Feature configuration is an essential part in recommendation solution configurations. The feature configuration platform allows you to configure desired features and then the platform automatically generates the corresponding MaxCompute and Flink SQL code. This process generates common statistical features, sequence features, MinMax features, and preference key-value statistical features. The final outputs are used by vector recall, coarse ranking, and fine ranking models. This section describes how to configure features.
1. Configure the Statistical Period and Behavior parameters
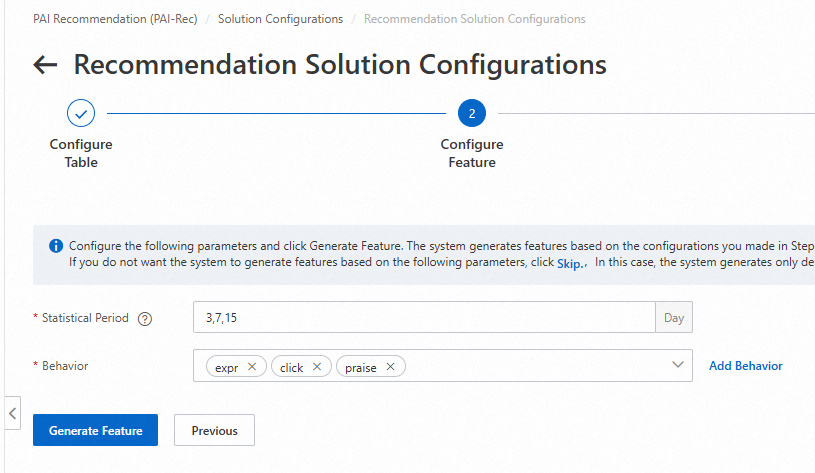
Statistical Period: the cycles for obtaining features. You can specify custom cycles. In most cases, we recommend that you configure short, medium, and long cycles. If you configure too many cycles, the number of obtained features will be extremely large. For example, if 200 features are obtained during one cycle, 600 features are obtained during three cycles. If you configure six cycles, 1,200 features are obtained.
Behavior: behavior values in the behavior log table. In most cases, we recommend that you configure up to five behavior values because too many behavior values result in an extremely large number of features like Statistical Period. If too many behavior types exist, you can merge some unimportant or similar behavior types when you prepare the behavior log table. Note that behavior values are set in the order of occurrence, such as the exposure, click, and praise order which corresponds to the expr, click, and praise values in the event field. An incorrect order affects the generation of ratio-based features and results in manual modifications in subsequent configurations.
