Simple Log Service provides time functions, date functions, date and time extraction functions, time interval functions, and time series padding functions. These functions allow you to perform operations such as format conversion, grouping, and aggregation on date and time data in your logs. This topic describes the basic syntax for these date and time functions and provides usage examples.
Overview of date and time functions
Simple Log Service supports the following date and time functions.
Log timestamps in Simple Log Service are accurate to the second. Therefore, when you configure the time format (format), specify the format only down to the second. Milliseconds and microseconds are not required.
You need to configure the time format (format) only for the time part of a time string, not for other content such as the time zone.
Each log in Simple Log Service contains the reserved
__time__field. The value of this field is a UNIX timestamp. For example, 1592374067 represents 2020-06-17 14:07:47.In a Simple Log Service analytic statement, you must enclose strings in single quotation marks (''). Unquoted characters or characters enclosed in double quotation marks ("") are interpreted as field or column names. For example,
'status'represents the string status, andstatusor"status"represents the log field status.
Function type | Function name | Syntax | Description | SQL support | SPL support |
Date and time functions | current_date | Returns the current date. | √ | × | |
current_time | Returns the current time and time zone. | √ | × | ||
current_timestamp | Returns the current date, time, and time zone. | √ | × | ||
current_timezone() | Returns the current time zone. | √ | × | ||
date(x) | Returns the date part of a datetime expression. | √ | × | ||
date_format(x, format) | Converts a timestamp datetime expression to a specified format. | √ | √ | ||
date_parse(x, format) | Converts a date and time string to a timestamp datetime expression in a specified format. | √ | √ | ||
from_iso8601_date(x) | Converts an ISO 8601 date expression to a date type expression. | √ | × | ||
from_iso8601_timestamp(x) | Converts an ISO 8601 datetime expression to a timestamp type expression. | √ | × | ||
from_unixtime(x) | Converts a UNIX timestamp to a timestamp datetime expression without a time zone. | √ | √ | ||
from_unixtime(x, time zone) | Converts a UNIX timestamp to a timestamp datetime expression with a time zone. | √ | × | ||
from_unixtime(x, hours, minutes) | Converts a UNIX timestamp to a timestamp datetime expression with a time zone, where hours and minutes are the time zone offset. | √ | × | ||
localtime | Returns the local time. | √ | × | ||
localtimestamp | Returns the local date and time. | √ | × | ||
now() | Returns the current date and time. The now function is equivalent to the current_timestamp function. | √ | × | ||
to_iso8601(x) | Converts a date or timestamp datetime expression to the ISO 8601 format. | √ | × | ||
to_unixtime(x) | Converts a timestamp datetime expression to a UNIX timestamp. | √ | √ | ||
current_unixtimestamp() | Returns the current Unix timestamp of the system. | × | √ | ||
Date and time extraction functions | day(x) | Extracts the day of the month from a datetime expression. The day function is equivalent to the day_of_month function. | √ | × | |
day_of_month(x) | Extracts the day of the month from a datetime expression. The day_of_month function is equivalent to the day function. | √ | × | ||
day_of_week(x) | Returns the day of the week from a datetime expression. The day_of_week function is equivalent to the dow function. | √ | √ | ||
day_of_year(x) | Extracts the day of the year from a datetime expression. The day_of_year function is equivalent to the doy function. | √ | √ | ||
dow(x) | Returns the day of the week from a datetime expression. The dow function is equivalent to the day_of_week function. | √ | √ | ||
doy(x) | Extracts the day of the year from a datetime expression. The doy function is equivalent to the day_of_year function. | √ | √ | ||
extract(field from x) | Uses the specified field to fetch a date or time part from a datetime expression. | √ | × | ||
hour(x) | Extracts the hour of the day (0-23) from a datetime expression. | √ | √ | ||
minute(x) | Extracts the minute of the hour from a datetime expression. | √ | √ | ||
month(x) | Extracts the month of the year from a datetime expression. | √ | √ | ||
quarter(x) | Returns the quarter of the year for a specified date. | √ | √ | ||
second(x) | Extracts the second of the minute from a datetime expression. | √ | √ | ||
timezone_hour(x) | Provides the time zone offset in hours. | √ | × | ||
timezone_minute(x) | Calculates the time zone offset in minutes. | √ | × | ||
week(x) | Returns the week of the year for a specified date. The week function is equivalent to the week_of_year function. | √ | × | ||
week_of_year(x) | Returns the week of the year for a specified date. The week_of_year function is equivalent to the week function. | √ | × | ||
year(x) | Extracts the year from a specified date. | √ | √ | ||
year_of_week(x) | Returns the year of the ISO week for a specified date. The year_of_week function is equivalent to the yow function. | √ | √ | ||
yow(x) | Returns the year of the ISO week for a specified date. The yow function is equivalent to the year_of_week function. | √ | √ | ||
Time interval functions | date_trunc(unit, x) | Truncates a datetime expression to a specified time unit, such as millisecond, second, minute, hour, day, month, or year. | √ | × | |
date_add(unit, N, x) | Adds N time units to x. | √ | √ | ||
date_diff(unit, x, y) | Returns the difference between two time expressions, x and y, in the specified time unit. | √ | √ | ||
Time series padding function | time_series(x, window, format, padding_data) | Pads missing data within the query time window. | √ | × |
Date and time functions
current_date function
The current_date function returns the current date in YYYY-MM-DD format.
Syntax
current_dateReturn value type
Data type.
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(current_date) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, current_date))Query and analysis results
current_time function
The current_time function returns the current time and time zone in HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone format.
Syntax
current_timeReturn value type
Specifies the time data type.
Example
Query the current time and time zone.
Query statement (Debug)
* | select current_timeQuery and analysis results
current_timestamp function
The current_timestamp function returns the current date, time, and time zone in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone format.
Syntax
current_timestampReturn value type
timestamp
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(current_timestamp) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, current_timestamp))Query and analysis results

