This topic describes how to integrate Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service (OSS) with Alibaba Cloud Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS). You can upload a file to OSS to automatically trigger a workflow that processes the file and generates a result.
Prerequisites
An OSS event notification is created.
A workflow cluster is created.
The Alibaba Cloud Argo command-line interface (CLI) is installed.
Step 1: Create an Event Bus
Event-driven workflows in a namespace can share an Event Bus. If you have already created an Event Bus, you can skip this step and proceed to Step 2: Create an Event Source.
When you create an Event Bus with Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS), a pod is not created.
To use the Trigger feature, you must create the EventBus using NATS. The Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) method does not support the open source Argo Events Sensor Trigger.
Method 1: Use NATS
Create an
event-bus.yamlfile. The following code is an example:apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: EventBus metadata: name: default spec: nats: native: replicas: 3 auth: tokenRun the following command to create the EventBus.
kubectl apply -f event-bus.yamlNoteAfter the command runs successfully, an Event Bus pod is created in the default namespace. You must perform all subsequent operations in the same namespace.
Run the following command to verify that the Event Bus pod has started.
kubectl get pod
Method 2: Use Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS)
Log on to the SMQ console.
On the Topics page, create a topic named
argoeventbus. On the Topic Details page, obtain the Endpoint from the Endpoint section.Log on to the RAM console as a RAM user who has administrative rights.
Create a RAM user, grant the
AliyunMNSFullAccesspermission to the user, and obtain the user's AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret.Run the following command to create a Secret to store the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret.
kubectl create secret generic mns-secret\ --from-literal=accesskey=*** \ --from-literal=secretkey=***Create an
event-bus-mns.yamlfile. The following code is an example:topic: Replace this with the name of the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) topic that you created in Step 2.endpoint: Replace this with the Endpoint that you obtained in Step 2.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: EventBus metadata: name: default spec: alimns: accessKey: key: accesskey name: mns-secret secretKey: key: secretkey name: mns-secret topic: argoeventbus # The name of the topic in Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS). endpoint: http://165***368.mns.<region>.aliyuncs.comRun the following command to apply the
event-bus-mns.yamlfile.kubectl apply -f event-bus-mns.yaml
Step 2: Create an Event Source
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM user who has administrative rights.
Create a RAM user, grant the
AliyunMNSFullAccesspermission to the user, and obtain the user's AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret. For more information, see Create a RAM user, Grant permissions to a RAM user, Create an AccessKey pair, and View the AccessKey information of a RAM user.Create an
event-source.yamlfile. The following code is an example:queue: Replace this with the name of the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue.endpoint: Replace this with the endpoint of Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS).
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: EventSource metadata: name: ali-mns spec: mns: example: jsonBody: true accessKey: key: accesskey name: mns-secret secretKey: key: secretkey name: mns-secret queue: oss-event-queue # The name of the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue. waitTimeSeconds: 20 endpoint: http://165***368.mns.<region>.aliyuncs.com # The endpoint of Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS).Run the following command to create the Event Source.
kubectl apply -f event-source.yamlRun the following command to verify that the Event Source pod has started.
kubectl get pod
Step 3: Create an Event Sensor
Create an
event-sensor.yamlfile and embed the workflow definition in the Event Sensor. The following code is an example:Run the following command to create the Event Sensor.
kubectl apply -f event-sensor.yamlRun the following command to verify that the Event Sensor pod has started.
kubectl get pod
When you create an EventBus using Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS), a corresponding Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue is automatically created after the Event Sensor is created. The queue is named in the following format: ackone-argowf-<namespace>-<sensor-name>-<sensor-uid>.
Step 4: Verify that uploading a file to OSS triggers a workflow
Log on to the OSS console.
Upload the following two files to an OSS bucket to trigger the workflow. You must prepare these files in advance.
datafile: A data file in text format with custom content.
datafile.complete: A trigger file. This can be an empty file.
