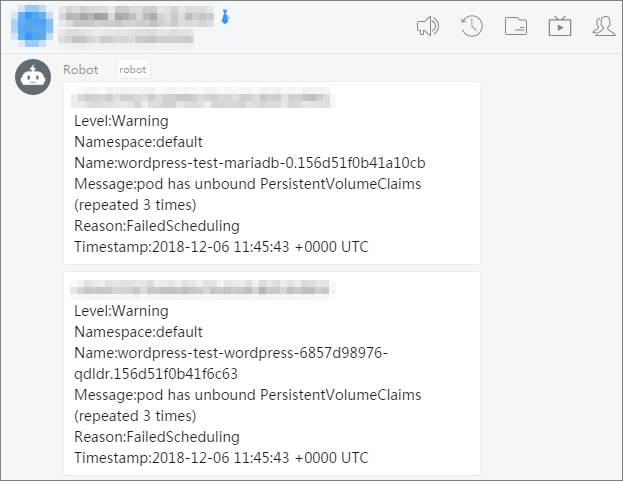
Event monitoring is a monitoring method provided by Kubernetes. It provides improvements over resource monitoring in terms of timeliness, accuracy, and scenarios. kube-eventer allows you to send Kubernetes events to sinks such as DingTalk, Simple Log Service (SLS), and EventBridge. kube-eventer also provides filter conditions to filter different levels of events. You can use kube-eventer to collect events in real time, trigger alerts upon specific events, and asynchronously archive events.
Background information
ACK Serverless provides out-of-the-box event monitoring solutions for container scenarios. ACK Serverless also provides container event monitoring capabilities by using the kube-eventer component maintained by ACK.

kube-eventer is an open source event emitter that is maintained by ACK. kube-eventer sends Kubernetes events to sinks such as DingTalk, SLS, and EventBridge. kube-eventer also provides filter conditions to filter different levels of events. You can use kube-eventer to collect events in real time, trigger alerts upon specific events, and asynchronously archive events. For more information, see kube-eventer.
This topic describes how to configure event monitoring in the following scenarios:
Prerequisites
The kube-eventer component is installed.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, choose . On the Logs and Monitoring tab, install the kube-eventer component. The components are free of charge but consume pod resources.
Scenario 1: Sink Kubernetes events to SLS
You can sink Kubernetes events to SLS for persistent storage, and archive and audit the events. For more information, see Create and use an event center.
Create a Simple Log Service project and a Logstore.
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
In the Projects section, click Create Project. In the Create Project panel, set the parameters and click OK.
In this example, a Simple Log Service project named k8s-log4j is created in the China (Hangzhou) region where the monitored ACK cluster is deployed.
NoteWe recommend that you create a Simple Log Service project in the same region as your cluster. When a Simple Log Service project and a cluster are deployed in the same region, the log is transmitted over the internal network. This enables the real-time collection and quick retrieval of log data. This also avoids cross-region transmission, which requires additional bandwidth and time costs.
In the Projects section, find and click the k8s-log4j project. The details page of the project appears.
On the left Logstores pane, click the + icon to open the Create Logstore panel.
In the Create Logstore panel, set the parameters and click OK.
In this example, a Logstore named k8s-logstore is created.
After the k8s-logstore Logstore is created, instructions on how to use the Data Import wizard appear on the page. Click Data Import Wizard. The Import Data dialog box appears.
Select Log4j 1/2 and configure the settings by following the steps on the page.
In this example, the default settings are used. You can also customize the settings to meet your business requirements.
Configure log4j for the cluster.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Helm page, find the kube-eventer component, click Update in the Actions column of the component, complete the following configurations, and then click OK:
An event is generated after an operation is performed on the cluster, such as a pod deletion or an application creation. You can log on to the Simple Log Service console to view the collected log data. For more information, see Consume log data by using Simple Log Service SDK.
Set indexes and archiving. For more information, see Create indexes.
Log on to the Simple Log Service console. In the Projects section, find and click the name of the project.
Click
 next to the name of the Logstore and then select Search & Analysis.
next to the name of the Logstore and then select Search & Analysis. In the upper-right corner of the page that appears, click Enable Index.