After you click Generate Feature, the system generates derived user and item features based on the values of the Statistical Period and Behavior parameters and the basic features in the behavior log, user, and item tables, such as categories, numerical values, and tags.
2. Configure basic derived features
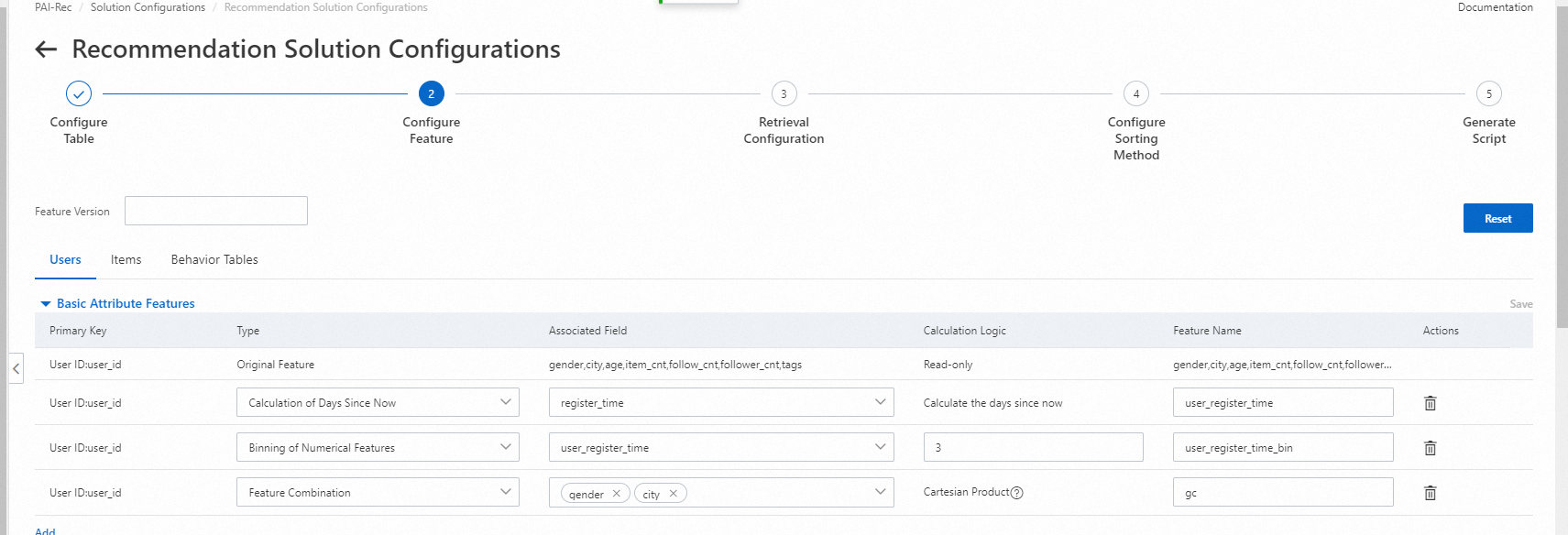
New features are derived from the behavior log, user, and item tables. You can also click Add to add basic derived features. Note that new features are derived from basic attribute features of items, users, and behaviors.
IP Address Resolution: This configuration takes effect only if the imported tables contain IP addresses. The following information about IP addresses can be obtained: province, city, and country. Note that some errors may exist in the resolution results.
Calculation of Days Since Now: The number of days from the registration date of a user or item to today is calculated.
Binning of Numerical Features: This configuration applies only to numerical features. Numerical features are divided into distinct groups based on binning points. After binning, categorical features are obtained.
Feature Combination: Various fields can be combined, such as combination of two categorical fields, combination of a categorical field and a tag field, and combination of two tag fields. In addition, the fields to be combined must belong to the same table, for example, the same user table or the same item table.
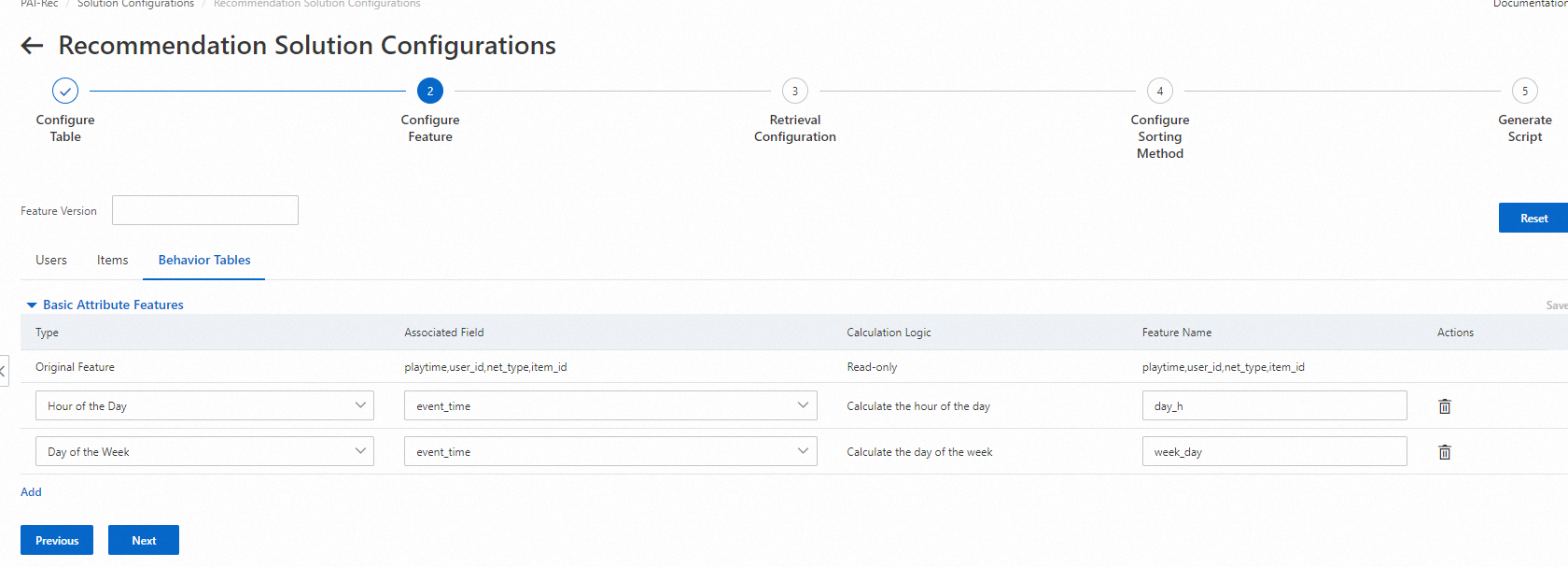
On the Behavior Tables tab, the following types of derivation are supported:
Hour of the Day: The hour at which logs were generated is calculated.