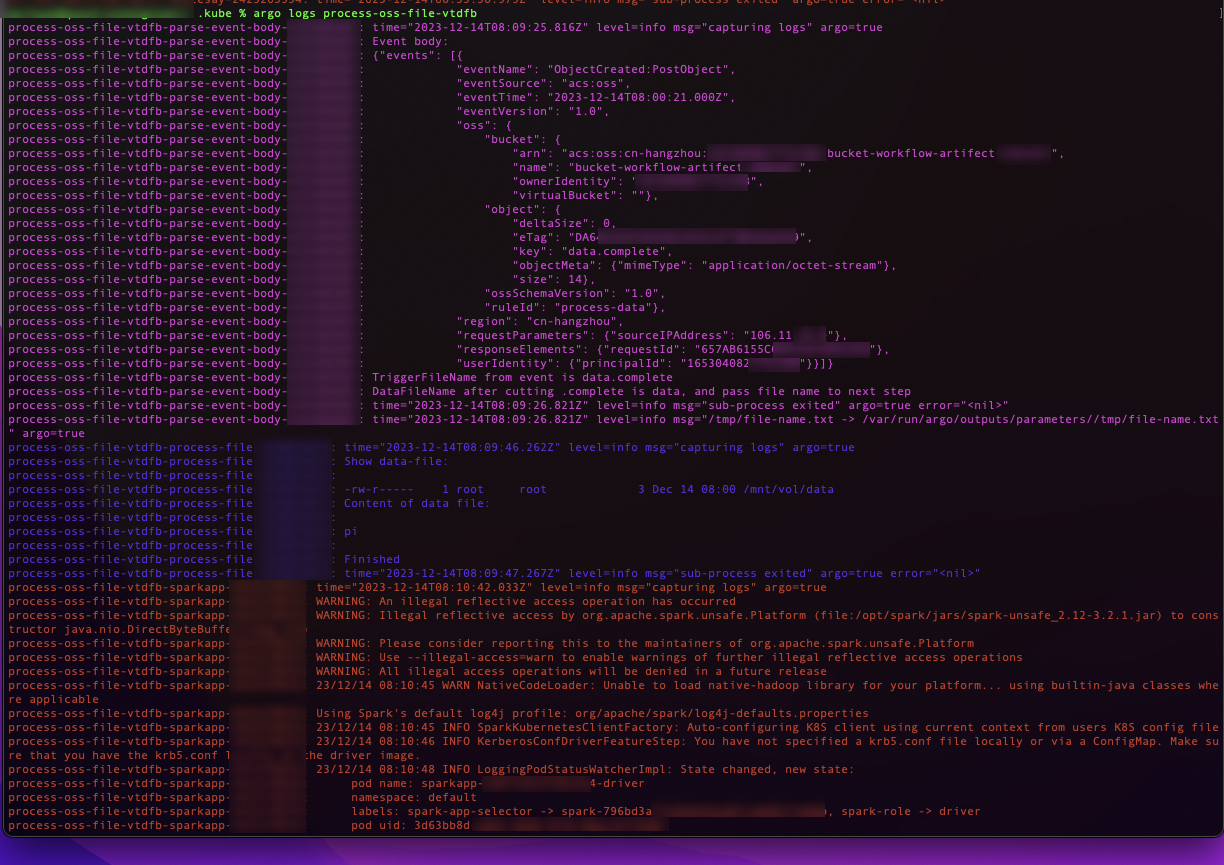
Run the following command in the workflow cluster to view the status of the workflow.
argo listThe expected output is as follows:
NAME STATUS AGE DURATION PRIORITY process-oss-file-kmb4k Running 13s 13s 0Run the following command to retrieve the workflow logs.
argo logs process-oss-file-kmb4kImportantThe workflow name in the command must match the name returned in the previous step. The name
ali-mns-workflow-5prz7is an example. Replace it with the actual name from your environment.The message content is Base64-encoded.
The expected output is as follows:
Step 5: Clean up event-related resources
Run the following commands to clean up the event-related resources.
kubectl delete sensor process-oss-file kubectl delete eventsource ali-mns kubectl delete eventbus defaultRun the following command to view the pods and confirm that all resources are deleted.
kubectl get pod