current_timezone function
The current_timezone function returns the current time zone.
Syntax
current_timezone()Return value type
varchar
Example
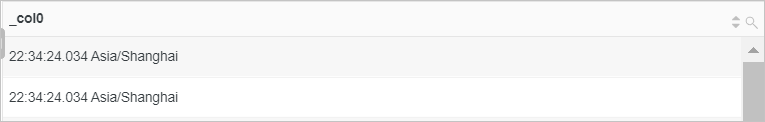
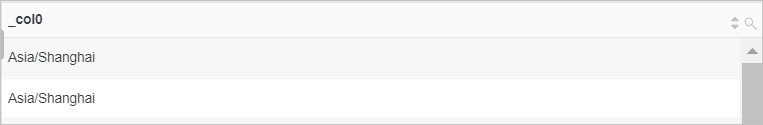
Query the current time zone.
Query statement (Debug)
* | select current_timezone()Query and analysis results
date function
The date function extracts the date part from a datetime expression. The date function is equivalent to cast(x as date). For more information, see Type conversion functions.
Syntax
date(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
The data type is Date.
Example
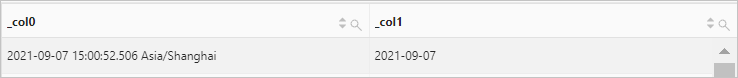
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the date function to extract the date part.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, date(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
date_format function
The date_format function converts a timestamp datetime expression to a specified format.
Syntax
date_format(x, format)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | A timestamp datetime expression. |
format | The conversion format of the datetime expression. For more information, see Format specifications. |
Return value type
The varchar data type.
Example
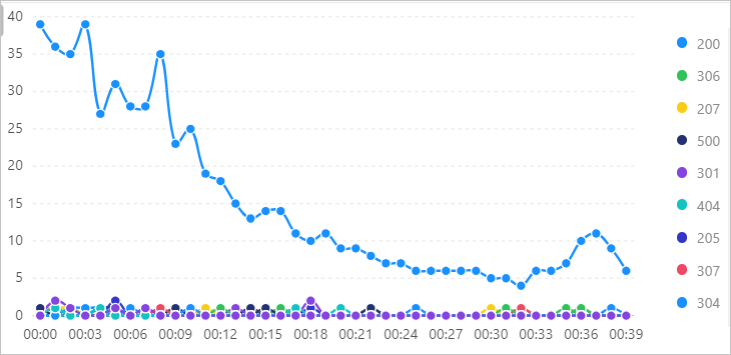
Calculate the number of NGINX requests for each request status and display the results in chronological order. First, use the date_trunc function to align log times to the minute. Then, use the date_format function to convert the time to the %H:%i format. Finally, calculate the number of requests for each status code per minute and display the query and analysis results in a flow chart.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT date_format(date_trunc('minute', __time__), '%H:%i') AS time, COUNT(1) AS count, status GROUP BY time, status ORDER BY timeQuery and analysis results
date_parse function
The date_parse function converts a date and time string to a timestamp datetime expression in a specified format.
Syntax
date_parse(x, format)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | A date and time string. |
format | The conversion format of the datetime expression. For more information, see Format specifications. |
Return value type
The type of the timestamp.
Example
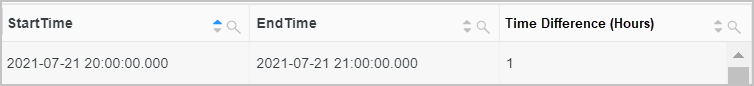
Convert the values of the StartTime and EndTime fields to the timestamp data type and calculate the time difference between them.
Query statement
*| SELECT date_parse(StartTime, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i') AS "StartTime", date_parse(EndTime, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i') AS "EndTime", date_diff('hour', StartTime, EndTime) AS "Time difference (hours)"Query and analysis results
from_iso8601_date function
