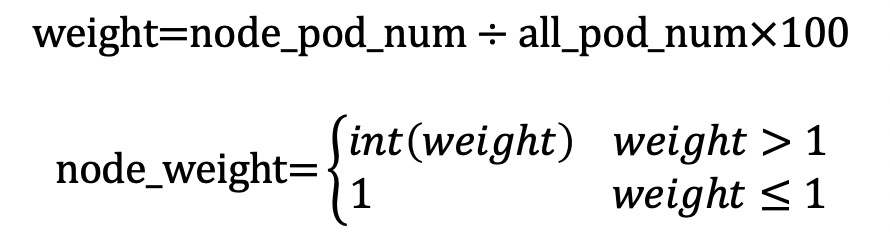This topic answers frequently asked questions (FAQs) about services in Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK). It provides solutions to common issues, such as the inaccessibility of a Server Load Balancer (SLB) IP address from within a cluster, failures when reusing an existing SLB instance, and how to handle a failed Cloud Controller Manager (CCM) upgrade.
Index
SLB-related questions
How to choose between the Local and Cluster external traffic policies when you create a service
Why are events for the service and LoadBalancer synchronization process not visible?
What to do if an SLB instance remains in the Pending state during creation
Why is an SLB IP address inaccessible from within a cluster?
How to query the IP addresses, names, and types of all SLB instances in a cluster
FAQ about reusing an existing SLB instance
Other questions
SLB-related questions
The specific purposes of SLB instances in an ACK cluster
If you install the Nginx Ingress Controller add-on when you create a Kubernetes cluster, the cluster creates two SLB instances by default.
The two SLB instances serve the following purposes:
API Server SLB: This SLB instance is the access endpoint for the API Server. All access requests to the cluster must pass through this SLB instance. It listens on TCP port 6443. The backend servers are API Server pods or master ECS instances.
Nginx Ingress Controller SLB: This SLB instance is associated with the
nginx-ingress-controllerservice in the kube-system namespace. The vServer group dynamically binds to Nginx Ingress Controller pods to load balance and forward external requests. It listens on ports 80 and 443 over TCP.
How to choose between the Local and Cluster external traffic policies when you create a service
The Local and Cluster external traffic policies provide different features for different network plug-ins. For more information about the differences between the Local and Cluster external traffic policies, see External traffic policies: Local and Cluster.
Why are events for the service and LoadBalancer synchronization process not visible?
If no event information is displayed after you run the kubectl -n {your-namespace} describe svc {your-svc-name} command, check the version of your CCM component.
Versions earlier than v1.9.3.276-g372aa98-aliyun: The CCM component does not display events for the service and LoadBalancer synchronization. Upgrade the component. For more information about how to view and upgrade the CCM version, see Upgrade the CCM component.
For versions v1.9.3.276-g372aa98-aliyun and later, you can submit a ticket.
What to do if an SLB instance remains in the Pending state during creation
Run the
kubectl -n {your-namespace} describe svc {your-svc-name}command to view event information.Resolve the errors reported in the events. For information about how to handle different error messages in events, see Error events and solutions.
If no error message is displayed, see Why are events for the service and LoadBalancer synchronization process not visible?.
What to do if an SLB vServer group is not updated
Run the
kubectl -n {your-namespace} describe svc {your-svc-name}command to view event information.Resolve the errors reported in the events. For information about how to handle different error messages in events, see Error events and solutions.
If no error message is displayed, see Why are events for the service and LoadBalancer synchronization process not visible?.
What to do if a service annotation does not take effect
Check for error messages.
Run the
kubectl -n {your-namespace} describe svc {your-svc-name}command to view event information.Resolve the errors reported in the events. For information about how to handle different error messages in events, see Error events and solutions.
If no error message is displayed, resolve the issue based on one of the following scenarios:
Make sure that your CCM version meets the version requirements of the annotation. For more information about the mappings between annotations and CCM versions, see Use annotations to configure a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instance.
Log on to the Container Service Management Console. On the Services page, click the name of the target service and confirm that the Service has the corresponding annotations. If the Service does not have annotations, configure them.
For more information about how to add an annotation, see Use annotations to configure a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instance.
For more information about how to view the list of services, see Manage services.
