Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) provides the inspection feature to help you detect security risks in the workloads of ACK clusters. After an ACK cluster completes an inspection task, the cluster generates an inspection report. You can view and address the failed inspection items in the inspection report. This way, you can learn the real-time health status of the cluster.
Prerequisites
An external Kubernetes cluster is registered in the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console. For more information, see Create ACK One registered clusters.
Logtail is installed. For more information, see Step 2: Install logtail-ds.
Perform an inspection task
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
Optional: Install and update the security-inspector component.
The security-inspector component is free of charge but occupies pod resources. For more information about the introduction and release notes for the security-inspector component, see security-inspector.
Perform an inspection task.
ImportantWe recommend that you perform inspection tasks during off-peak hours.
By default, all inspection items are enabled for an inspection task. In the upper-right corner of the Inspections page, click Configure Periodic Inspection. In the panel that appears, you can configure inspection items for inspection tasks. For more information, see Inspection items.
Immediately perform an inspection task: In the upper-right corner of the Inspections page, click Inspect.
Perform inspection tasks on a regular basis: In the upper-right corner of the Inspections page, click Configure Periodic Inspection. Then, select Configure Periodic Inspection and configure the inspection cycle.
After the inspection task is completed, go to the Inspections tab, find the inspection result, and then click Details in the Actions column.
Inspection details
The Inspections page provides a table to show the inspection results of different workloads. The following features are provided to display the inspection results:
Filters inspection results based on conditions such as Passed or Failed, Namespace, and Workload Type. Displays the values of Number of Passed Items and Number of Failed Items for each inspected workload.
