This topic describes how to use ExternalDNS to automatically create DNS records in an Alibaba Cloud DNS Private Zone for Services and Ingresses in an Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster. This allows services within the cluster to access one another by domain name.
Step 1: Configure RAM permissions
Grant the required Resource Access Management (RAM) permissions to the worker RAM role of your ACK cluster.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the target cluster and click its name. In the navigation pane on the left, click Cluster Information.
On the Cluster Information page, click the Basic Information tab. Click the link next to Worker RAM Role to navigate to the RAM console and create a permission policy.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Policies. On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
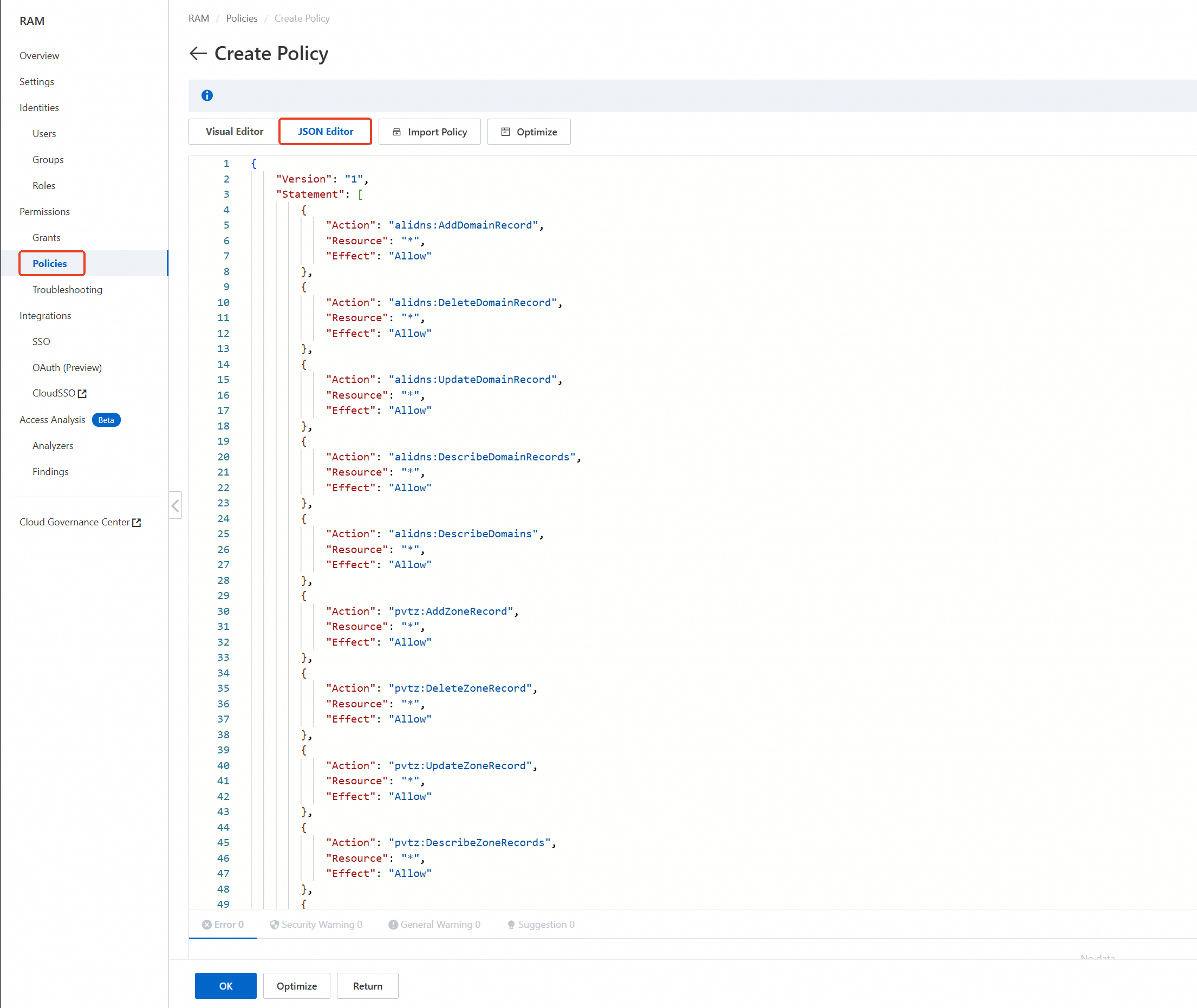
On the Create Policy page, click the JSON Editor tab. Copy the following content into the policy editor, then click OK.
On the Create Policy page, enter a Policy Name, then click OK.
In the left navigation pane, click Roles. Find the target worker RAM role and click Attach Policy in the Actions column. From the All Types drop-down list in the Policy section, select Custom Policy. Select the custom policy that you created and click OK.
Step 2: Deploy the ExternalDNS service
On the Clusters page, click the name of the target cluster. In the left navigation pane, select .
On the Helm page, click Deploy. Configure the Basic Information parameters as described in the following table.
Parameter
Example
Application Name
external-dns
Namespace
kube-system
Source
Default: Marketplace
Chart
Use Scenarios: Select All.
Supported Architecture: Select amd64.
Search box: Search for external-dns.
Select external-dns and click Next.
On the Parameters page, select a Chart Version, specify values for
alibabaCloudZoneTypeandpolicyas needed, and then click OK.alibabaCloudZoneType: The DNS service used by ExternalDNS. The default value ispublic.public: Alibaba Cloud DNS.private: Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone.
policy: The policy for syncing DNS records of Services in the cluster to PrivateZone.upsert-only: Writes or updates records. Does not delete records.sync: Writes, updates, and deletes records.
# public or private alibabaCloudZoneType: public # upsert-only or sync # upsert-only would prevent ExternalDNS from deleting any records, omit to enable full synchronization # sync would delete records once target service or ingress are released policy: upsert-only
Step 3: Use the ExternalDNS service
ExternalDNS supports only Services of the LoadBalancer type and Ingresses.
Configure Alibaba Cloud DNS for a Service
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console to obtain public domain name information.
NoteMake sure that the domain name is valid and has passed identity verification.
Create a test application using a domain name that has passed identity verification.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx annotations: external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: nginx.<public_domain_name> # Replace <public_domain_name> with your domain name that has passed identity verification. spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 name: http targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: nginx name: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - image: nginx name: nginxNoteThe
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostnameannotation specifies the DNS name to assign. ExternalDNS automatically creates a DNS record for the corresponding IP address.Shortly after the test application is created, the automatically created DNS record appears in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
Test the DNS resolution.
curl nginx.****.comExpected output:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p>Thank you for using nginx.
Configure Alibaba Cloud DNS for an Ingress
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console to obtain public domain name information.
NoteMake sure that the domain name is valid and has passed identity verification.
Create a test application using a domain name that has passed identity verification.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 name: http targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: nginx name: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - image: nginx name: nginx --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: nginx spec: ingressClassName: nginx rules: - host: nginx-ing.<public_domain_name> # Replace <public_domain_name> with your domain name that has passed identity verification. http: paths: - backend: service: name: nginx port: number: 80 path: / pathType: ImplementationSpecificNoteThe
hostfield specifies the DNS name to assign. ExternalDNS automatically creates a DNS record for the corresponding IP address.Shortly after the test application is created, the automatically created DNS record appears in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
Run the following command to test the DNS resolution.
curl nginx-ing.****.comExpected output:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p>Thank you for using nginx.
Configure Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone for a Service
To use the PrivateZone feature of Alibaba Cloud DNS, set the alibabaCloudZoneType value to private in the deployment parameters and ensure that the private domain name for the PrivateZone is associated with a VPC.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
In the left navigation pane, click Private Zone. On the Private Zone (Compatible with on-premises DNS) page, click Add Zone. Enter a name in Authoritative Zone and click OK.
Find the target zone and click Settings in the Actions column. You must manually add a DNS record before you can associate the zone with a VPC.