Check whether the annotation is correctly configured.
Why was the configuration of my SLB instance modified?
CCM uses a declarative API and automatically updates the SLB configuration based on the service configuration under certain conditions. Any configurations that you modify in the SLB console are at risk of being overwritten. We recommend that you configure the SLB instance using annotations. For more information about how to use annotations, see Use annotations to configure a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instance.
Do not manually modify any configurations of an SLB instance that is created and maintained by Kubernetes in the SLB console. Otherwise, configurations may be lost and the service may become inaccessible.
Why is an SLB IP address inaccessible from within a cluster?
Scenario 1: If you use a private IP address for an SLB instance that was not created by a service, access from within the cluster may fail. This failure occurs if the pod accessing the SLB instance is on the same node as a backend pod.
For Layer 4 load balancing services, an ECS instance cannot act as both a backend server and a client that accesses the service. To resolve this issue and prevent the client and destination from being on the same node, use one of the following methods.
Change the SLB IP address to a public IP address.
Create the SLB instance using a service and set the external traffic policy to Cluster. In this case, kube-proxy intercepts the traffic sent to the SLB instance from within the cluster, which bypasses the SLB limitation.
Scenario 2: You set the external traffic policy to Local when you expose the service. This causes access to the SLB IP address from within the cluster to fail.
For more information about the cause and solution of this issue, see How do I resolve the issue where the SLB address exposed by a LoadBalancer service is inaccessible from within a Kubernetes cluster?.
How do I resolve the issue where the SLB address exposed by a LoadBalancer service is inaccessible from within a Kubernetes cluster?
Problem description
In a Kubernetes cluster, some nodes can access the SLB instance with an external traffic policy of Local that is exposed by the cluster, but other nodes cannot. This issue frequently occurs with Ingresses.
Cause
The SLB instance is configured with externalTrafficPolicy: Local. With this policy, the SLB address is accessible only from nodes that host the corresponding backend pods. Because the SLB address is intended for external use, if a node or pod within the cluster tries to access it, the request is not sent to the SLB instance. Instead, kube-proxy intercepts the request and forwards it based on local routing rules (iptables or IPVS).
If the node where the client pod resides does not host a backend pod for the service, the network connection fails. If the node hosts a backend pod, the service can be accessed as expected. For more information about this issue, see kube-proxy adds external-lb address to local node iptables rules.
Solutions
You can use one of the following methods to resolve the issue. We recommend that you use the first method.
Access internal services from within the Kubernetes cluster using their ClusterIP addresses or service names. The service name of the Ingress is
nginx-ingress-lb.kube-system.Change the externalTrafficPolicy of the LoadBalancer service to Cluster. This method ensures that traffic can be forwarded to pods on all nodes. However, it causes the loss of source IP addresses because the cluster performs source network address translation (SNAT). This means the backend application cannot retrieve the real IP address of the client. Run the following command to modify the Ingress service:
kubectl edit svc nginx-ingress-lb -n kube-systemIf you use a Terway cluster with ENIs or multiple IP addresses per ENI, change the externalTrafficPolicy of the LoadBalancer service to Cluster and add an annotation for ENI passthrough, such as
annotation: service.beta.kubernetes.io/backend-type: "eni". The following code block shows the format. This method preserves the source IP address and allows access from within the cluster. For more information, see Use annotations to configure a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instance.apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/backend-type: eni labels: app: nginx-ingress-lb name: nginx-ingress-lb namespace: kube-system spec: externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
When are SLB instances automatically deleted?
The policy for automatically deleting an SLB instance depends on whether the SLB instance was automatically created by CCM. The following table describes the deletion policies.
Service operation | SLB instance automatically created by CCM | Reused SLB instance |
Delete the service | The SLB instance is deleted. | The SLB instance is retained. |
Change the service type from LoadBalancer to another type | Delete an SLB instance | The SLB instance is retained. |
Does deleting a service also delete the SLB instance?
If you reuse an existing SLB instance (the service has the service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-id: {your-slb-id} annotation), deleting the service does not delete the SLB instance. Otherwise, deleting the service also deletes the corresponding SLB instance.
If you change the service type (for example, from LoadBalancer to NodePort), the corresponding SLB instance that was automatically created by CCM is also deleted.
