For real-time applications that rely on long-lived WebSocket connections, the default timeout settings of NGINX Ingress can cause unexpected disconnects. To ensure a stable connection, use Ingress annotations to increase the timeout values.
Core configuration
The default proxy timeouts in NGINX Ingress are designed for short-lived HTTP requests. To support long-lived connections for applications such as online games and real-time dashboards that use WebSocket, adjust the following timeout Annotations in your Ingress resource. These timeouts specify the maximum interval between two successful read/write operations, not the total time to transmit the entire response/request.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: Sets the timeout for reading a response from the backend service. The default value is 60 seconds. We recommend setting this to 3600 (1 hour) or longer for WebSocket Services.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: Sets the timeout for sending a request to the backend service. The default value is 60 seconds. We recommend setting this to 3600 (1 hour) or longer for WebSocket Services.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "3600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "3600"
name: ws
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
# ... rest of your Ingress specStep 1: Deploy a sample WebSocket application
This topic uses a simple WebSocket echo server for demonstration. For the complete code, see websocket-echo-server.
Console
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Deployments page, click Create from YAML. Copy the following content to the template area and click Create.
In the dialog box that appears, find the target deployment and click View, then confirm the pod is
Running.
kubectl
Get a cluster kubeconfig and connect to the cluster using kubectl.
Create a file named
websocket.yamlwith the following content to define the Deployment and Service.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: ws name: websocket-server namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: ws template: metadata: labels: app: ws spec: containers: - image: registry-cn-hangzhou.ack.aliyuncs.com/ack-demo/websocket-echo-server:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: echo env: - name: BIND_PORT value: "3000" ports: - containerPort: 3000 protocol: TCP resources: limits: cpu: 1000m memory: 1000Mi requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: ws name: websocket-server namespace: default spec: ports: - name: ws port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 3000 selector: app: ws type: ClusterIPDeploy the WebSocket application and create a Service.
kubectl apply -f websocket.yamlConfirm the target application pod is
Running.kubectl get pod | grep websocket-server
Step 2: Configure an Ingress to expose the Service
Set the proxy send timeout and proxy read timeout rules for the Ingress.
Log on to the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console, and click the target cluster. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
In the search box, enter
Nginx Ingress Controllerto find the component. On the component card, click Install.The component versions earlier than 1.2 are no longer maintained. Update the NGINX Ingress controller to the latest version.
Configure Ingress routing rules and timeout annotations.
Console
In the left navigation pane, choose . Select the
defaultnamespace and click Create Ingress.Configure the Ingress with the following settings and click OK.
Gateway Type: select
Nginx IngressName:
wsDomain Name:
test.example.comMappings
Path:
/Rule:
ImplementationSpecific (Default Value)Service:
websocket-serverPort:
3000
Annotations: Add two annotations.
Set Name to
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeoutand Value to3600.Set Name to
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeoutand Value to3600.
On the Ingress list page, get the Endpoint of the new Ingress.
The NGINX Ingress configuration takes about 10 seconds to take effect. Click the refresh button to retrieve the endpoint. If the endpoint information does not appear after a long time, click the Ingress name, go to the Events tab, and follow the instructions in troubleshooting for exceptions.
kubectl
Create a file named
websocket-ingress.yamlwith the following content. Replacetest.example.comwith your actual domain.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "3600" # Proxy read timeout: 3600 seconds nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "3600" # Proxy send timeout: 3600 seconds name: ws namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: nginx rules: - host: test.example.com # Access domain name of the Service http: paths: - backend: service: name: websocket-server # Name of the Service created in the previous step port: number: 3000 # Exposed port of the Service created in the previous step path: / pathType: ImplementationSpecificDeploy the Ingress resource.
kubectl apply -f websocket-ingress.yamlGet the access Endpoint. It may take a moment for the IP to be assigned. If no address is returned, wait 10 seconds and try again.
ADDRESS=$(kubectl get ingress ws -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}') echo $ADDRESS
Step 3: Access the WebSocket Service
For testing purposes, add an entry to your local hosts file to map your domain to the Ingress IP address.
macOS/Linux:
sudo vi /etc/hostsWindows: Open Notepad as an administrator, then open
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.
Replace the following address with your access Endpoint. Add the following domain name mapping record to the end of the file and save it.
47.102.XX.XX test.example.comInstall websocat and use the WebSocket (WS) or WebSocket Secure (WSS) protocol to access the Service.
WS protocol
For unencrypted WebSocket:
websocat ws://test.example.comAfter connecting, type any text and press Enter. The server should echo the text back to you.

WSS protocol
To use encrypted WebSocket, first enable HTTPS access for the NGINX Ingress Controller.
Obtain an SSL certificate.
Production environment: Purchase a valid certificate from a certificate authority (CA) or purchase one from Alibaba Cloud.
Test environment: Generate a self-signed certificate.
(Optional) If you purchased a certificate from Alibaba Cloud, download the SSL Certificate.
Create a Kubernetes Secret to store the certificate and private key.
