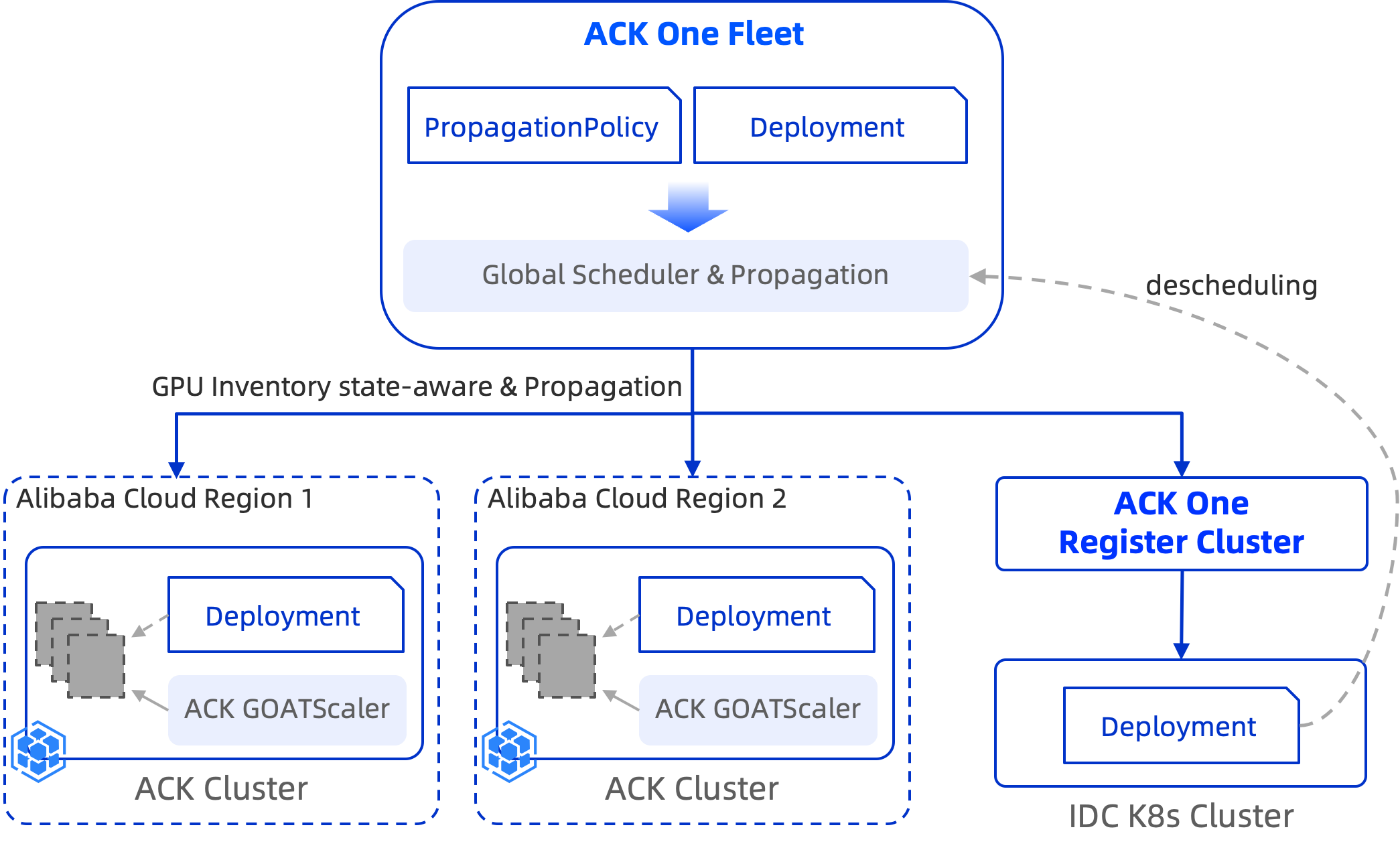
Alibaba Cloud Distributed Cloud Container Platform (ACK One) fleet supports AI inference services. In multi-region Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster and hybrid cloud multi-cluster scenarios, you can define cluster priorities. This lets you prioritize resources from on-premises data centers (IDCs) or primary regions and use resources from Alibaba Cloud or backup regions for supplemental computing power. This inventory-aware scheduling ensures business continuity.
How it works
This feature applies to the following scenarios.
Multi-region ACK cluster scenario: Set Region A as the primary region for AI inference services and Region B as the backup region. Clusters in Region A have a higher priority. When GPU resources are insufficient and you need to scale out, ACK One fleet first schedules inference services to Region A based on cluster priority. If resources in Region A are insufficient, it schedules the services to Region B. When scaling in, the inference service replicas in the lower-priority Region B are scaled in first, followed by the replicas in Region A.
Hybrid cloud multi-cluster scenario: You can use a fleet to manage both on-premises IDC and cloud-based ACK resources, where cloud resources supplement the on-premises IDC resources. When scaling out, ACK One fleet first schedules inference services to the IDC cluster. If IDC resources are insufficient, it schedules them to the ACK cluster to use cloud computing power. When scaling in, it first scales in the inference service replicas on the cloud, followed by the replicas in the IDC.
The following example applies to the hybrid cloud multi-cluster scenario.
Prerequisites
Instant node elasticity is enabled for the member clusters. The ACK cluster version must be 1.24 or later.
If node autoscaling is already enabled for a member cluster, you can switch to instant node elasticity by following the steps in Step 1: Enable instant node elasticity
The AMC command-line tool is installed.