For more information, see Record Type List.
After adding the DNS record, click Effective Scope in the Actions column. In the Effective in VPCs drop-down list, select the VPC that contains the target cluster and click OK to associate the VPC.
Verify the domain name resolution.
Create a test application in the target cluster.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx annotations: external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: nginx.<Zone_Name> # Replace <Zone_Name> with the name of the zone that you added on the PrivateZone page. service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-address-type: "intranet" # An internal-facing Server Load Balancer instance. spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 name: http targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: nginx name: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest name: nginxNoteThe
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostnameannotation specifies the domain name of the PrivateZone. ExternalDNS automatically creates a DNS record for the corresponding IP address.Shortly after the test application is created, the automatically created DNS record appears in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.

Test the DNS resolution.
curl nginx.****Expected output:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p>Thank you for using nginx.
Configure Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone for an Ingress
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
In the left navigation pane, click Private Zone. On the Private Zone (Compatible with on-premises DNS) page, click Add Zone. Enter a name in Authoritative Zone and click OK.
Find the target zone and click Settings in the Actions column. You must manually add a DNS record before you can associate the zone with a VPC.

For more information, see Record Type List.
After adding the DNS record, click Effective Scope in the Actions column. In the Effective in VPCs drop-down list, select the VPC that contains the target cluster and click OK to associate the VPC.
Verify the domain name resolution.
Create a test application in the target cluster.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-address-type: "intranet" # An internal-facing Server Load Balancer instance. spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 name: http targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: nginx name: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest name: nginx --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: nginx spec: ingressClassName: nginx rules: - host: nginx-ing.<Zone_Name> # Replace <Zone_Name> with the name of the zone that you added on the PrivateZone page. http: paths: - backend: service: name: nginx port: number: 80 path: / pathType: ImplementationSpecificShortly after the test application is created, the automatically created DNS record appears in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.

Test the DNS resolution.
curl nginx-ing.****Expected output:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p>Thank you for using nginx.