The from_iso8601_date function converts an ISO 8601 date expression to a date data type in YYYY-MM-DD format.
Syntax
from_iso8601_date(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | An ISO 8601 date expression. |
Return value type
Date data type.
Example
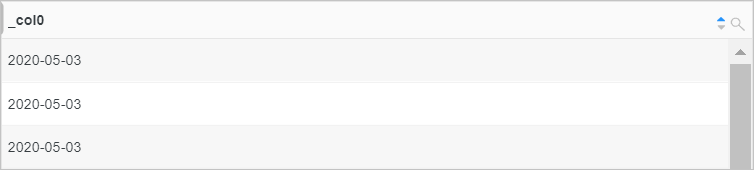
Convert the value of the time field to a date data type.
Sample field
time:2020-05-03Query statement
* | select from_iso8601_date(time)Query and analysis results
from_iso8601_timestamp function
The from_iso8601_timestamp function converts an ISO 8601 datetime expression to a timestamp data type in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone format.
Syntax
from_iso8601_timestamp(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | An ISO 8601 datetime expression. |
Return value type
Timestamp data type.
Example
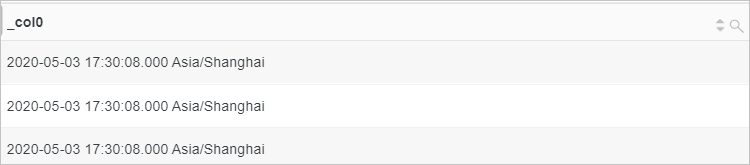
Convert the value of the time field to a timestamp data type.
Sample field
time:2020-05-03T17:30:08Query statements
* | select from_iso8601_timestamp(time)Query and analysis results
from_unixtime function
The from_unixtime function converts a UNIX timestamp to a timestamp. The format is YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms or YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone.
Syntax
Returns a timestamp without a time zone from a datetime expression.
from_unixtime(x)Convert a datetime expression to a timestamp with a time zone
from_unixtime(x,time zone)Converts a value to a `timestamp with time zone` datetime expression, where hours and minutes specify the time zone offset.
from_unixtime(x, hours, minutes)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The parameter value is a UNIX timestamp. |
time zone | The time zone. For example, Asia/shanghai. |
hours | The hour of the time zone offset. For example, +07 or -09. |
minutes | The minute of the time zone offset. For example, +30 or -45. |
Return value type
timestamp
Example
Convert the value of the time field to a timestamp with a time zone.
Sample field
time:1626774758Query statement
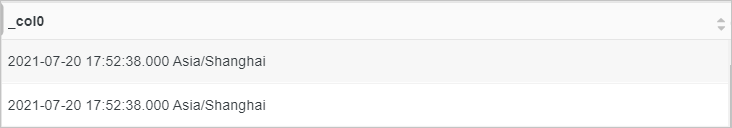
* | select from_unixtime(time,'Asia/shanghai')Query and analysis results
localtime function
The localtime function returns the local time in HH:MM:SS.Ms format.
Syntax
localtimeReturn value type
Time Type
Example
Query the local time.
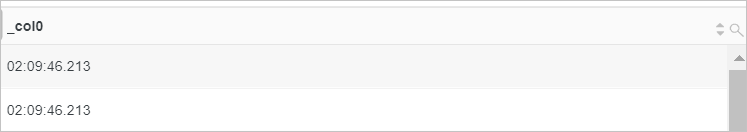
Query statement (Debug)
* | select localtimeQuery and analysis results
localtimestamp function
The localtimestamp function returns the local date and time in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone format.
Syntax
localtimestampReturn value type
Timestamp data type.
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(localtimestamp) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, localtimestamp))Query and analysis results