Day of the Week: The weekday on which logs were generated is calculated.
After you manually add basic derived features, you need to click Save in the upper-right corner for these features to take effect.
3. Configure behavior preference features
The following figure shows that a variety of statistical features are automatically derived for users and items. User IDs and item IDs are automatically used as the primary keys for feature aggregation. The following types of statistics are supported:
Behavior Statistics
Conversion Rate Calculation
Number of Behaviors on Top Preferred Attribute Features
Conversion Rate of Top Preferred Attribute Features
Calculation of Values of Preferred Numerical Features
Calculation of Values of Top Combined Features
If you do not need a specific feature, you can click the delete button on the right side to delete it or click the edit button to delete it. To add features, click Add in the lower-left corner. The following section describes the supported types of statistical features:
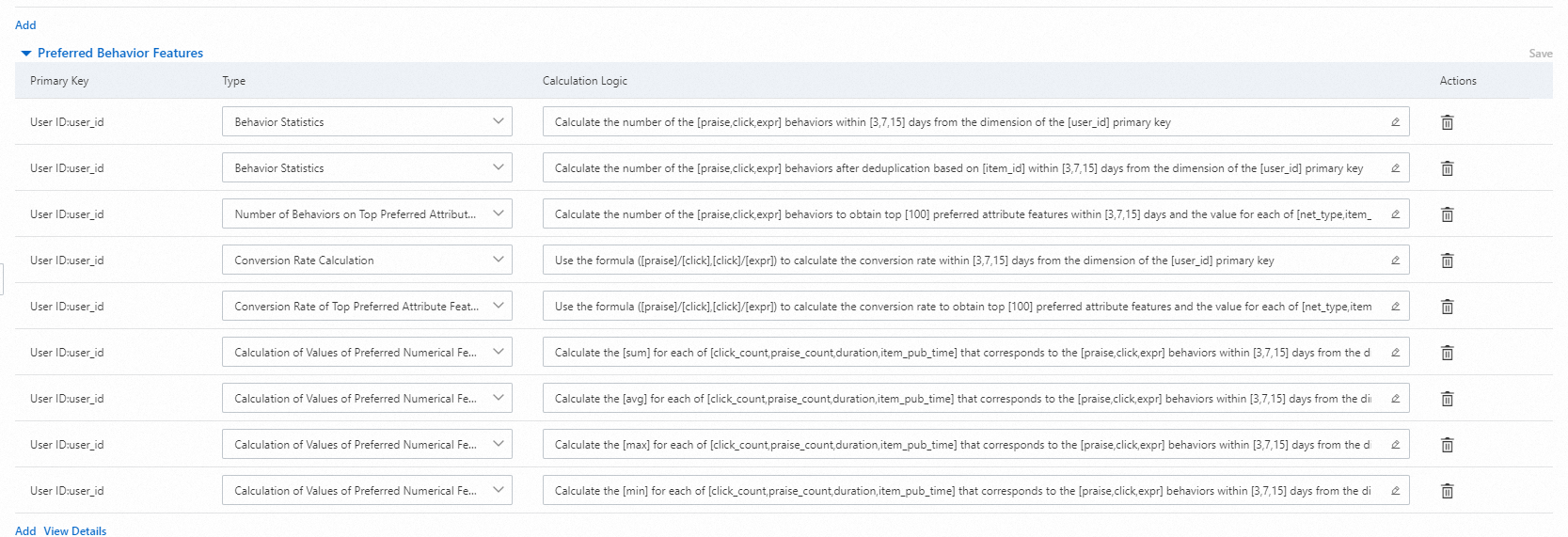
Behavior Statistics

The number of times for which behaviors occurred is calculated for the specified periods of time. For example, the value 3, 7, 15 indicates three statistical periods, and the value expr, click, and praise indicates three types of behaviors. If an ID is set for the Deduplication parameter, deduplication is performed based on the ID and the number of times is calculated after deduplication. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred in this scenario are collected. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, nine features are generated, which equals the number (3) of statistical periods multiplied by the number (3) of behaviors.