Displays detailed information about each inspection item on the inspection details page, including the passed and failed inspection items of each pod and container, description of each inspection item, and suggestions on security reinforcement. To ignore failed inspection items, add them to the whitelist.
View the YAML files of the workloads.
Inspection items
The following table describes the inspection items.
Inspection item ID | Inspection item | Inspection content and potential security risk | Suggestion |
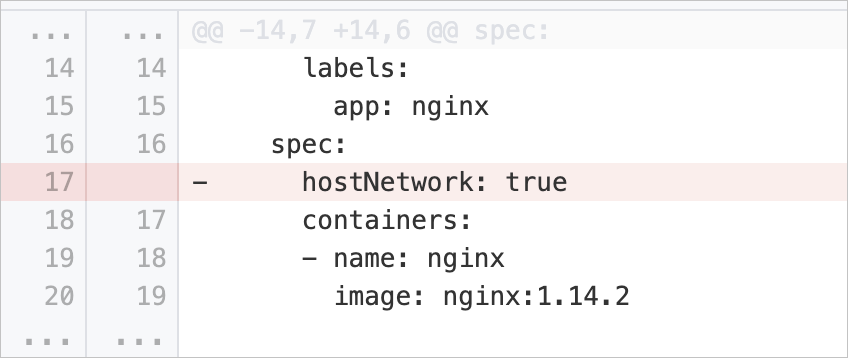
hostNetworkSet | Disable sharing of network namespaces between containers and hosts | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Delete the Example: |
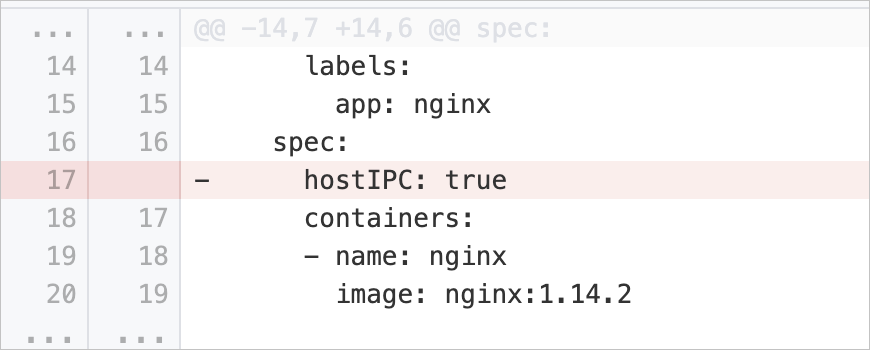
hostIPCSet | Disable sharing of IPC namespaces between containers and hosts | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Delete the Example: |
hostPIDSet | Disable sharing of PID namespaces between containers and hosts | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Delete the Example: |