now function
The now function returns the current date and time in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.Ms Time_zone format. The now function is equivalent to the current_timestamp function.
Syntax
now()Return value type
This is the timestamp data type.
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(now()) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, now()))Query and analysis results

to_iso8601 function
The to_iso8601 function converts a date or timestamp datetime expression to the ISO 8601 format.
Syntax
to_iso8601(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
varchar
Example
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the to_iso8601 function to convert the current datetime expression to the ISO 8601 format.
Query statement (Debug)
* | select to_iso8601(current_timestamp) AS ISO8601Query and analysis results

to_unixtime function
The to_unixtime function converts a timestamp datetime expression to a UNIX timestamp.
Syntax
to_unixtime(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | A timestamp datetime expression. |
Return value type
double
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(now()) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, now()))Query and analysis results

current_unixtimestamp function
This function returns the current Unix timestamp. A Unix timestamp is the total number of seconds that have elapsed since 00:00:00 Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on January 1, 1970.
Syntax
current_unixtimestamp()Return value
Return value type:
BIGINT(long)Description: Returns an integer that represents the current number of seconds.
Precision: The value is accurate to the second by default.
Examples
Example 1: Retrieve the current timestamp.
A common use case is to record the time when data is inserted.
* | extend now_ts =current_unixtimestamp() -- Sample output: 1734913028Example 2: Format conversion
This function is often used with
from_unixtimeto convert a numeric timestamp to a human-readable date format.* | extend readable_time = date_format(from_unixtime(cast(current_unixtimestamp() as double)), '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s') -- Sample output: 2025-12-23 00:17:08
Date and time extraction functions
day function
The day function extracts the day of the month from a datetime expression. The day function is equivalent to the day_of_month function.
Syntax
day(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the day function to extract the day of the month from the current date.
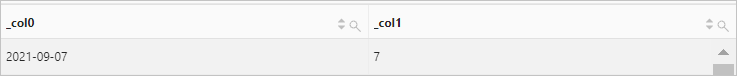
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, day(current_date)Query and analysis results
day_of_month function
The day_of_month function extracts the day of the month from a datetime expression. The day_of_month function is equivalent to the day function.
Syntax
day_of_month(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the day_of_month function to extract the day of the month from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, day_of_month(current_date)Query and analysis results