Conversion Rate Calculation
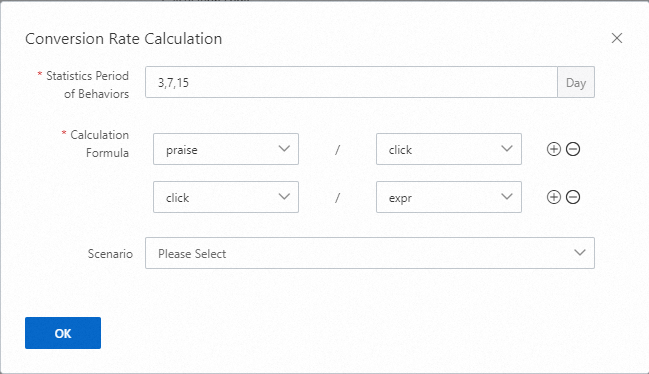
The ratio of the number of behaviors of a type to the number of behaviors of another type is calculated for the specified periods of time, such as 3, 7, and 15 days. For example, the number of clicks is divided by the number of exposures and the number of praises is divided by the number of clicks. You can modify the configurations to generate features and add or delete features based on your business requirements. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred only in this scenario are collected. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, six features are generated, which equals the number of statistical periods multiplied by the number of conversion rate calculation formulas.
Number of Behaviors on Top Preferred Attribute Features
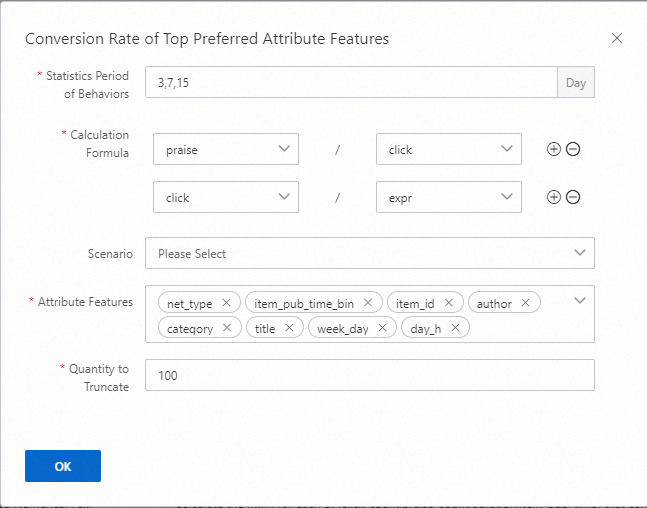
Behavior statistics under attribute feature categories or multi-value categories are collected for the specified periods of time, such as 3, 7, and 15 days. Examples of behaviors include exposure, click, and praise. The number of behavior occurrences under each attribute feature category is collected and then key-value features are generated. For example, day_h is selected for the Attribute Features parameter and click is selected for the Behavior parameter. The feature "12:27.0,8:26.0,1:1.0" is generated, which indicates that the user performed 27 clicks at 12 o'clock, 26 clicks at 8 o'clock, and 1 click at 1 o'clock in the current statistical period. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred in this scenario are collected. If the number of keys is too large, 100 keys are retained by default. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, 54 features are generated, which equals the number of statistical periods multiplied by the number of behaviors multiplied by the number of attribute features.