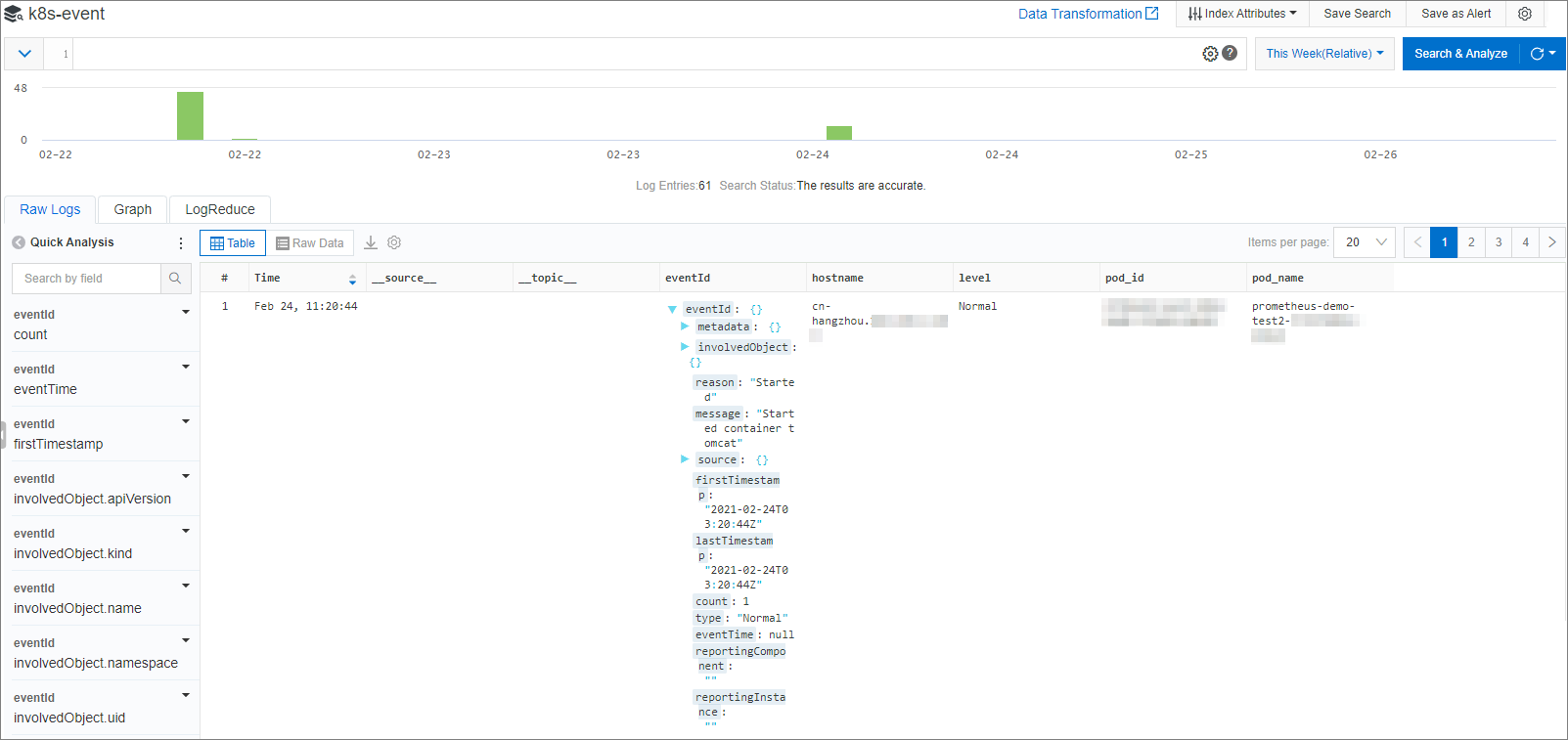
In the Search & Analysis panel, set the parameters, and click OK.
The log query and analysis page appears.
 Note
NoteThe index configuration takes effect within 1 minute.
A newly enabled or modified index applies only to data that is imported after the index is enabled or modified.