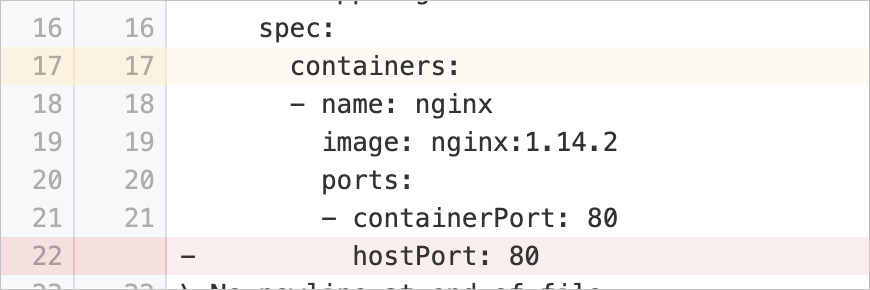
hostPortSet | Prevent processes in containers from listening on host ports | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Delete the Example: |
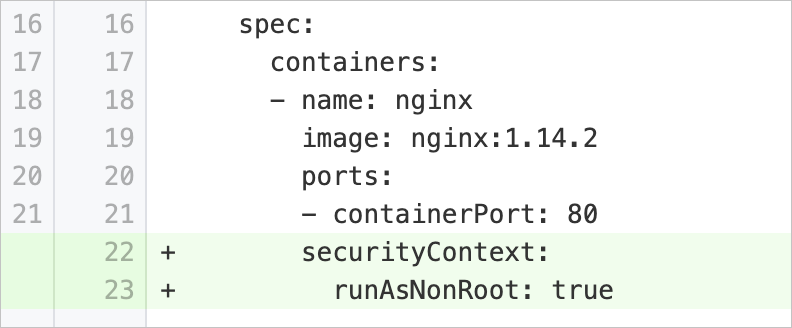
runAsRootAllowed | Disable container startup as a root user | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example: |
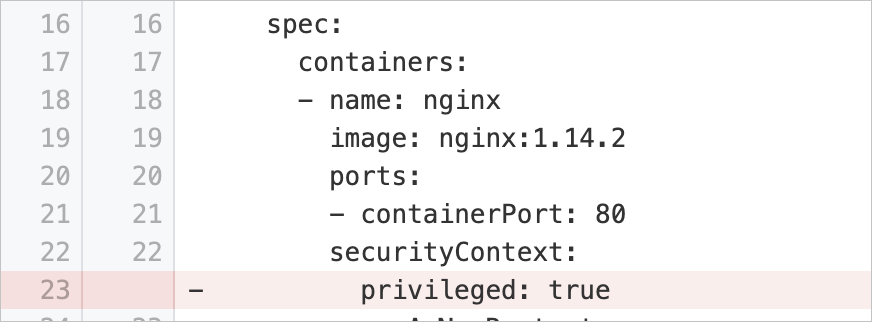
runAsPrivileged | Disable container startup in privileged mode | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Delete the Example: |
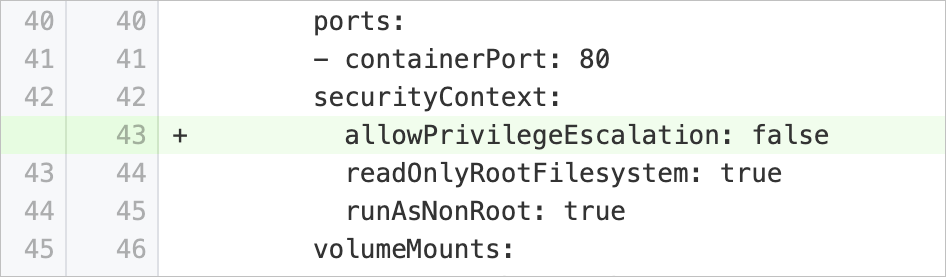
privilegeEscalationAllowed | Disable privilege escalation for child processes in containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example: |
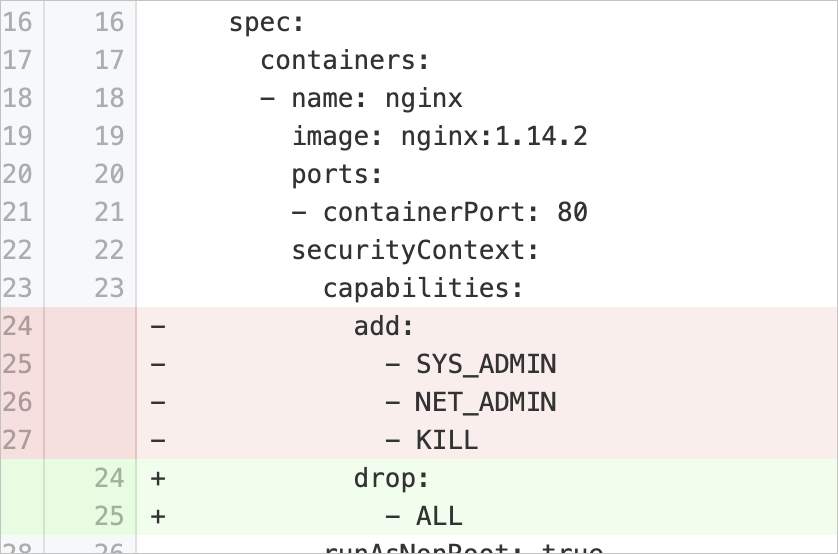
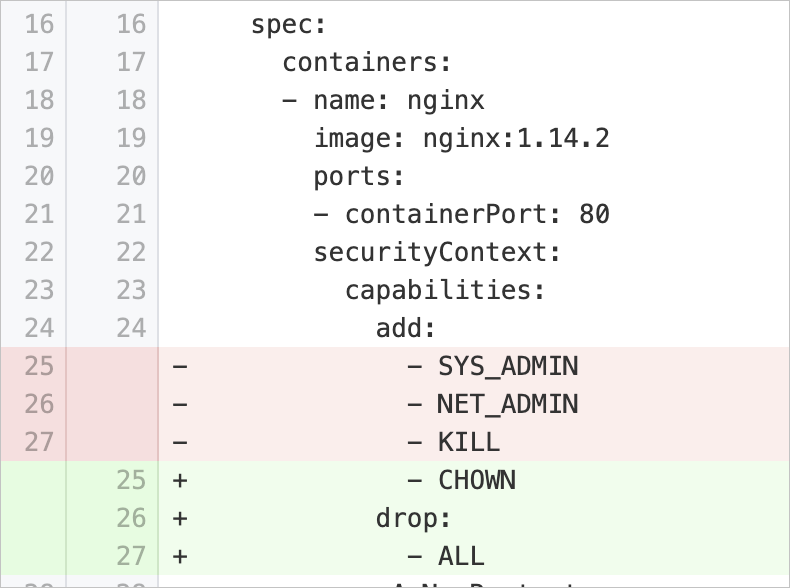
capabilitiesAdded | Disable unnecessary Linux capabilities | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Modify the pod specification to retain only the required Linux capabilities and remove other capabilities. If processes in the containers do not require Linux capabilities, remove all Linux capabilities. Example:
If processes in the containers require Linux capabilities, specify only the required Linux capabilities and remove other capabilities. Example: |
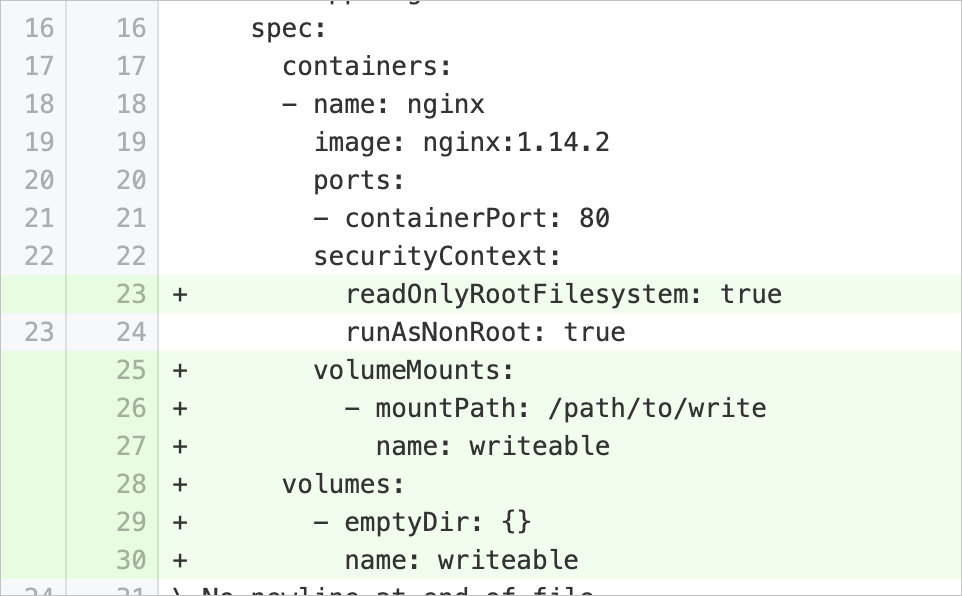
notReadOnlyRootFileSystem | Enable the read-only mode for file systems in containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
If you want to modify files in a specific directory, set the Example: |
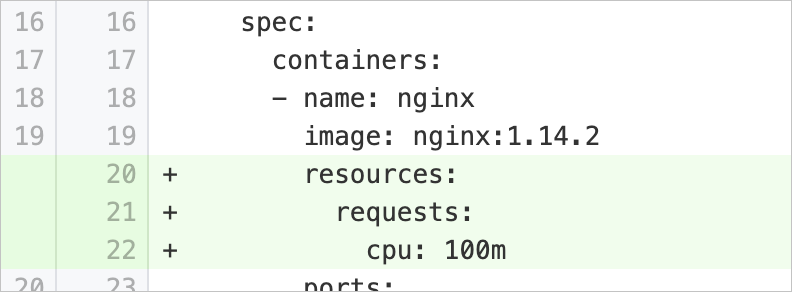
cpuRequestsMissing | Set the minimum usage of CPU resources available for running containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
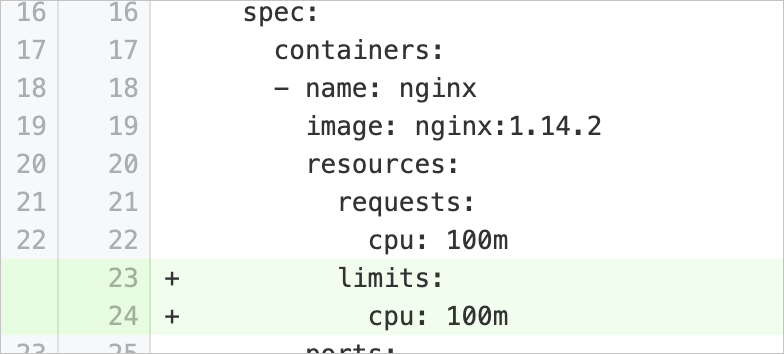
cpuLimitsMissing | Set the maximum amount of CPU resources available for running containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
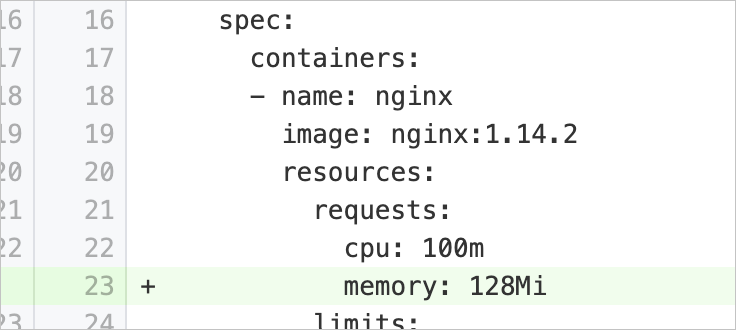
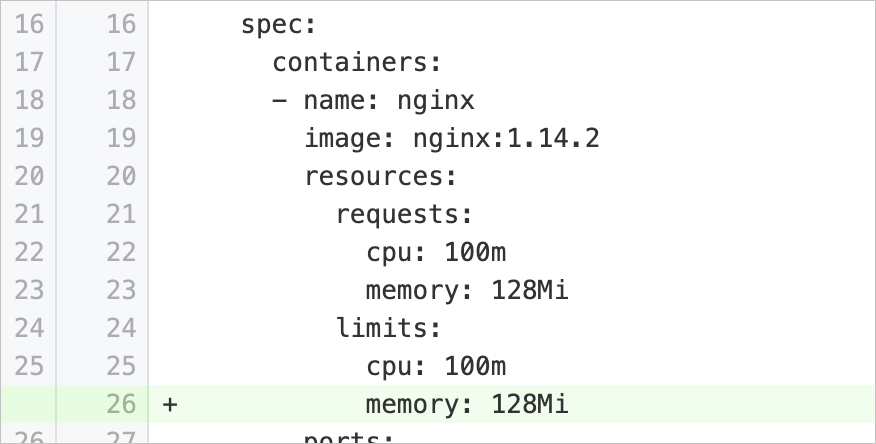
memoryRequestsMissing | Set the minimum memory resources available for running containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