Do not manually edit a service to change an SLB instance that was automatically created by CCM to a reused SLB instance. This disassociates the service from the automatically created SLB instance. When you delete the service, the corresponding SLB instance cannot be automatically deleted.
What to do if I accidentally delete an SLB instance
Scenario 1: What to do if you accidentally delete the API Server SLB instance
The instance cannot be recovered. You must recreate the cluster. For more information, see Create an ACK Pro cluster.
Scenario 2: What to do if you accidentally delete the Ingress SLB instance
The following steps use Nginx Ingress as an example to show how to recreate an SLB instance.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
At the top of the Services page, select kube-system from the Namespace drop-down list.
In the service list, find the target service nginx-ingress-lb, click Edit YAML in the Actions column, remove the
status.loadBalancerfield and its content, and then click OK to trigger the CCM to rebuild the SLB.If nginx-ingress-lb does not appear in the service list, click Create from YAML in the upper-left corner of the page and use the following template to create a Service named nginx-ingress-lb.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: nginx-ingress-lb name: nginx-ingress-lb namespace: kube-system spec: externalTrafficPolicy: Local ports: - name: http port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 80 - name: https port: 443 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 selector: app: ingress-nginx type: LoadBalancer
Scenario 3: What to do if you accidentally delete an application-specific SLB instance
If the service corresponding to the SLB instance is no longer needed, delete the service.
If the corresponding service is still in use, perform the following steps:
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
From the Namespace drop-down list at the top of the Services page, click All Namespaces, and then find your service in the service list.
In the Actions column for the target service, click Edit YAML, delete the
status.loadBalancercontent, and click OK to allow CCM to rebuild the SLB.
How to enable SLB renaming for older CCM versions
SLB instances created by Cloud Controller Manager (CCM) v1.9.3.10 and later are automatically tagged to support renaming. For SLB instances created by v1.9.3.10 and earlier versions, you must manually add a specific tag to enable renaming.
Manually adding a tag to enable renaming is required only for SLB instances created by CCM v1.9.3.10 and earlier.
The service type must be LoadBalancer.
Log on to the master node of the Kubernetes cluster. For more information, see Connect to an ACK cluster using kubectl.
Run the
kubectl get svc -n ${namespace} ${service}command to view the service type and IP address. Note
NoteReplace namespace and service with the namespace and service name of your cluster.
Run the following command to generate the required tag for the SLB instance.
kubectl get svc -n ${namespace} ${service} -o jsonpath="{.metadata.uid}"|awk -F "-" '{print "kubernetes.do.not.delete: "substr("a"$1$2$3$4$5,1,32)}'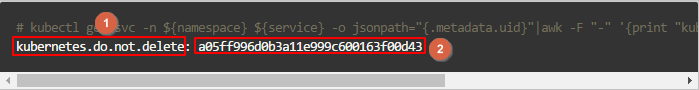
Log on to the Server Load Balancer console. Based on the IP address retrieved in Step 2, search for the SLB instance in the corresponding region.
Add a tag to the SLB instance using the key and value generated in Step 3. The key and value correspond to 1 and 2 in the preceding figure. For more information, see Create and manage a CLB instance.