Conversion Rate of Top Preferred Attribute Features
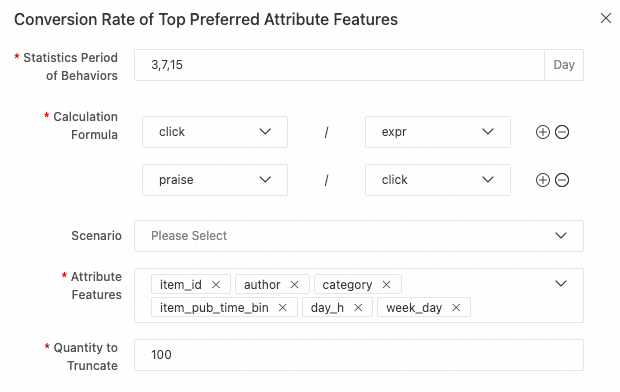
Behavior ratios under attribute feature categories or multi-value categories are collected for the specified periods of time, such as, 3, 7, and 15 days. For example, CTR (the number of clicks/the number of exposures) and CVR (the number of praises/the number of clicks) are collected. CTR is short for click-through rate and CVR is short for conversion rate. Then, key-value features are generated. For example, category is selected for the Attribute Features parameter and the formula click/expr is set for the Calculation Formula parameter. The feature "12:0.27,8:0.26" is generated, which indicates that CTR of the user is 0.27 for category 12 and 0.26 for category 8 in the current statistical period. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred in this scenario are collected. If the number of keys is too large, 100 keys are retained by default. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, 36 features are generated, which equals to the number of statistical periods multiplied by the number of calculation formulas multiplied by the number of attribute features.
Calculation of Values of Preferred Numerical Features
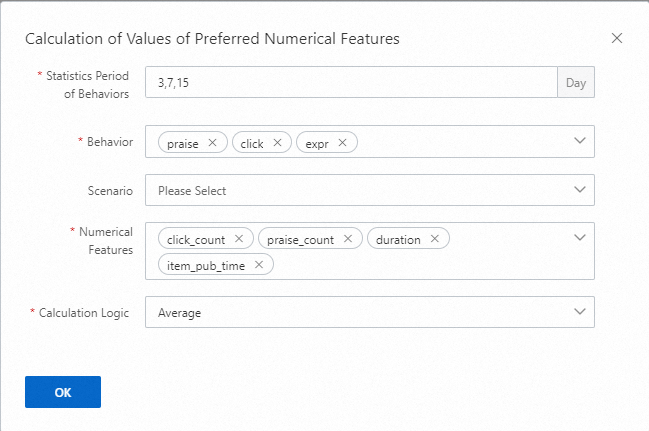
Numerical features of behaviors such as exposure, click, and praise are collected for the specified periods of time, such as, 3, 7, and 15 days, based on the specified calculation logic. The calculation logic includes Sum, Min, Max, and Average. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred in this scenario are collected. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, 36 features are generated, which equals to the number of statistical periods multiplied by the number of behaviors multiplied by the number of numerical features.
Calculation of Values of Top Combined Features
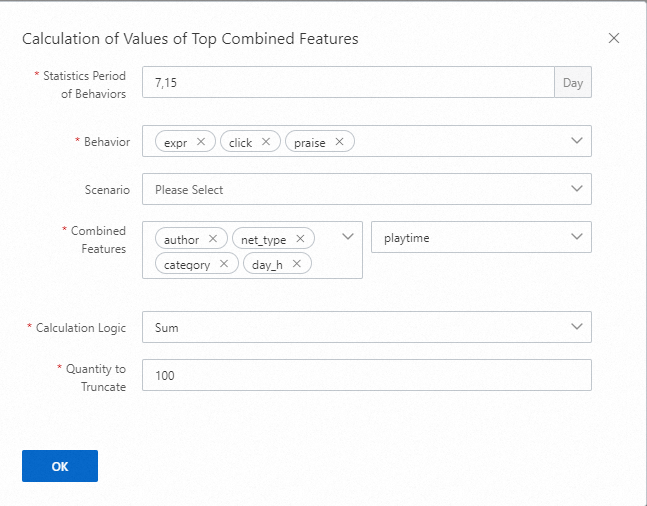
Combined features related to behaviors such as exposure, click, and praise are collected for the specified periods of time, for example, 3, 7, and 15 days, based on the specified calculation logic. That is, the numerical features under specified categories for a user are calculated. The calculation logic includes Sum, Min, Max, and Average. If a scenario is configured, statistics about behaviors occurred in this scenario are collected. If you use the configurations in the preceding example, 27 features are generated, which equals to the number of statistical periods multiplied by the number of behaviors multiplied by the number of combined categorical features.