day_of_week function
The day_of_week function extracts the day of the week from a datetime expression.
Syntax
day_of_week(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the day_of_week function to extract the day of the week from the current date.
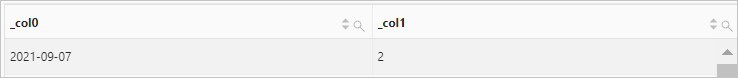
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, day_of_week(current_date)Query and analysis results
day_of_year function
The day_of_year function extracts the day of the year from a datetime expression.
Syntax
day_of_year(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the day_of_year function to extract the day of the year from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, day_of_year(current_date)Query and analysis results

dow function
The dow function extracts the day of the week from a datetime expression. The dow function is equivalent to the day_of_week function.
Syntax
dow(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the dow function to extract the day of the week from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, dow(current_date)Query and analysis results

doy function
The doy function extracts the day of the year from a datetime expression. The doy function is equivalent to the day_of_year function.
Syntax
doy(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp or date type. |
Return value type
The bigint data type.
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the doy function to extract the day of the year from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_date, doy(current_date)Query and analysis results

extract function
The extract function extracts a date or time part from a datetime expression based on the specified field.
Syntax
extract(field from x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
field | Valid values: year, quarter, month, week, day, day_of_month, day_of_week, dow, day_of_year, doy, year_of_week, yow, hour, minute, second, timezone_hour, and timezone_minute. |
x | The value is of the date, time, timestamp, or interval (actual varchar(9)) type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_date function to retrieve the current date. Then, use the extract function to extract the year from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT extract(year from current_date)Query and analysis results

hour function
The hour function extracts the hour of the day (0-23) from a datetime expression.
Syntax
hour(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
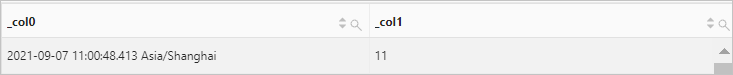
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the hour function to extract the hour from the current time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, hour(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
minute function
The minute function extracts the minute of the hour from a datetime expression.
Syntax
minute(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
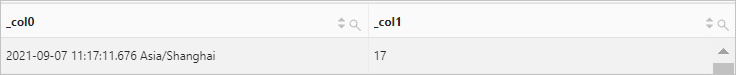
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the minute function to extract the minute from the current time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, minute(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
month function
The month function extracts the month of the year from a datetime expression.
Syntax
month(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
BIGINT data type.
Example
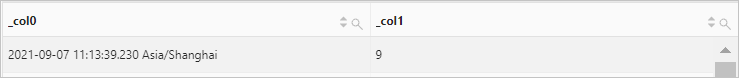
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the month function to extract the month from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, month(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
quarter function
The quarter function returns the quarter of the year for a specified date.
Syntax
quarter(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
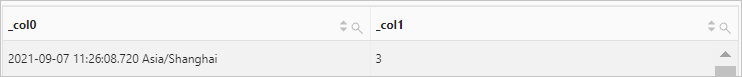
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the quarter function to calculate the quarter of the year to which the current date belongs.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp,quarter(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
second function
The second function extracts the second of the minute from a datetime expression.
Syntax
second(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the second function to extract the second from the current time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp,second(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
timezone_hour function
The timezone_hour function returns the hour of the time zone offset.
Syntax
timezone_hour(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
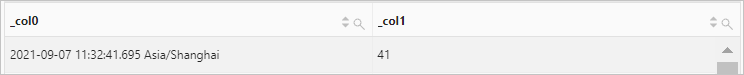
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the timezone_hour function to calculate the hour of the time zone offset for the current time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, timezone_hour(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
timezone_minute function
The timezone_minute function returns the minute of the time zone offset.
Syntax
timezone_minute(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
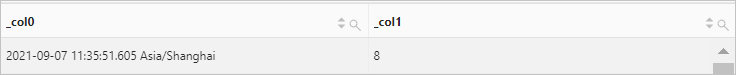
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the timezone_minute function to calculate the minute of the time zone offset for the current time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp,timezone_minute(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results