Step 1: Deploy a demo service in the fleet
The following example uses the qwen3-0.6b model, downloaded from ModelScope and run with vllm. For testing, you can run this deployment on T4 or A10 GPUs.
Create the `test` namespace in the fleet and ensure all member clusters also have this namespace.
kubectl create ns testCreate and save a file named
demo.yaml. Then, runkubectl apply -f demo.yamlin the fleet to deploy the demo Deployment and Service.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: qwen3 namespace: test spec: progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 replicas: 2 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 selector: matchLabels: app: qwen3 template: metadata: labels: app: qwen3 spec: containers: # Use the qwen3-0.6b model, downloaded from ModelScope - command: - sh - -c - export VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE=True; vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B --served-model-name qwen3-0.6b --port 8000 --trust-remote-code --tensor_parallel_size=1 --max-model-len 2048 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.8 image: kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/vllm-openai:v0.9.1 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: vllm ports: - containerPort: 8000 name: restful protocol: TCP readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 30 periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 tcpSocket: port: 8000 timeoutSeconds: 1 resources: limits: nvidia.com/gpu: "1" requests: nvidia.com/gpu: "1" dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: {} terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: qwen3 namespace: test labels: app: qwen3 spec: ports: - port: 8000 selector: app: qwen3
Step 2: Deploy a propagation policy for elastic scheduling in a hybrid cloud
In the following PropagationPolicy, you can enable inventory-aware scheduling and configure cluster priorities. This configuration prioritizes scheduling to the IDC. If IDC resources are insufficient, scheduling falls back to the cloud to trigger node elasticity.
Replace ${registered cluster ID} and ${ACK Cluster ID} in the example with your cluster IDs. Create and save a file named demo-pp.yaml. Then, run kubectl apply -f demo-pp.yaml in the fleet to deploy the PropagationPolicy.
In the example below, the spec.resourceSelectors field is populated with the sample resources created in Step 1: Deploy a demo service in the fleet. In a production environment, use your actual resource information.apiVersion: policy.one.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: vllm-deploy-pp
namespace: test
spec:
autoScaling:
ecsProvision: true
placement:
clusterAffinities:
- affinityName: idc
clusterNames:
- ${registered cluster ID}
- affinityName: ack
clusterNames:
- ${ACK Cluster ID}
replicaScheduling:
replicaSchedulingType: Divided
replicaDivisionPreference: Weighted
weightPreference:
dynamicWeight: AvailableReplicas
preserveResourcesOnDeletion: false
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
namespace: test
schedulerName: default-scheduler
---
apiVersion: policy.one.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: demo-svc
namespace: test
spec:
preserveResourcesOnDeletion: false
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: qwen3
placement:
replicaScheduling:
replicaSchedulingType: DuplicatedStep 3: Verify elastic scaling
Run
kubectl amc get pod -ntest -Mto view the deployment status.Initially, when the IDC cluster has sufficient resources, pods are deployed to the IDC cluster first:
NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE qwen3-5665b88779-7k*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18m qwen3-5665b88779-ds*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18mScale out the number of replicas for the inference service in the fleet:
kubectl scale deploy qwen3 -ntest --replicas=4After the scale-out is complete, run
kubectl amc get pod -ntest -Mto view the pod deployment status.New pods are scheduled to the ACK cluster. Two pods are in the Pending state, which indicates that the ACK cluster has insufficient resources:
NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES ADOPTION qwen3-5665b88779-7k*** c043******** cluster-bj-demo 0/1 Pending 0 33s <none> <none> <none> <none> N qwen3-5665b88779-ds*** c043******** cluster-bj-demo 0/1 Pending 0 33s <none> <none> <none> <none> N qwen3-5665b88779-7k*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18m 172.20.245.125 x.x.x.x <none> <none> N qwen3-5665b88779-ds*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18m 172.19.8.159 x.x.x.x <none> <none> NRun the
kubectl amc get node -Mcommand to check the status of the nodes. The output shows that two new nodes have been elastically provisioned and are joining the ACK cluster:After an inference service is scaled in, the elastically added nodes are automatically removed after 10 minutes.
NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ADOPTION cn-beijing.172.19.8.*** c043******** cluster-bj-demo NotReady <none> 20s N cn-beijing.172.20.245.** c043******** cluster-bj-demo Ready <none> 18h v1.34.1-aliyun.1 N cn-beijing.172.21.3.*** c043******** cluster-bj-demo NotReady <none> 20s N cn-beijing.172.21.3.** c043******** cluster-bj-demo Ready <none> 18h v1.34.1-aliyun.1 N cn-beijing.172.20.245.** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo Ready <none> 3h14m v1.34.1-aliyun.1 N cn-beijing.172.21.3.** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo Ready <none> 3h16m v1.34.1-aliyun.1 N cn-beijing.172.21.3.** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo Ready <none> 3h13m v1.34.1-aliyun.1 NWhen scaling in, replicas are removed based on the cluster priorities defined in the PropagationPolicy, from the lowest to the highest priority.
Scale in the number of replicas for the inference service in the fleet:
kubectl scale deploy qwen3 -ntest --replicas=2Run
kubectl amc get pod -ntest -Mto view the pod deployment status. The output shows that the two replicas on the ACK cluster have been scaled in:NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE qwen3-5665b88779-7k*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18m qwen3-5665b88779-ds*** c6b4******** cluster-idc-demo 1/1 Running 0 18m