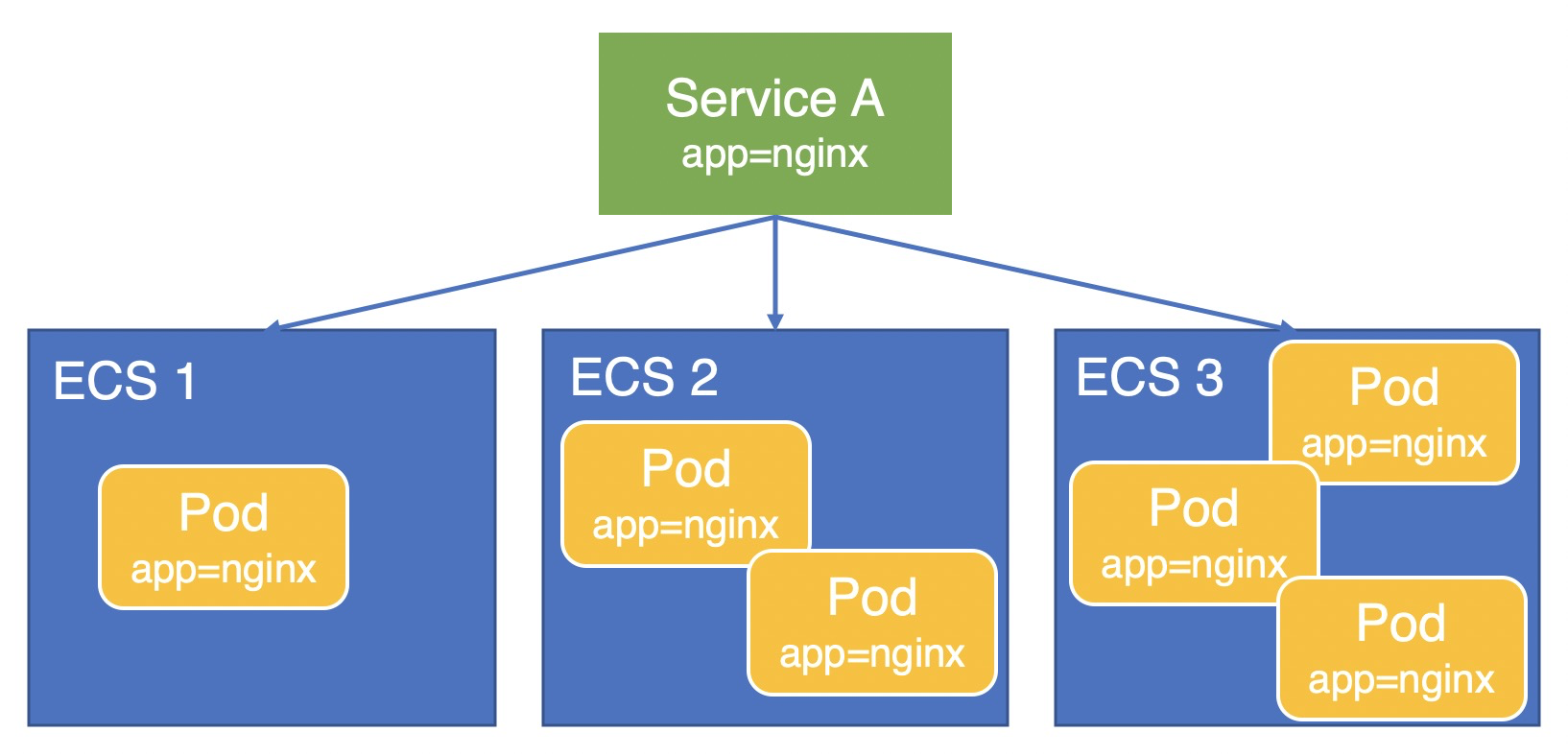
How are node weights automatically set in Local mode?
This section uses a scenario where an application pod (app=nginx) is deployed on three ECS instances and exposed through Service A to explain how node weights are calculated in Local mode.
