or Secondary Key that you configured in Configure and enable URL signing.
TTL
Enter the validity period of the signed URL in seconds, based on your configuration in Configure and enable URL signing.
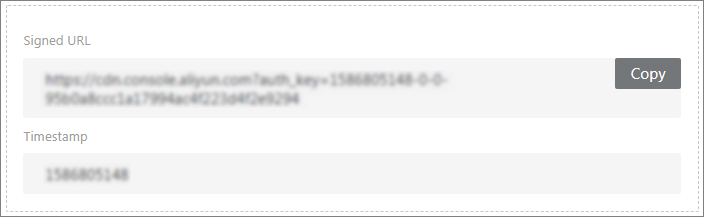
Click Generate to obtain the Signed URL and Timestamp.
Disable URL signing
If you disable the URL signing feature in CDN but client requests still include signing parameters in the URL, CDN cannot revert the request URL to its original form. As a result, all requests miss the cache and are forwarded to the origin server. This causes a sharp increase in origin traffic and origin server costs. Therefore, to stop using URL signing, you must disable the feature on both your application server and in the CDN console.

In the URL Signing area of the CDN console, click Modify and turn off the URL signing switch.
Remove the signing parameters from the request URLs in your application server.