Deploying applications across multiple clusters involves repetitive tasks, is prone to errors, and makes synchronization difficult. You can use the AMC command line interface to quickly deploy applications to multiple clusters. This provides unified management and automatic synchronization for future updates.
How it works
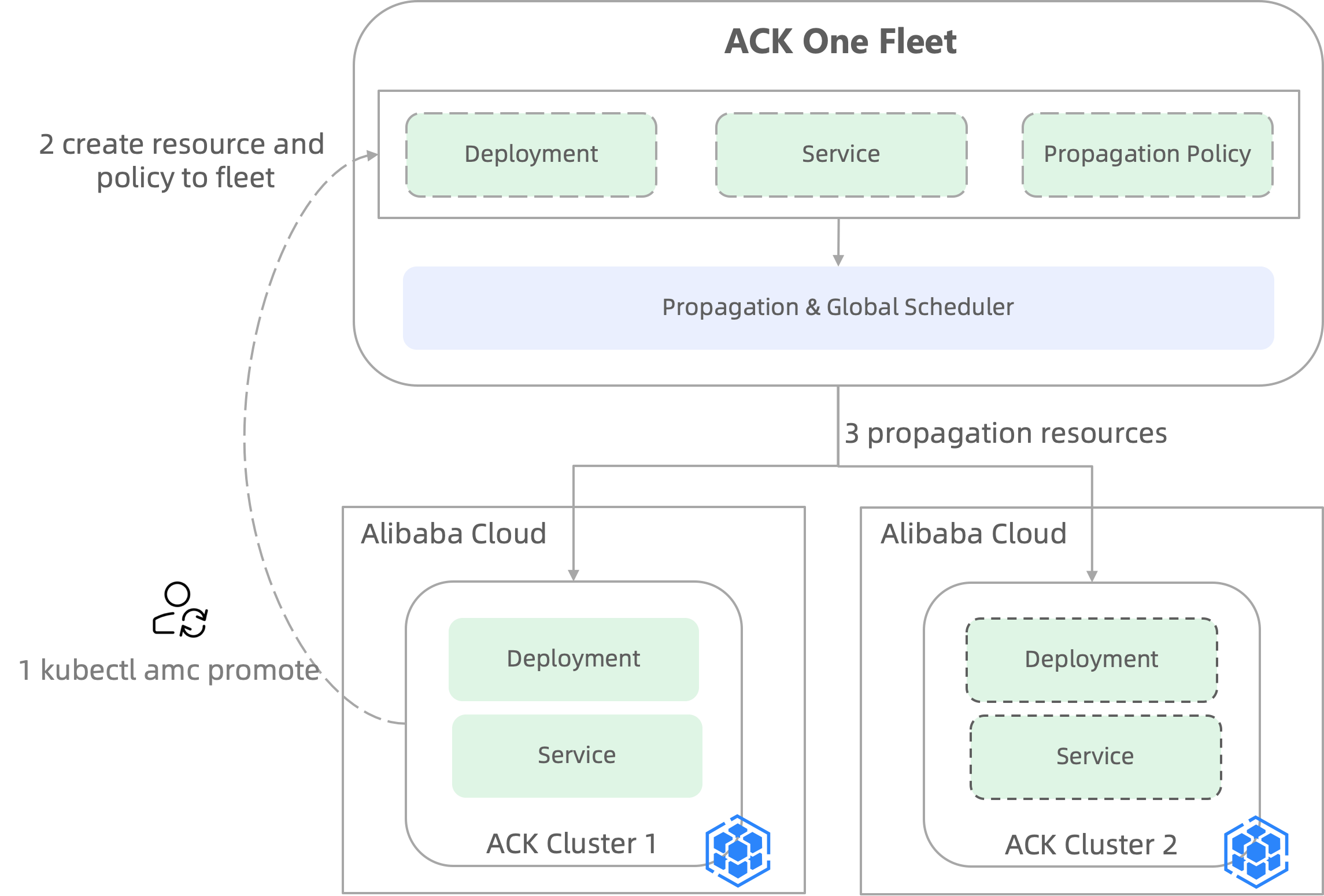
A user runs the
kubectl amc promotecommand to sync selected resources from a cluster to the fleet.Resources are created in the fleet, and a PropagationPolicy is automatically generated. The policy includes the clusters specified by
target-clustersand the source cluster, cluster-1.The fleet distributes the resources to the clusters specified in
target-clusters, such as cluster-2 in the diagram. The synchronized resources in all target clusters, including cluster-1, are then managed by the fleet.
Prerequisites
Multiple clusters are associated with the fleet. For more information, see Manage associated clusters.