week function
The week function returns the week of the year for a specified date. The week function is equivalent to the week_of_year function.
Syntax
week(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the week function to calculate the week of the year to which the current date belongs.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, week(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
week_of_year function
The week_of_year function returns the week of the year for a specified date. The week_of_year function is equivalent to the week function.
Syntax
week_of_year(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
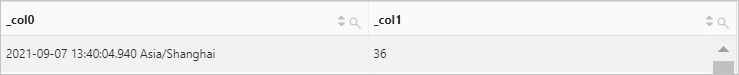
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the week_of_year function to calculate the week of the year to which the current date belongs.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, week_of_year(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results

year function
The year function extracts the year from a specified date.
Syntax
year(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the year function to extract the year from the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp,year(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results
year_of_week function
The year_of_week function returns the year of the ISO week for a specified date. The year_of_week function is equivalent to the yow function.
Syntax
year_of_week(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
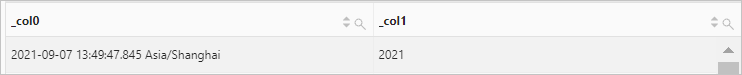
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the year_of_week function to return the year of the ISO week for the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp,year_of_week(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results

yow function
The yow function returns the year of the ISO week for a specified date. The yow function is equivalent to the year_of_week function.
Syntax
yow(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the date or timestamp type. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Use the current_timestamp function to retrieve the current date and time. Then, use the yow function to return the year of the ISO week for the current date.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT current_timestamp, yow(current_timestamp)Query and analysis results

Time interval functions
date_trunc function
The date_trunc function truncates a datetime expression to a specified time unit, such as millisecond, second, minute, hour, day, month, or year. This function is often used in scenarios that require time-based statistical analysis.
Syntax
date_trunc(unit, x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
unit | The time unit. Valid values: millisecond, second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, and year. For more information, see Unit specifications. |
x | A datetime expression. |
The date_trunc function can calculate statistics only based on fixed time intervals, such as per minute or per hour. To calculate statistics based on flexible time dimensions, you can use the modulo operation to group data. For example, you can calculate statistics for every 5 minutes.
* | SELECT count(1) AS pv, __time__ - __time__ %300 AS time GROUP BY time LIMIT 100Return value type
The data type must match that of the parameter value.
Example
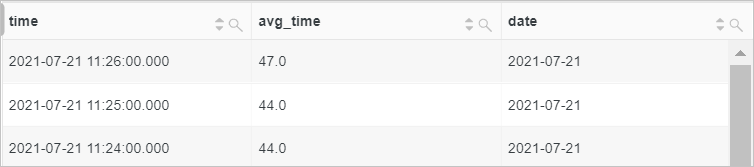
Calculate the average request time at a 1-minute granularity, and then group and sort the results by time.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT date_trunc('minute', __time__) AS time, truncate (avg(request_time)) AS avg_time, current_date AS date GROUP BY time ORDER BY time DESC LIMIT 100Query and analysis results
date_add function
The date_add function adds or subtracts a specified time interval from a date or time value.
Syntax
date_add(unit, n, x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
unit | The time unit. Valid values: millisecond, second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, and year. For more information, see Unit specifications. |
n | The time interval. |
x | A timestamp datetime expression. |
Return value type
timestamp
Example
Query the logs from the previous day.
Query statement (Debug)
* | SELECT * FROM log WHERE __time__ < to_unixtime(current_timestamp) AND __time__ > to_unixtime(date_add('day', -1, current_timestamp))Query and analysis results

