This topic describes how to stop or restart an instance using a Cloud Assistant command.
Prerequisites
The status of the instance must be Running.
The Cloud Assistant Agent is installed on the target instance. You can view the status of Cloud Assistant. If the agent is not installed, see Install Cloud Assistant Agent.
(Recommended) Use a special exit code to stop or restart an instance
When you execute a command in Cloud Assistant to stop or restart an instance, you must add an exit code to the end of the command. This ensures the accuracy and real-time status of the command execution. Otherwise, the Cloud Assistant Agent cannot report the execution result, and the command status may not be updated correctly.
Make sure that the Cloud Assistant Agent on the target instance is not an earlier version than the following:
Linux: 2.2.3.317
Windows: 2.2.3.317
If an error occurs when you run a command, you must update the Cloud Assistant Agent to the latest version. For more information, see Upgrade or disable automatic upgrades of Cloud Assistant Agent.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create/Run Command.
In the Command Information section, configure the parameters. For more information, see Create and run commands.
At the end of the Command content, set the corresponding exit code.
To stop an instance, specify one of the following exit codes.
Operating system
Exit code
Command example
Linux
193
# This Shell command returns exit code 193, which triggers an action to stop the instance. exit 193Windows
3009
# This PowerShell command returns exit code 3009, which triggers an action to stop the instance. exit 3009To restart an instance using a command, specify one of the following exit codes.
Operating system
Exit code
Command example
Linux
194
# This Shell command returns exit code 194, which triggers an action to restart the instance. exit 194Windows
3010
# This PowerShell command returns exit code 3010, which triggers an action to restart the instance. exit 3010
In the Select Instance or Select Managed Instances section, select the instances on which you want to run the command.
NoteA managed instance is an instance that is not provided by Alibaba Cloud but is managed by Cloud Assistant. For more information, see Alibaba Cloud managed instances.
Click Run and Save or Run to immediately run the command.
Use OpenAPI to run a Cloud Assistant command to restart instances in batches
Alibaba Cloud provides a rich set of OpenAPI operations for you to manage cloud resources. This section provides an example of how to run Python code in a local Linux environment to call OpenAPI operations. The example shows how to execute a command and restart instances in batches.
Prepare the information required to execute the command.
Obtain the
AccessKeypair of the Resource Access Management (RAM) user that you want to use. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.Call the
DescribeRegionsoperation to retrieve the list of regions. For a detailed description of the parameters, see DescribeRegions.Call the
DescribeInstancesoperation to filter instances that meet specified conditions. For descriptions of the parameters in the DescribeInstances operation, see DescribeInstances.
Configure the local environment and run the sample code.
Install and upgrade the Alibaba Cloud SDK for Python.
sudo pip install --upgrade alibabacloud_ecs20140526Create a
.pyfile and write the following sample code to the file.Click to view the sample code
Replace the following information in the sample code with the information that you obtained:
AccessKey ID:
access_key = os.environ['ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID']AccessKey secret:
access_key_secret = os.environ['ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']Region ID:
region_id = '<yourRegionId>'Instance IDs:
ins_ids= ["i-bp185fcs****","i-bp14wwh****","i-bp13jbr****"]
Run the
.pyfile.The following figure shows the result: a command is executed on three instances to output
helloworld, and then the instances are automatically restarted.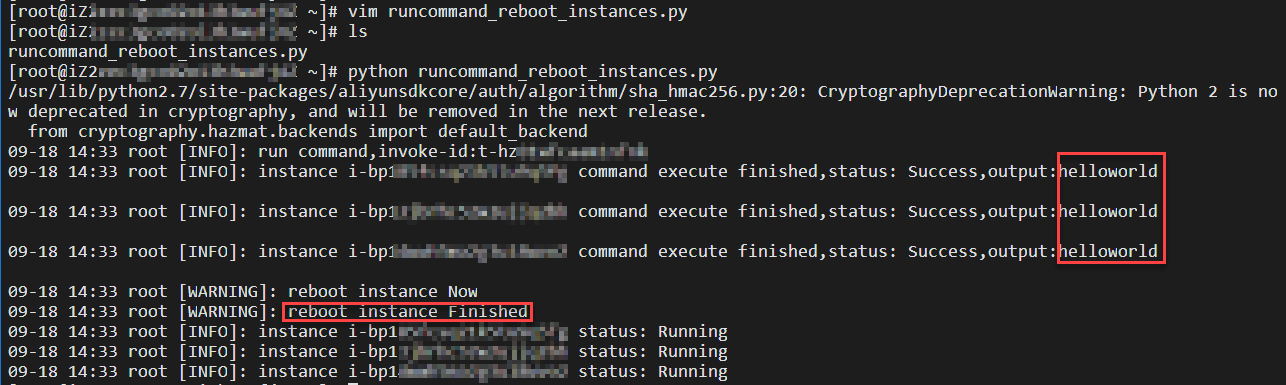
Use OOS to run a Cloud Assistant command to restart instances in batches
CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) is an automated O&M service from Alibaba Cloud. You can define O&M actions in templates and then execute the templates to run automated O&M tasks.