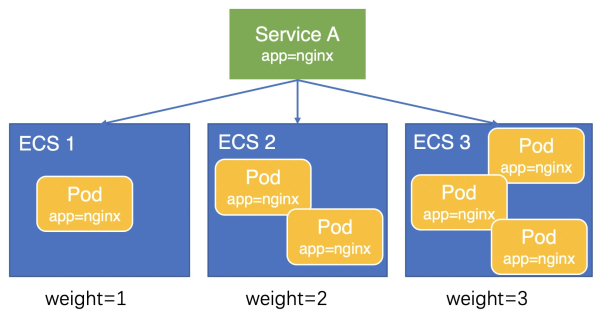
Versions v1.9.3.276-g372aa98-aliyun and later
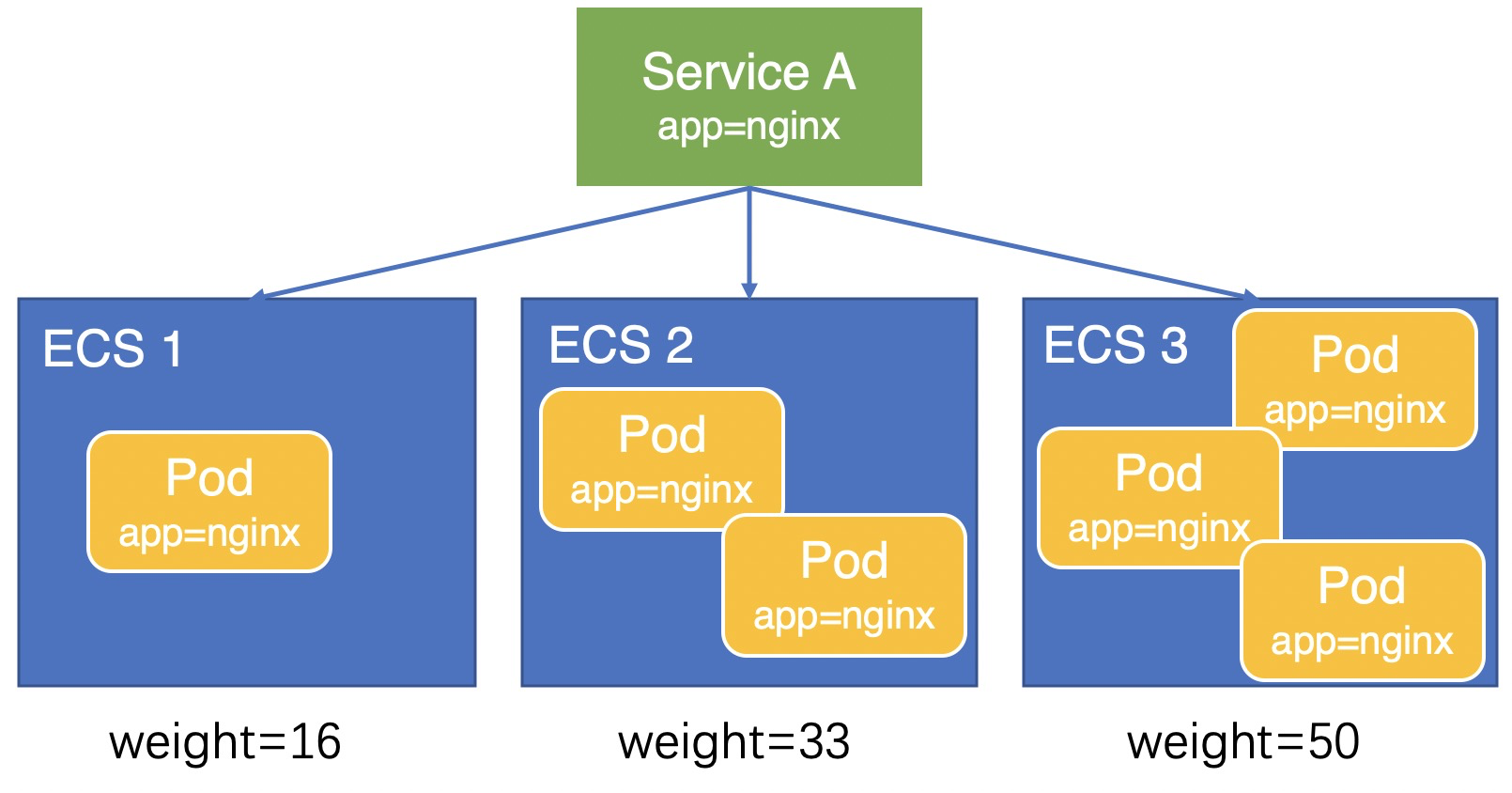
Due to precision issues in the weight calculation, a slight load imbalance may still occur among pods. In CCM v1.9.3.276-g372aa98-aliyun and later, CCM sets the node weight to the number of pods deployed on the node. As shown in the following figure, the weights of the three ECS instances are 1, 2, and 3. Traffic is distributed to the three ECS instances at a ratio of 1:2:3, resulting in a more balanced load across the pods.
