The intra-container operation audit feature audits commands that members or applications run after they access a container. This topic describes how to use this feature. It also explains how to use Simple Log Service (SLS) to collect and analyze audit logs and set custom alert rules.
Billing
The intra-container operation audit feature is free of charge. However, after you enable this feature, you are charged for using Simple Log Service (SLS) features. For more information about SLS billing, see Billing overview.
This is a whitelist feature. To use it, please submit a ticket.
Limits
Cluster type: This feature is supported only for ACK Managed Cluster Pro Edition, ACK Managed Cluster Basic Edition, and ACK Dedicated Cluster.
Cluster version and operating system: This feature is supported only for Alibaba Cloud Linux, Ubuntu, and ContainerOS with a kernel version later than 4.19.
Alibaba Cloud Linux: Cluster version 1.18 or later.
ContainerOS: Cluster version 1.24 or later.
Ubuntu:
The cluster version is 1.30 or later. To upgrade the cluster, see Manually upgrade a cluster.
During node initialization, automatic OS upgrades are disabled.
During node initialization, the
/etc/resolv.confsymbolic link points to/run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf, and the DNS server is configured by DHCP.Features such as Cloud Parallel File System (CPFS) persistent volumes (PVs), image acceleration plugins, and security hardening are not currently supported.
Step 1: Enable the intra-container operation audit feature
When you enable the intra-container operation audit feature, the following two components are installed:
Log collection component: Collects audit logs, sends them to Simple Log Service, and creates a default audit report.
ack-advanced-audit component: Audits operations within containers.