Go to the template configuration page.
Log on to the OOS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, click .
Click Create Template.
Complete the template configuration.
On the Create Template page, keep the default configurations and click Next Step.
Click the YAML tab and enter the following code.
Click to view the sample code
Click Create Template.
In the dialog box that appears, enter the template name
runcommand_reboot_instancesand click OK.
Execute the template.
Find the template that you just created and click Create Execution in the Actions column.
Complete the execution configuration.
Follow the prompts to complete the configuration. On the Parameter Settings page, select multiple instances and keep the default values for the other settings.
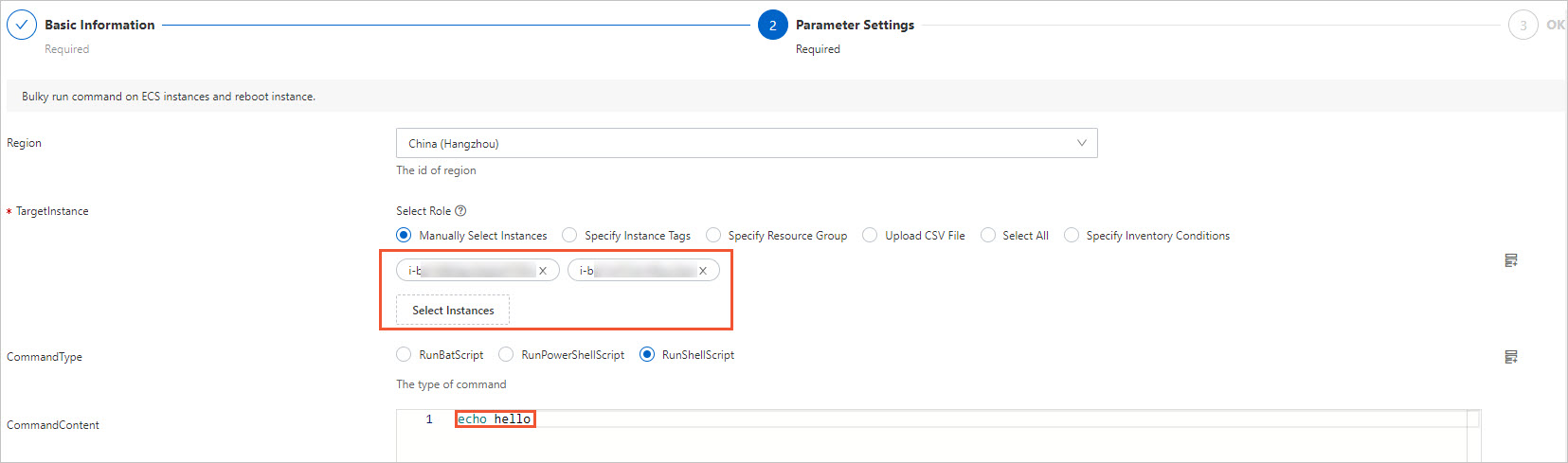
On the OK page, click Create.
After the execution is created, the template starts to execute automatically. You are redirected to the Basic Information page of the execution. Wait until the Execution Status changes to Successful.