(Optional) In scenarios requiring offline archiving and computing, you can ship data from the Logstore to MaxCompute or Object Storage Service (OSS). For more information, see Create a data shipping job of the new version to ship data to MaxCompute and Create an OSS data shipping job (new version).
Scenario 2: Sink Kubernetes events to EventBridge
EventBridge is a serverless event service provided by Alibaba Cloud. Alibaba Cloud services, custom applications, and software as a service (SaaS) applications can connect to EventBridge in a standardized and centralized manner. ACK events can be sunk to EventBridge, which allows you to build a loosely-coupled and distributed event-driven architecture in EventBridge. For more information about EventBridge, see What is EventBridge?.
Activate EventBridge. For more information, see Activate EventBridge and grant permissions to a RAM user.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Helm page, find the kube-eventer component, click Update in the Actions column, and then set the
eventer.sinks.eventbridge.enableparameter totrueto configure the Event center and activate EventBridge. Then, click OK.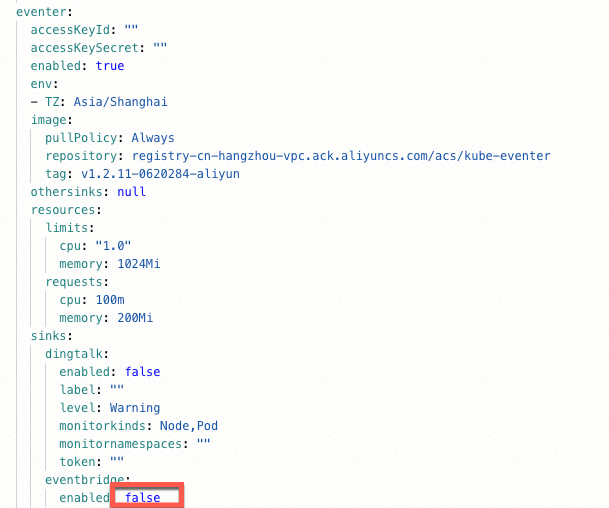
After EventBridge is enabled as a sink of Kubernetes events, you can view Kubernetes events in the EventBridge console.
Log on to the EventBridge console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Buses.
- On the Event Buses page, click the name of the target event bus.
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Tracking.
Select a query method, set query conditions, and then click Query.
In the list of events, find the event that you want to view and click Details in the Actions column.
For more information, see Query events by event ID.
Scenario 3: Use DingTalk chatbot to raise alerts upon Kubernetes events
Using a DingTalk chatbot to monitor Kubernetes events and generate alerts is a common scenario of ChatOps. To use a DingTalk chatbot, perform the following steps:
DingTalk chatbot
Click
 in the upper-right corner of the chatbox of a DingTalk group to open the Group Settings page.
in the upper-right corner of the chatbox of a DingTalk group to open the Group Settings page. Click Bot and click Add Robot to add a chatbot. Custom is selected in this example.
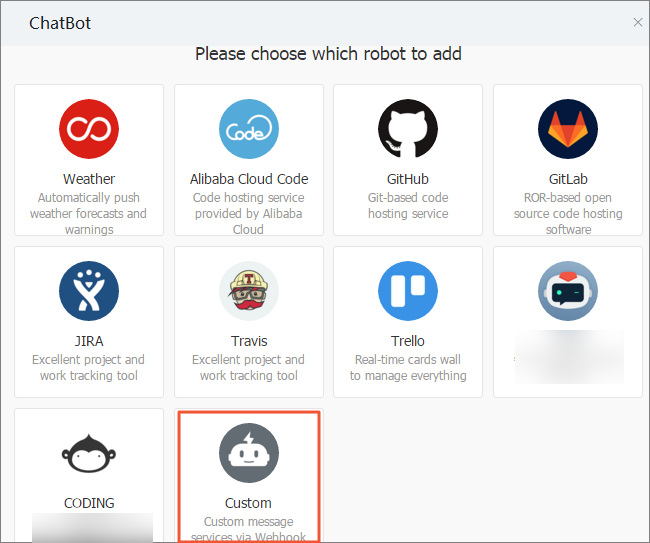
On the Robot details page, click Add to go to the Add Robot page.