4. Configure sequence features
Sequence features are obtained only from user behavior features. At the initial stage of a project, real-time sequence features are simulated to reduce the time used to obtain sequence features online and speed up service rollout. In most cases, expr is set for the Simulated Event parameter. The Period to Prevent Feature Leakage parameter indicates the exclusion period for recent behaviors. For example, setting it to 3 seconds excludes behaviors occurred in the latest 3 seconds from the current behavior sequence. (Reason: Latency occurs in log collection. If behaviors occurred during the latest period of time are simulated, feature leakage occurs.) The Sequence Feature Separator parameter indicates the delimiter used to separate sequence features. The Sub-feature Separator parameter indicates the delimiter used to separate sub-features in a sequence.

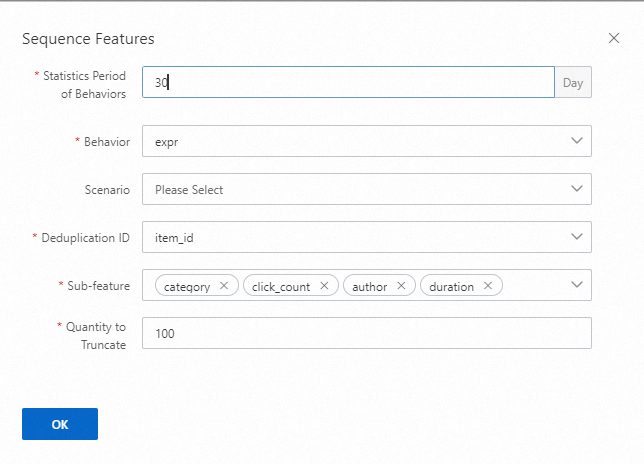
Statistics Period of Behaviors: the number of the recent days over which behaviors are collected. If multiple sequences are configured, the maximum statistical period takes effect.
Behavior: the behavior type.
Scenario: the scenario in which behaviors occurred are collected. If you do not configure this parameter, behaviors occurred in all scenarios are collected.
Deduplication ID: the sub-feature ID for deduplication. Only the latest behavior is retained.
Sub-feature: the sub-features of sequence features, which are generally non-statistical features of items, such as categorical features, multi-value categorical features, and numerical features.
Quantity to Truncate: the maximum number of sequence features that can be retained.