The formula is as follows: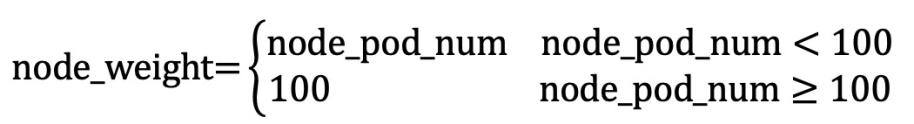
Versions later than v1.9.3.164-g2105d2e-aliyun and earlier than v1.9.3.276-g372aa98-aliyun
Versions earlier than v1.9.3.164-g2105d2e-aliyun
How to query the IP addresses, names, and types of all SLB instances in a cluster?
Run the following command to retrieve the name, IP address, and address type of each LoadBalancer service in all namespaces.
kubectl get services -A -ojson | jq '.items[] | select(.spec.type == "LoadBalancer") | {name: .metadata.name, namespace: .metadata.namespace, ip: .status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip, lb_type: .metadata.annotations."service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-address-type"}'The following output is expected:
{ "name": "test", "namespace": "default", "ip": "192.168.*.*", "lb_type": "intranet" } { "name": "nginx-ingress-lb", "namespace": "kube-system", "ip": "47.97.*.*", "lb_type": "null" }
How to ensure that a LoadBalancer can gracefully close existing connections when backend servers of a LoadBalancer service are replaced?
You can configure connection draining using the service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-connection-drain and service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-connection-drain-timeout annotations. After a backend server is removed from the service, the LoadBalancer continues to process existing connections within the drain-timeout period. For more information, see Enable connection draining for a listener.
FAQ about reusing an existing SLB instance
Why does reusing an existing SLB instance fail?
Check the CCM version. CCM versions earlier than v1.9.3.105-gfd4e547-aliyun do not support reusing SLB instances. For more information about how to view and upgrade the CCM version, see Upgrade the CCM component.
Check whether the SLB instance that you want to reuse was created by the cluster. You cannot reuse an SLB instance that was created by the cluster.
Check whether the SLB instance is the SLB instance for the API Server. You cannot reuse the SLB instance for the API Server.
If you want to reuse a private-facing SLB instance, make sure that the SLB instance and the cluster are in the same VPC. You cannot reuse an SLB instance across VPCs.
Why is a listener not configured when I reuse an existing SLB instance?
Check whether the service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-force-override-listeners annotation is set to "true". If this annotation is not configured, a listener is not automatically created.
The CCM does not overwrite the listeners of an existing CLB instance due to the following reasons:
If the listeners of the CLB instance are associated with applications, service interruptions may occur after the listeners are overwritten.
The CCM supports limited backend configurations and cannot handle complex configurations. To use complex backend configurations, you can create listeners in the console. The listeners do not overwrite the existing ones.
Therefore, we recommend that you do not overwrite the listeners of an existing CLB instance. You can forcibly overwrite the listeners if the ports on which these listeners listen are no longer used.
Other questions
What to do if a CCM upgrade fails
For more information about how to resolve a failed CCM component upgrade, see Cloud Controller Manager (CCM) upgrade check fails.
Service error messages and solutions
The following table describes the solutions for different error messages.
Error message | Description and solution |
| The number of backend servers for the CLB instance has reached the quota limit. Solution: Optimize your quota usage in one of the following ways:
|
| Shared CLB instances do not support ENIs. Solution: If the CLB backend uses ENIs, you must select a high-performance CLB instance. You can add the Important Make sure that the annotation is compatible with your CCM version. For more information about the mapping between annotations and CCM versions, see Use annotations to configure a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instance. |
| The CLB instance has no backend servers. Check whether the service is associated with a pod and whether the pod is running as expected. Solution:
|
| The CLB instance cannot be associated based on the service. Solution: Log on to the Server Load Balancer console. In the region where the service resides, search for the CLB instance based on the
|
| Your account has an overdue payment. |
| Your account balance is insufficient. |
| The CLB OpenAPI is being throttled. Solution:
|
| The listener associated with the vServer group cannot be deleted. Solution:
|
| This error occurs if you reuse an internal-facing CLB instance that is not in the same VPC as the cluster. Solution: Make sure that your CLB instance and cluster are in the same VPC. |
| The number of available IP addresses in the vSwitch is insufficient. Solution: Use |
| The ENI mode does not support a string value for Solution: Change the value of the |
| Earlier versions of CCM create shared CLB instances by default. However, shared CLB instances are discontinued. Solution: Upgrade the CCM component. |
| The resource group of a CLB instance cannot be changed after the instance is created. Solution: Remove the |
| The specified ENI IP address cannot be found in the VPC. Solution: Check whether the |
| The billing method of the CLB instance cannot be changed from pay-as-you-go to pay-by-specification. Solution:
|
| This error occurs when a CLB instance created by CCM is reused. Solution:
|
| The type of a CLB instance cannot be changed after the instance is created. This error occurs if you change the CLB type after you create the service. Solution: Delete and recreate the service. |
| The service is already attached to a CLB instance and cannot be attached to another one. Solution: You cannot reuse an existing CLB instance by changing the CLB ID in the |
How to configure a listener for a NodePort service
CCM supports configuring listeners only for LoadBalancer services. You need to change the service type from NodePort to LoadBalancer.