By default, a Logstore named advaudit-${cluster_id} is created in the log project that is used by the log collection component. This Logstore stores audit logs. The log retention period for this Logstore is 180 days. To change the log retention period, see Manage a Logstore.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Audit page, click the Container Audit tab and then click Install.
Step 2: View audit reports
On the Audit page, click the Container Audit tab and then click the Container Audit Overview tab to view the audit report.
View the number of times pods were accessed and related pod information.
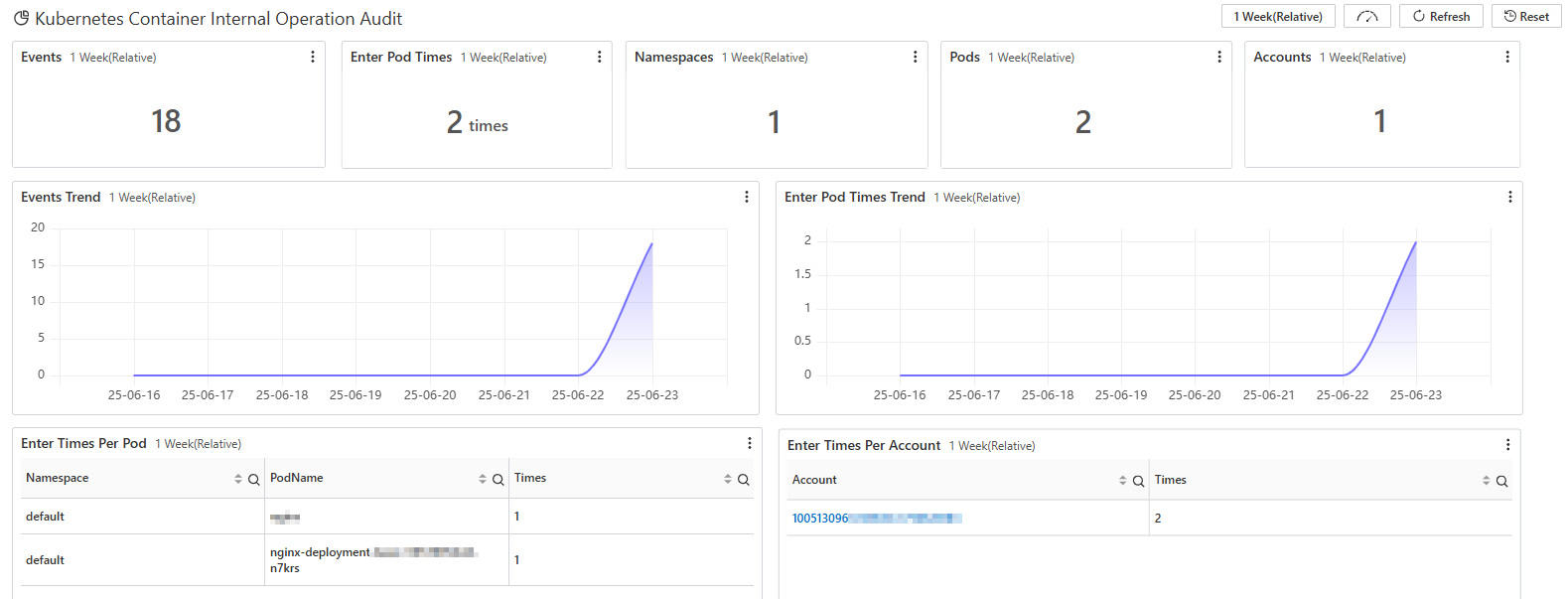
View information about the Kubernetes accounts that performed operations, a list of commands that were run after containers were accessed, and a list of common important threats.
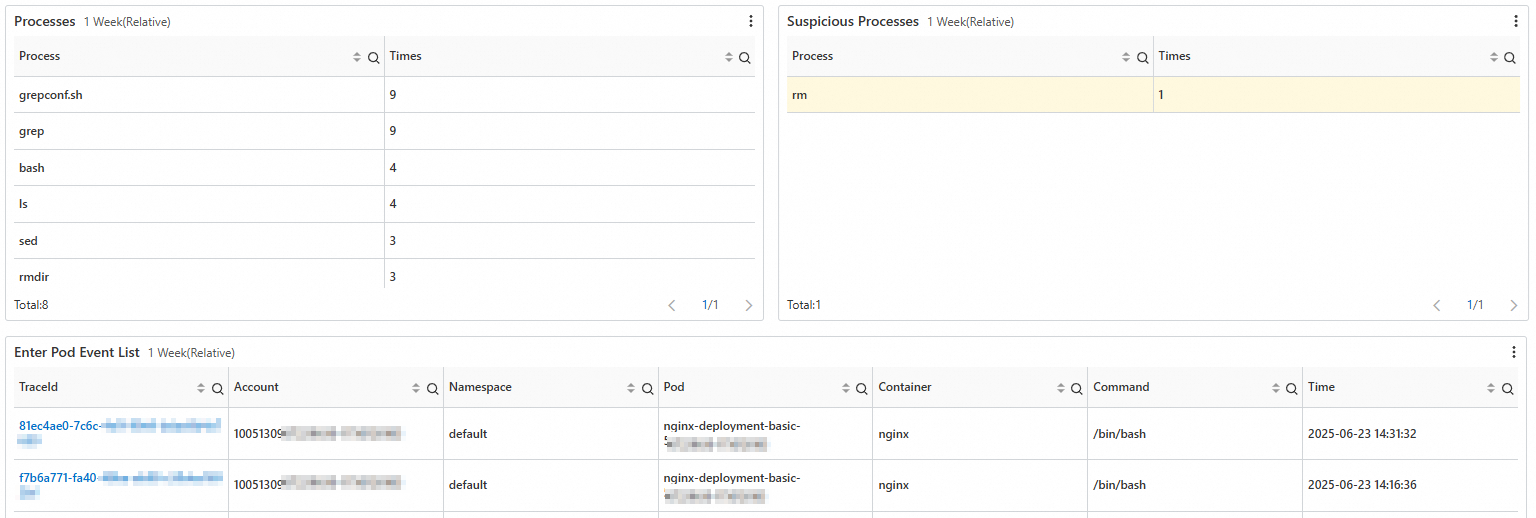
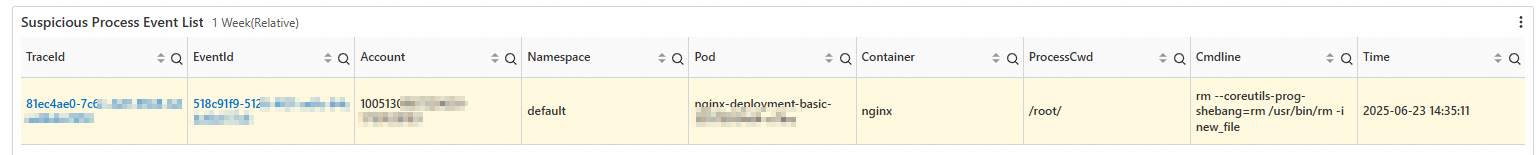
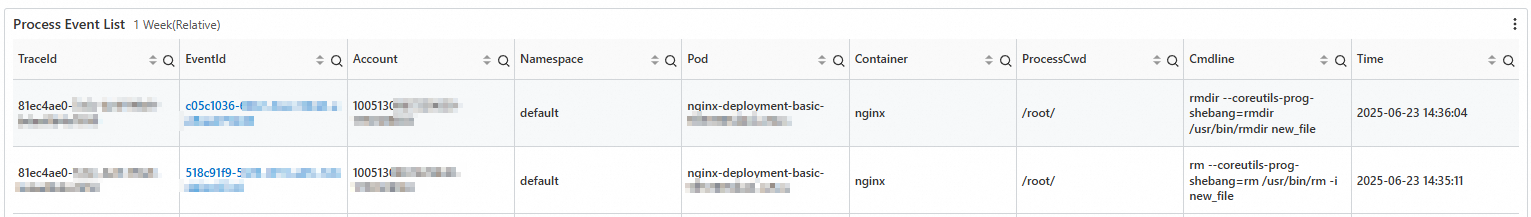
Step 3: View detailed log records
You can view detailed log records in one of the following two ways.
On the audit report page: This method is suitable for viewing log records of recent individual events.
On the Logstore page using search statements: This method is suitable for complex scenarios where you need to view more historical information and events.
View on the audit report page
On the Container Audit Overview tab, click the links in the traceId and eventId columns of the Suspicious Process Event List section to view the details of the corresponding audit logs.
Click a link in the traceId column to view the audit logs of all commands that were run after a container was accessed.
Click a link in the eventId column to view the details of a single command that was run.
View on the Logstore page using search statements
On the Query Container Audit Logs tab, use search statements to view detailed audit log records.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Audit page, click the Container Audit tab and then click the Query Container Audit Logs tab.
In the search box, enter a query statement.