Console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the one you want to change. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Secrets page, select the
defaultnamespace, and click Create in the upper-left corner. In the panel that appears, configure the Secret. After the configuration is complete, click OK.Name:
nginx-ingress-tlsType: TLS Certificate
Click Add
Name: The full content of the certificate file (
.crtor.pem)Value: The full content of the private key file (
.key)
kubectl
Replace
<PUBLIC_CERT>and<PRIVATE_KEY>with the paths to your certificate file (.crtor.pem) and private key file (.key) respectively. Then, run the command to store the certificate and private key as a Secret.# The --key flag specifies the private key file, and the --cert flag specifies the certificate file. kubectl create secret tls nginx-ingress-tls --cert <PUBLIC_CERT> --key <PRIVATE_KEY>Update the Ingress to reference the created Secret.
Console
In the left navigation pane, choose , and select the
defaultnamespace. In the Actions column of the target Ingress, click Update.Update the Ingress with the following configuration and click OK.
TLS Settings: Enable this option.
Domain Name:
test.example.comSecret:
nginx-ingress-tls
kubectl
Update your
websocket-ingress.yamlto include atlssection for thewsIngress.Domain name:
test.example.comCertificate Secret:
nginx-ingress-tls
kubectl patch ingress ws -p '{"spec":{"tls":[{"hosts":["test.example.com"],"secretName":"nginx-ingress-tls"}]}}'Connect to the WebSocket Service using the WSS protocol.
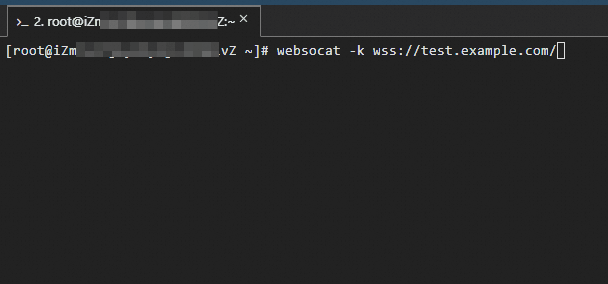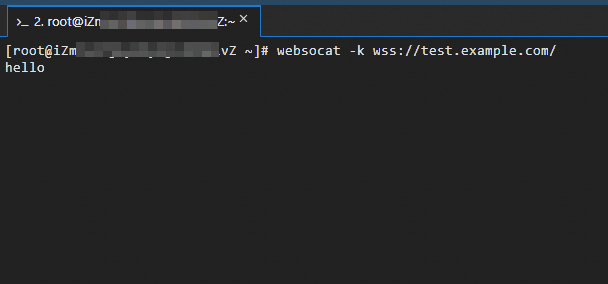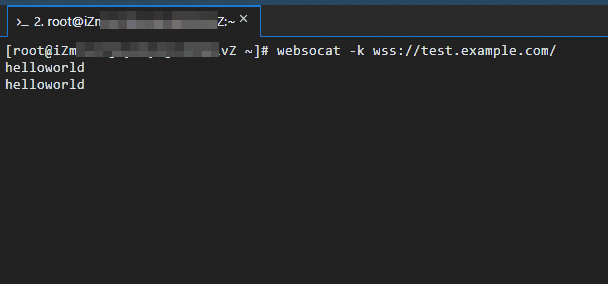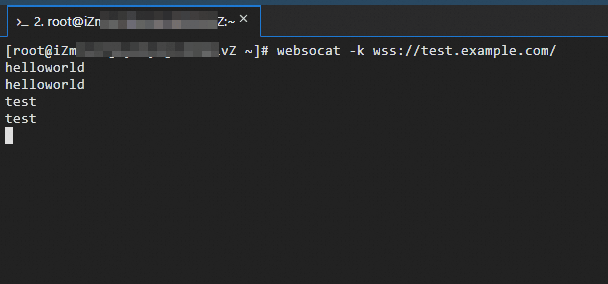
If the Service uses a self-signed certificate, use the
-kflag to skip certificate validation.websocat wss://test.example.comAfter connecting, type any text and press Enter. The server should echo the text back to you.
FAQ
How can I generate a self-signed certificate for testing?
Run the following command to generate a self-signed certificate (ws.crt) and a private key (ws.key) for the domain name test.example.com with a validity period of 365 days:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ws.key -out ws.crt -days 365 -nodes \
-subj "/CN=test.example.com" \
-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:test.example.com"Self-signed certificates are not trusted by browsers and other clients by default and trigger security warnings. Do not use self-signed certificates in production environments.
What is the difference between an SSL certificate and a TLS certificate?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is an older encryption protocol that has been replaced by the more secure Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol.
In modern terminology, "SSL certificate" is often used colloquially to refer to what is technically a "TLS certificate".
References
To learn which gateway in ACK support the WebSocket protocol, see Comparison of NGINX Ingress, ALB Ingress, and MSE Ingress.
To maintain a long-lived WebSocket connection, configure custom timeout settings. For custom timeout annotation details, see Custom timeouts.