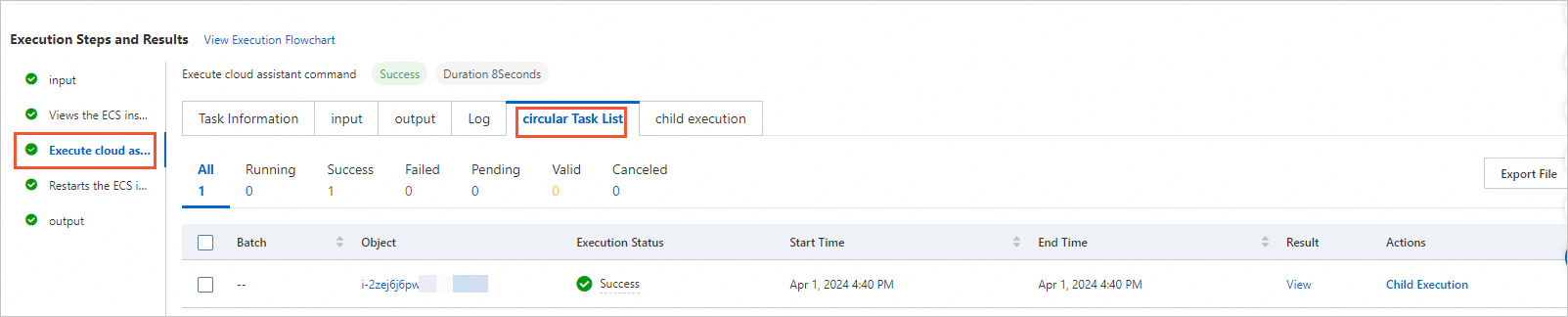
View the task execution process and the details of each task node.
In the Execution Steps And Results section, click View Execution Flowchart to view the execution process.
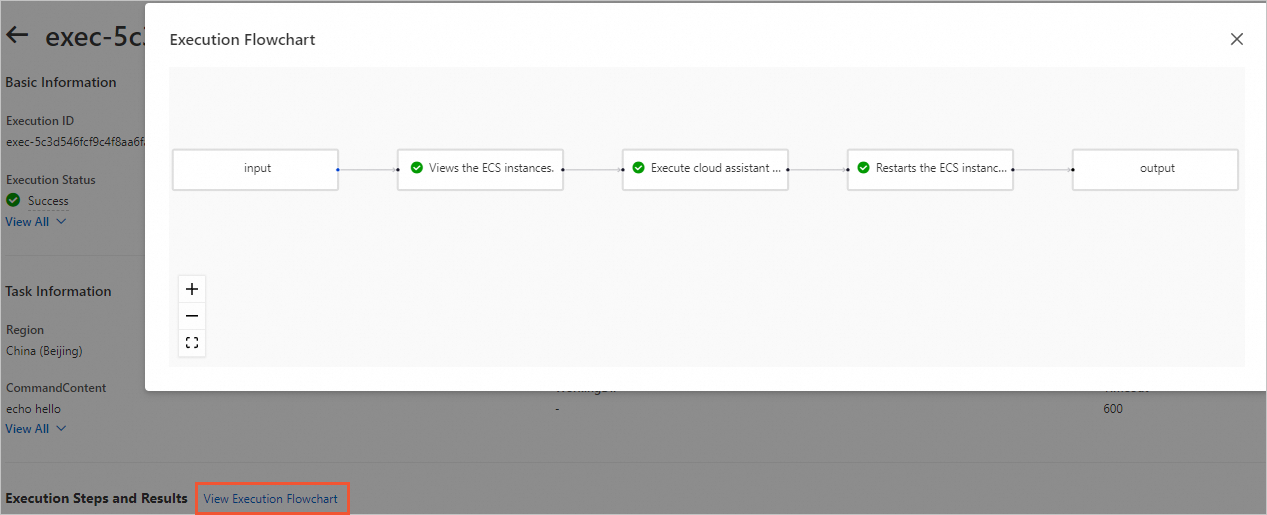
Click the Cloud Assistant command execution step. On the loop task list tab, view the execution details of each task node. The following figure shows that the scheduled actions are completed successfully.