memoryLimitsMissing | Set the maximum memory resources available for running containers | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
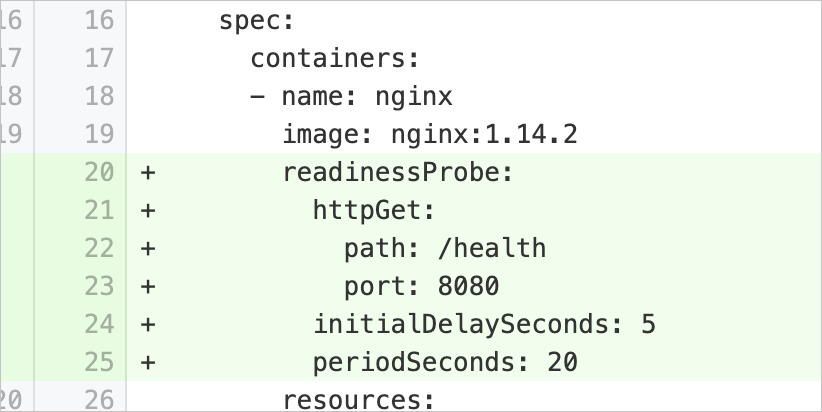
readinessProbeMissing | Configure container readiness probes | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
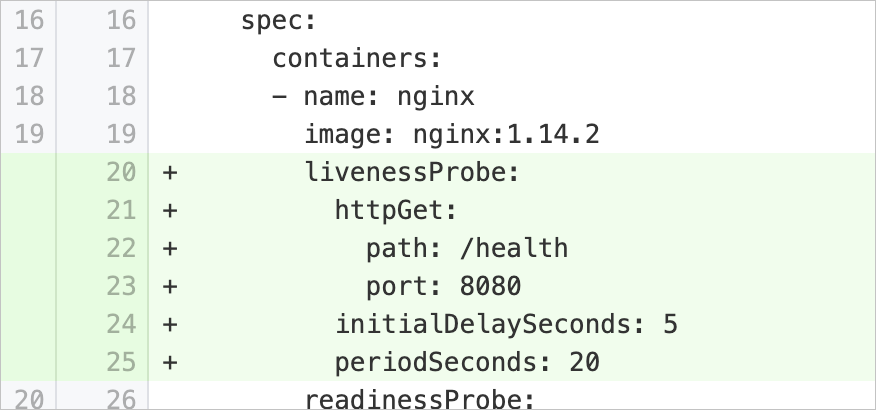
livenessProbeMissing | Configure container liveness probes | Checks whether the pod specification of a workload contains the | Add the Example:
|
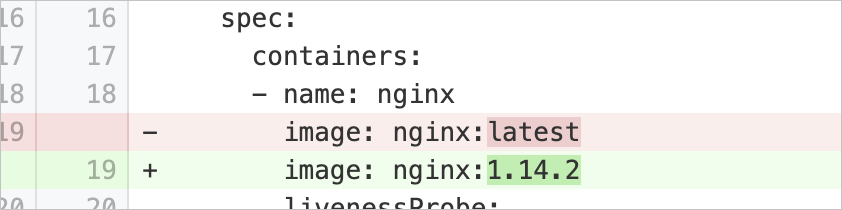
tagNotSpecified | Specify image versions for containers | Checks whether the | Modify the Example:
|
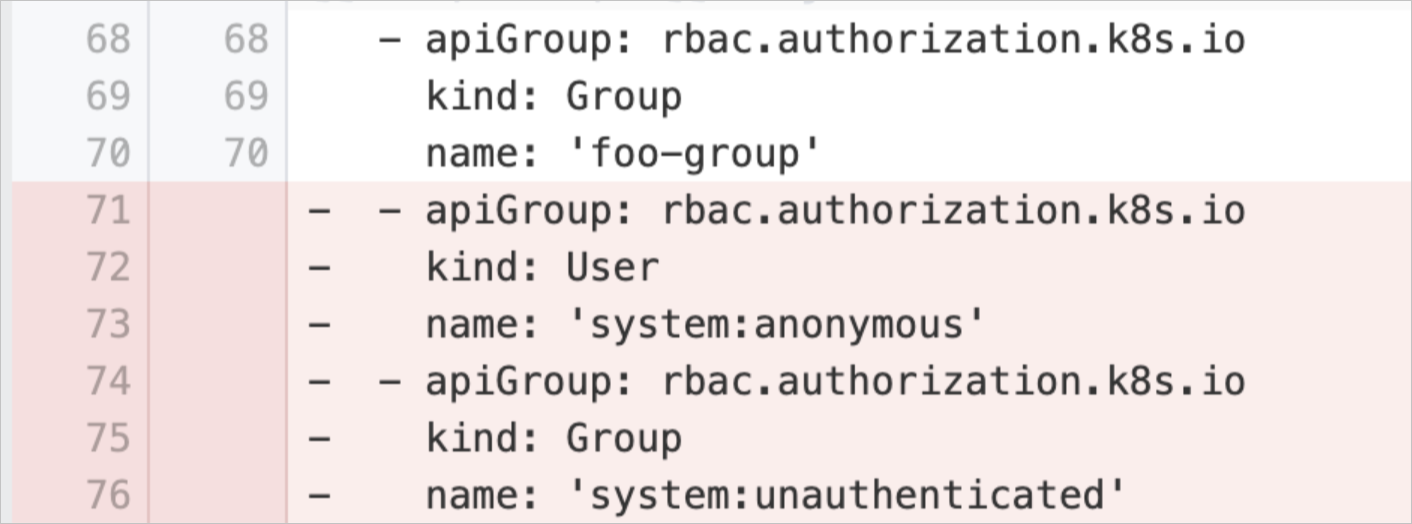
anonymousUserRBACBinding | Prohibit Anonymous Access to Cluster | Checks RBAC role bindings in the cluster and identifies the configurations that allow access from anonymous users. If anonymous users are allowed to access the cluster, they may gain access to sensitive information, attack the cluster, and intrude into the cluster. | Remove the configurations that allow access from anonymous users from the RBAC role bindings. Example:
|