date_diff function
The date_diff function calculates the difference between two dates or times.
Syntax
date_diff(unit, x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
unit | The time unit. Valid values: millisecond, second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, and year. For more information, see Unit specifications. |
x | A timestamp datetime expression. |
y | A timestamp datetime expression. |
Return value type
bigint
Example
Calculate the total runtime of a server based on the UsageStartTime and UsageEndTime fields.
Query statement
* | SELECT date_diff('hour', UsageStartTime, UsageEndTime) AS "Time difference (hours)"Query and analysis results

Time series padding function
time_series function
The time_series function pads missing data points within your query time window.
The time_series function must be used with the GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses. The ORDER BY clause does not support DESC sorting. If the time_series function is used in a subquery, the outer query cannot contain GROUP BY or ORDER BY clauses.
Syntax
time_series(x, window_time, format, padding_data)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The time column, for example, |
window_time | The size of the time window. Unit: s (second), m (minute), h (hour), or d (day). Examples: 2h, 5m, and 3d. |
format | The time format of the returned result. For more information, see Format specifications. |
padding_data | The content includes the following:
|
Return value type
varchar
Example
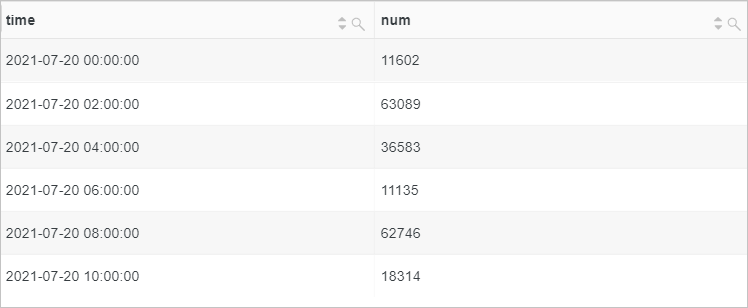
Pad data at a 2-hour granularity and set the missing values to 0.
Query statement (Debug)
* | select * from (select time_series(__time__, '2h', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s', '0') as time, count(*) as num from log group by time order by time) a limit 100Query and analysis results
Format specifications
Format | Description |
%a | The abbreviated name of the day of the week. For example, Sun or Sat. |
%b | The abbreviated name of the month. For example, Jan or Dec. |
%c | The month as a numeric value. Valid values: 1 to 12. |
%D | The day of the month with a suffix. For example, 0th, 1st, 2nd, or 3rd. |
%d | The day of the month in decimal format. Valid values: 01 to 31. |
%e | The day of the month in decimal format. Valid values: 1 to 31. |
%H | The hour in 24-hour format. |
%h | The hour in 12-hour format. |
%i | The minute as a numeric value. Valid values: 00 to 59. |
%j | The day of the year. Valid values: 001 to 366. |
%k | The hour. Valid values: 0 to 23. |
%l | The hour. Valid values: 1 to 12. |
%M | The full name of the month. For example, January or December. |
%m | The month as a numeric value. Valid values: 01 to 12. |
%p | AM or PM. |
%r | The time in 12-hour format. The format is |
%S | The second. Valid values: 00 to 59. |
%s | The second. Valid values: 00 to 59. |
%f | The microsecond. Valid values: 000000 to 999999. |
%T | The time in 24-hour format. The format is |
%v | The week of the year, where Monday is the first day of the week. Valid values: 01 to 53. |
%W | The full name of the day of the week. For example, Sunday or Saturday. |
%Y | The four-digit year. For example, 2020. |
%y | The two-digit year. For example, 20. |
%% | The escape character for the percent sign (%). |
Unit specifications
Unit | Description |
millisecond | Millisecond |
second | Second |
minute | Minute |
hour | Hour |
day | Day |
week | Week |
month | Month |
quarter | Quarter |
year | Year |