To query the audit logs of commands that were run after a pod was accessed, enter * and k8s.pod.namespace: <namespace> and k8s.pod.name: <pod_name>. Replace <namespace> with the namespace of the pod and <pod_name> with the name of the pod.
To query the audit logs of operations for a specific program, enter * and process.name: <name>. Replace <name> with the name of the program.
For more information about query and analysis methods, see Log search and analysis.
Set a time range for the query and click Search & Analyze to view the results.
(Optional) Step 4: Configure operation audit alerts
You can use the alerting feature of Simple Log Service to configure real-time alerts for intra-container operation audits. This lets you monitor key operational events within containers. Alerting methods include DingTalk robots, custom webhooks, and the Notification Center. For more information about other alert configurations, see Alerting.
Disable the intra-container operation audit feature
You can disable the intra-container operation audit feature by uninstalling the ack-advanced-audit component.
Disabling the intra-container operation audit feature does not delete the advaudit-${cluster_id} Logstore that is automatically created. You must log on to the Simple Log Service console to manually delete the Logstore. For more information, see Stop billing for or delete a Logstore.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the one you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, find the ack-advanced-audit component, click Uninstall in the lower-right corner of the component card, and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation.
References
For the release notes and description of ack-advanced-audit, see ack-advanced-audit.
The API Server audit log feature helps cluster administrators determine who performed which operation on which resource and at what time. For more information, see Use the cluster API Server audit feature.