How to access a NodePort service
To access the Service from within the cluster (on a cluster node), you can use ClusterIP + Port or Node IP + Service NodePort. The default port number exposed by a NodePort Service is greater than 30000.
To access the Service from outside the cluster (outside the cluster nodes), you can use the node IP address and the NodePort of the Service. The default port number exposed by a NodePort Service is greater than 30000.
To access the service from outside the VPC (from another VPC or the Internet), you need to expose a LoadBalancer service and then access the service through its external endpoint.
NoteIf you set the external traffic policy of your service to Local, make sure that the node you access hosts a backend pod of the service. For more information about external traffic policies, see External traffic policies: Local and Cluster.
How to correctly configure the NodePort range
In Kubernetes, the API Server provides the ServiceNodePortRange parameter ( --service-node-port-range command-line parameter). This parameter limits the range of NodePorts that NodePort or LoadBalancer services can listen on. The default value is 30000 to 32767. In an ACK Pro cluster, you can modify this port range by customizing the parameters of the control plane. For more information, see Customize the parameters of the control plane for an ACK Pro cluster.
You must be very careful when you modify the NodePort range. Make sure that the NodePort range does not conflict with the port range specified by the
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_rangekernel parameter on the cluster nodes. Theip_local_port_rangekernel parameter controls the range of local port numbers that any application on the Linux system can use. The default value ofip_local_port_rangeis 32768 to 60999.With the default configurations of your ACK cluster, the ServiceNodePortRange parameter and the
ip_local_port_rangeparameter do not conflict. If you have previously adjusted either of these parameters to increase the port limit, causing their ranges to overlap, sporadic network exceptions may occur on the nodes. In severe cases, this can lead to business health check failures and offline cluster nodes. We recommend that you restore the default values or adjust both port ranges so that they do not overlap at all.After you adjust the port range, some NodePort or LoadBalancer services in the cluster may still use ports within the
ip_local_port_rangeparameter's range as NodePorts. You need to reconfigure these services to avoid conflicts. You can run thekubectl edit <service-name>command to directly change the value of thespec.ports.nodePortfield to an unused NodePort.
How to add required permissions when you upgrade the CCM component to a later version in an ACK dedicated cluster
To improve performance, later versions of CCM gradually introduce Alibaba Cloud APIs that require additional RAM permissions (for example, v2.11.2 for route management in Flannel networks and v2.12.1 for batch management of NLB).
Therefore, if you want to upgrade the component to v2.11.2 or later in an ACK dedicated cluster, you must grant the required permissions to its RAM role before the upgrade to ensure that the component works as expected.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the target cluster and click its name. In the navigation pane on the left, click Cluster Information.
Click the Basic Information tab, then click the role name for Master RAM Role.
On the role details page in the Resource Access Management console, click in the navigation panel on the left, find the custom policy that starts with
k8sMasterRolePolicy-Ccm-in the policy list, and click the policy name to go to the access policy management page.For clusters that were created at an earlier time, the policy may not exist. You can select a custom policy whose name starts with
k8sMasterRolePolicy-.Click Edit Policy Document and add the
nlb:ListAsynJobspermission to the NLB permissions.
If you use a Flannel cluster, you must also add the vpc:CreateRouteEntries and vpc:DeleteRouteEntries permissions to the VPC-related permissions.

After you add the permissions, submit the policy as prompted on the page. After the changes are saved, you can upgrade the CCM component.