In scenarios such as Web application hosting, serverless application deployment, AI tasks, and event-driven applications, we recommend that you deploy workloads as Knative Services. This approach allows you to allocate resources based on demands and focus more on developing business logic. You can also benefit from Knative features, such as request-based auto scaling and simplified version management. By using these feature, Knative can automatically reduce the number of pods to zero when no requests are received from applications, and can automatically scale out pods when requests are received.
Prerequisites
Knative is deployed in your cluster. For more information, see Deploy and manage Knative.
Step 1: Deploy a Knative Service
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the Services tab. Select the namespace to which the Service belongs in the top navigation bar on the Services tab. Then, deploy a Knative Service.
You can deploy a Knative Service by using the wizard or the YAML editor.
Use the console
On the Services tab, click Create Service, and finish the configuration as prompted.
Parameter
Description
Service Name
Enter a name for the Service.
Image Name
Click Select Image. In the dialog box that appears, select your target image.
You can also enter private images and tags in the format
domainname/namespace/imagename:tag.Alternatively, follow on-screen prompts to directly use ACK-provided demo images. In this example,
registry-vpc.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/knative-sample/helloworld-go:73fbdd56is used (Replacecn-hangzhouwith your actual region).Access Protocol
HTTP and gRPC are supported.
Container Port
The container port that you want to expose. The port number must be in the range of 1 to 65535.
Advanced
Click Advanced to configure the advanced settings.
Use the YAML editor
In the upper-right part of the Services tab, click Create from YAML.
Enter the YAML content of the Service into the YAML editor and click Create.
For example, copy the following YAML content to the editor to create a Service named
helloworld-go.apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service metadata: name: helloworld-go spec: template: spec: containers: - image: registry-vpc.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/knative-sample/helloworld-go:73fbdd56 # Replace the region with your actual one. env: - name: TARGET value: "Knative"
After the Service is created, you can view, modify, or delete the Service on the Services tab.
Step 2: Access the Knative Service
After the Knative Service is deployed, you can point its domain name to the IP address of a gateway to associate the Service with the gateway. This allows you to access the Knative Service by using its domain name. To do this, perform the following operations:
On the Services tab, click the name of the Service.
In the Basic Information section, you can view information about the gateway and domain name.
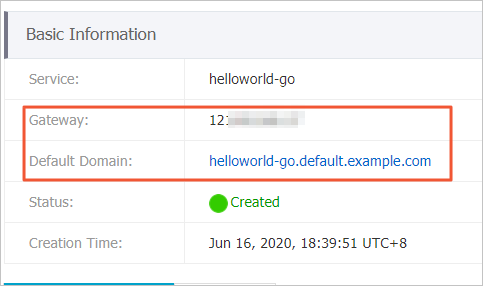
Add the following information to the hosts file to point the domain name of the Service to the IP address of the gateway.
Example:
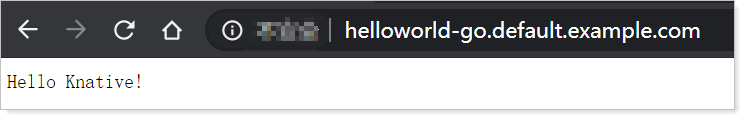
121.xx.xxx.xx helloworld-go.default.example.comAfter you modify the hosts file, you can use the domain name to access the Knative Service.
References
You can specify a custom domain name for the Knative Service. For more information, see Use a custom domain name.
For more information about how to configure a certificate to access a Knative Service over HTTPS through a custom domain name, see Configure a certificate to access Services over HTTPS.
You can create revisions and manage Knative Services versions based on revisions. For more information, see Create a revision.
If your business traffic spikes unexpectedly, you can use elastic container instances to deploy Knative Services. For more information, see Use elastic container instances in Knative.
For more information about how to implement auto scaling for a Knative Service based on the the number of requests, see Enable auto scaling to withstand traffic fluctuations.
For more information about how to deploy Knative Eventing for the event-driven mode in Knative, see Knative Eventing.