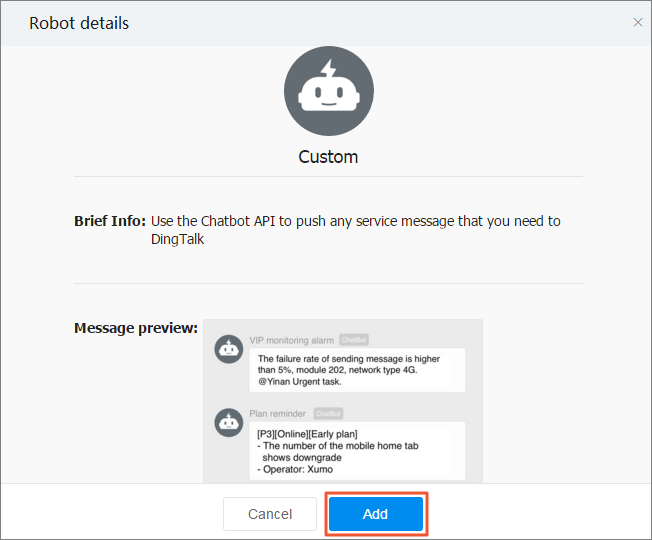
Set the following parameters, read and accept the DingTalk Custom Robot Service Terms of Service, and then click Finished.
Parameter
Description
Edit profile picture
The avatar of the chatbot. This parameter is optional.
Chatbot name
The name of the chatbot.
Add to Group
The DingTalk group to which the chatbot is added.
Security settings
Three types of security settings are supported: custom keywords, additional signatures, and IP addresses (or CIDR blocks).
Only Custom Keywords are supported for filtering alerts that are raised upon cluster events.
Select Custom Keywords and enter
Warningto receive alerts. If the chatbot frequently sends messages, you can add more keywords to filter the messages. You can add up to 10 keywords. Messages from ACK Serverless are also filtered through these keywords before the chatbot sends them to the DingTalk group.Click Copy to copy the webhook URL.
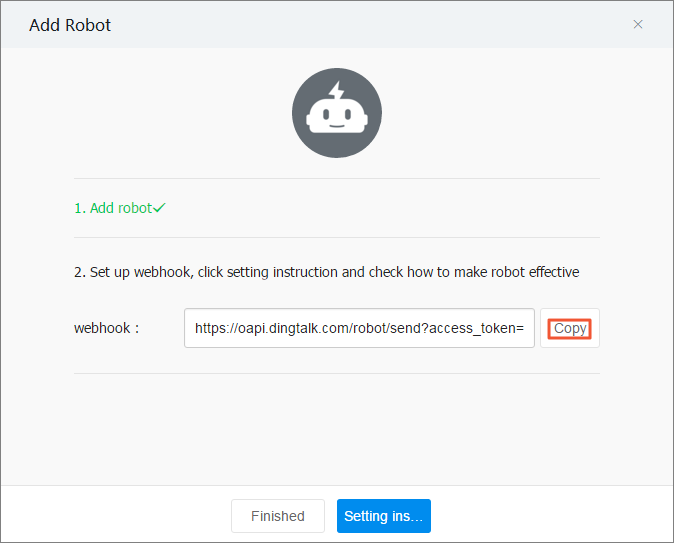 Note
NoteOn the ChatBot page, find the chatbot and click
 to perform the following operations:
to perform the following operations:Modify the avatar and name of the chatbot.
Enable or disable message push.
Reset the webhook URL.
Remove the chatbot.
Update the configuration of the kube-eventer component.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side pane of the cluster details page, choose .
On the Helm page, find the kube-eventer component. Then, click Update in the Actions column of the component, modify the following parameters, and click OK.
In the
npdsection, set theenabledparameter tofalse.Set
eventer.sinks.dingtalk.enabledtotrue.Enter the token that is contained in the webhook URL generated in Step 1.
Expected output:
eventer takes effect 30 seconds after the deployment is complete. When an event whose severity level exceeds the threshold occurs, an alert is sent to the DingTalk group.