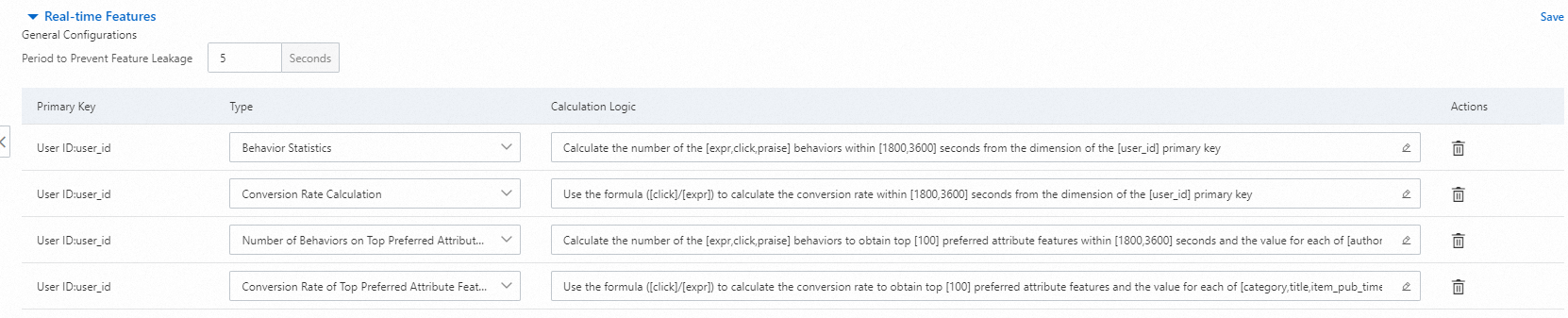
5. Configure real-time features
You can use user IDs and item IDs as primary keys to create real-time features. The Period to Prevent Feature Leakage parameter for real-time features is similar to the Period to Prevent Feature Leakage parameter for sequence features. This parameter indicates the latest period of time over which behaviors are not collected. The latest period of time refers to the time period before the generation time of the corresponding log. (Reason: It takes time to collect behavior logs from clients to the message-oriented middleware and then to the online storage service. If you do not set the Period to Prevent Feature Leakage parameter, the recommendation engine cannot use the data related to the behaviors occurred in the latest period of time, resulting in data inconsistency between offline training and online inference.) The unit of the Statistics Period of Behaviors parameter for real-time features is seconds. The following types of statistics are collected:
Behavior Statistics
Conversion Rate Calculation
Number of Behaviors on Top Preferred Attribute Features
Conversion Rate of Top Preferred Attribute Features
The types of statistics have the same meaning as those in behavior preference statistics.
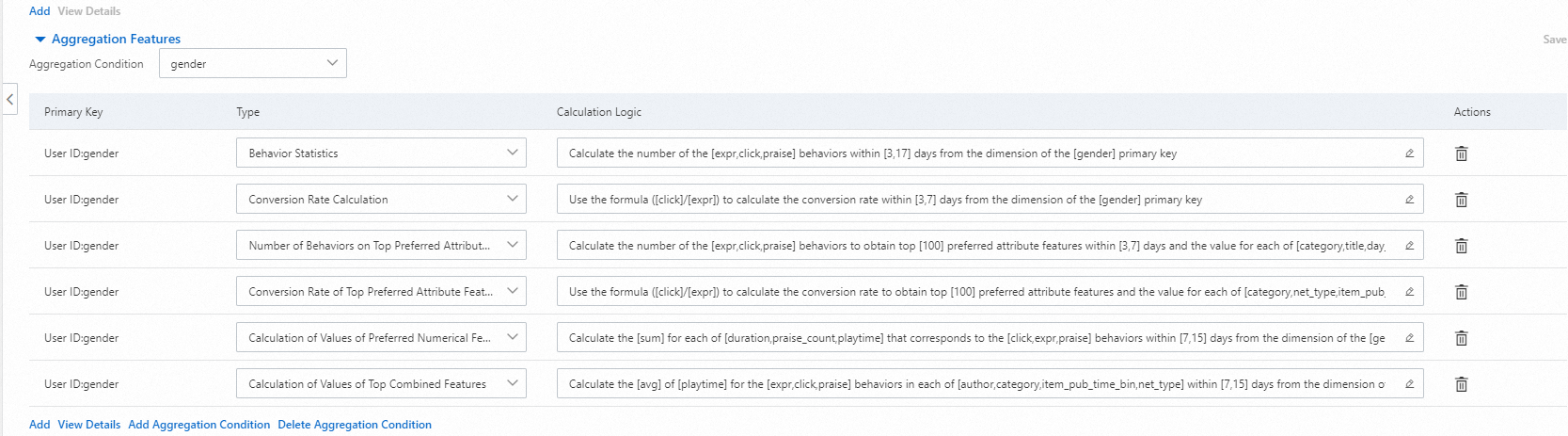
6. Configure aggregation features
Aggregation features are derived from user features and item features. You need to select an aggregation condition. You can only select a categorical feature as the aggregation condition. You can configure multiple aggregation features.
Features are collected based on the specified aggregation condition. The options of the Type parameter are the same as those in the Preferred Behavior Features section and their meanings are also the same. For example, the Behavior Statistics parameter in the following figure collects the number of clicks, praises, and exposures regardless of the gender. The number of clicks by women is significantly greater than the number of clicks by men.