The AliyunAdcpFullAccess permission is granted to a Resource Access Management (RAM) user. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
Obtain the kubeconfig file for the fleet instance from the ACK One console and connect to the fleet using
kubectl.
Step 1: Create a namespace in the fleet and target clusters
Before you distribute resources to multiple clusters, you must ensure that the corresponding namespace exists in both the fleet and all target clusters. Otherwise, the distribution fails. In the following example, the resources to be distributed belong to the gateway-demo namespace.
If the namespace already exists in the fleet and all target clusters, you can skip this step.
Use the fleet kubeconfig to run the following command and create the
gateway-demonamespace in the fleet.kubectl create ns gateway-demoCopy and save the following YAML content to a file named
web-demo-ns-policy.yaml.apiVersion: policy.one.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: ClusterPropagationPolicy metadata: name: web-demo-ns-policy spec: resourceSelectors: - apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace name: gateway-demo placement: clusterAffinity: clusterNames: - ${cluster1_id} # Replace with your cluster ID - ${cluster2_id} # Replace with your cluster ID replicaScheduling: replicaSchedulingType: DuplicatedUse the fleet kubeconfig to run the following command. This creates the
ClusterPropagationPolicyin the fleet and distributes the namespace.kubectl apply -f web-demo-ns-policy.yaml
Step 2: Run the promote command to sync resources to the fleet
Use the kubectl amc promote command to sync single-cluster resources to the fleet and distribute them to multiple clusters.
Use the
amc getcommand to check the initial state. The output shows thatservice1andweb-demoexist only in thegateway-demonamespace of cluster-1.ADOPTIONis `N`, which indicates that the resources are not managed by a PropagationPolicy in the ACK One fleet.kubectl amc -ngateway-demo get svc -M kubectl amc -ngateway-demo get deployment -MExpected output:
NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE ADOPTION service1 c8xxxxxx cluster-1 ClusterIP 192.168.**.** <none> 80/TCP 104m N NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE ADOPTION web-demo c8xxxxxx cluster-1 2/2 2 2 104m NRun the following commands to place the resources of cluster-1 under fleet management and distribute them to other clusters.
Replace the
${cluster1_id}and${cluster2_id}parameters with your cluster IDs. Thetarget-clustersparameter specifies the clusters to which the promoted resources are distributed. To specify multiple clusters, use the format${cluster2_id},${cluster3_id}.kubectl amc promote service service1 -ngateway-demo -m ${cluster1_id} --target-clusters ${cluster2_id} kubectl amc promote deployment web-demo -ngateway-demo -m ${cluster1_id} --target-clusters ${cluster2_id}Expected output:
ResourceTemplate (gateway-demo/service1) is created successfully PropagationPolicy (gateway-demo/service1-67676f499c) is created successfully Resource "/v1, Resource=services"(gateway-demo/service1) is promoted successfully ResourceTemplate (gateway-demo/web-demo) is created successfully PropagationPolicy (gateway-demo/web-demo-6675b99c65) is created successfully Resource "apps/v1, Resource=deployments"(gateway-demo/web-demo) is promoted successfullyRun the
amc getcommand again to view the result. The output shows thatservice1andweb-demohave been distributed to cluster-2 and that the resources in both clusters are managed by the ACK One fleet (ADOPTIONis Y). The web-demo application in cluster-1 is now a multi-cluster deployment.kubectl amc -ngateway-demo get svc -M kubectl amc -ngateway-demo get deployment -MExpected output:
NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE ADOPTION service1 cfxxxxxx cluster-2 ClusterIP 192.168.**.*** <none> 80/TCP 19s Y service1 c8xxxxxx cluster-1 ClusterIP 192.168.**.** <none> 80/TCP 5h58m Y NAME CLUSTER CLUSTER_ALIAS READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE ADOPTION web-demo c8xxxxxx cluster-1 2/2 2 2 6h1m Y web-demo cfxxxxxx cluster-2 2/2 2 2 24s Y
Modify the default distribution policy
By default, the promote command automatically creates a `Duplicated` type distribution policy (PropagationPolicy). This sets replicaSchedulingType: Duplicated, which replicates the application to each cluster. You can run the following command in the fleet to view the default distribution policy.
kubectl get pp -ngateway-demo xx -oyamlExpected output:
apiVersion: policy.one.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
...
spec:
...
placement:
clusterAffinity:
...
replicaScheduling:
replicaSchedulingType: Duplicated # Duplicated distribution policyTo use other policies, such as static or dynamic replica weights, add the --auto-create-policy=false parameter to the command to prevent automatic policy creation. Then, you can manually configure the desired policy. For more information, see Distribution policies and differentiation policies.