After integrating with ARMS Application Monitoring, the ARMS agent automatically instruments common Go components without requiring any code modifications to collect trace information. For applications using github.com/gorilla/websocket, ARMS does not provide instrumentation by default. To include the execution of business methods in your trace information, you can import the OpenTelemetry Go SDK and add custom instrumentation to your business code.
Prerequisites
You have installed the Golang agent for your application.
You have enabled the opentelemetry-plugin switch.
Step 1: Client instrumentation
Place the Span creation information in the body to pass it to the server.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"flag"
"fmt"
"github.com/gorilla/websocket"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/attribute"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/propagation"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
tracex "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/trace"
"log"
"net/url"
"os"
"os/signal"
"time"
)
func init() {
tp := trace.NewTracerProvider(trace.WithSampler(trace.AlwaysSample()))
otel.SetTracerProvider(tp)
prop := propagation.TraceContext{}
otel.SetTextMapPropagator(prop)
}
var addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:8080", "http service address")
func main() {
flag.Parse()
log.SetFlags(0)
interrupt := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(interrupt, os.Interrupt)
u := url.URL{Scheme: "ws", Host: *addr, Path: "/echo"}
log.Printf("connecting to %s", u.String())
c, _, err := websocket.DefaultDialer.Dial(u.String(), nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dial:", err)
}
defer c.Close()
done := make(chan struct{})
go func() {
defer close(done)
for {
_, message, err := c.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Println("read:", err)
return
}
log.Printf("recv: %s", message)
}
}()
ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-done:
return
case t := <-ticker.C:
tracer := otel.GetTracerProvider().Tracer("")
opts := append([]tracex.SpanStartOption{}, tracex.WithSpanKind(tracex.SpanKindClient))
//Write the trace information of the created span into the body to pass to the server, this is just a demo, you can adjust according to your code situation
ctx, span := tracer.Start(context.Background(), "Client/User defined span", opts...)
defer span.End()
var headerMap propagation.MapCarrier
headerMap = make(map[string]string)
otel.GetTextMapPropagator().Inject(ctx, headerMap)
xx, _ := json.Marshal(headerMap)
y := t.String() + "|" + string(xx)
err := c.WriteMessage(websocket.TextMessage, []byte(y))
if err != nil {
log.Println("write:", err)
return
}
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("client", "client-with-ot"))
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Bool("user.defined", true))
case <-interrupt:
log.Println("interrupt")
// Cleanly close the connection by sending a close message and then
// waiting (with timeout) for the server to close the connection.
err := c.WriteMessage(websocket.CloseMessage, websocket.FormatCloseMessage(websocket.CloseNormalClosure, ""))
if err != nil {
log.Println("write close:", err)
return
}
select {
case <-done:
case <-time.After(time.Second):
}
return
}
}
}
Step 2: Server instrumentation
Parse the Trace information received from the client, restore it, and create a server Span.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"flag"
"fmt"
"github.com/gorilla/websocket"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/propagation"
tracex "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/trace"
"html/template"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
var addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:8080", "http service address")
var upgrader = websocket.Upgrader{} // use default options
func init() {
tp := tracex.NewTracerProvider()
otel.SetTracerProvider(tp)
prop := propagation.TraceContext{}
otel.SetTextMapPropagator(prop)
}
func echo(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
c, err := upgrader.Upgrade(w, r, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Print("upgrade:", err)
return
}
defer c.Close()
for {
mt, message, err := c.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Println("read:", err)
break
}
log.Printf("recv: %s", message)
var headerMap propagation.MapCarrier
headerMap = make(map[string]string)
ctxRequest := context.Background()
xx := strings.Split(string(message), "|")
//header := make(map[string]string)
err = json.Unmarshal([]byte(xx[1]), &headerMap)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
xxCtx := otel.GetTextMapPropagator().Extract(ctxRequest, headerMap)
tracer := otel.GetTracerProvider().Tracer("")
opts := append([]trace.SpanStartOption{}, trace.WithSpanKind(trace.SpanKindServer))
_, span := tracer.Start(xxCtx, "Server/User defined span", opts...)
err = c.WriteMessage(mt, message)
if err != nil {
log.Println("write:", err)
break
}
fmt.Println(span.SpanContext().TraceID())
span.End()
}
}
func home(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
homeTemplate.Execute(w, "ws://"+r.Host+"/echo")
}
func main() {
flag.Parse()
log.SetFlags(0)
http.HandleFunc("/echo", echo)
http.HandleFunc("/", home)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil))
}
var homeTemplate = template.Must(template.New("").Parse(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script>
window.addEventListener("load", function(evt) {
var output = document.getElementById("output");
var input = document.getElementById("input");
var ws;
var print = function(message) {
var d = document.createElement("div");
d.textContent = message;
output.appendChild(d);
output.scroll(0, output.scrollHeight);
};
document.getElementById("open").onclick = function(evt) {
if (ws) {
return false;
}
ws = new WebSocket("{{.}}");
ws.onopen = function(evt) {
print("OPEN");
}
ws.onclose = function(evt) {
print("CLOSE");
ws = null;
}
ws.onmessage = function(evt) {
print("RESPONSE: " + evt.data);
}
ws.onerror = function(evt) {
print("ERROR: " + evt.data);
}
return false;
};
document.getElementById("send").onclick = function(evt) {
if (!ws) {
return false;
}
print("SEND: " + input.value);
ws.send(input.value);
return false;
};
document.getElementById("close").onclick = function(evt) {
if (!ws) {
return false;
}
ws.close();
return false;
};
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr><td valign="top" width="50%">
<p>Click "Open" to create a connection to the server,
"Send" to send a message to the server and "Close" to close the connection.
You can change the message and send multiple times.
<p>
<form>
<button id="open">Open</button>
<button id="close">Close</button>
<p><input id="input" type="text" value="Hello world!">
<button id="send">Send</button>
</form>
</td><td valign="top" width="50%">
<div id="output" style="max-height: 70vh;overflow-y: scroll;"></div>
</td></tr></table>
</body>
</html>
`))
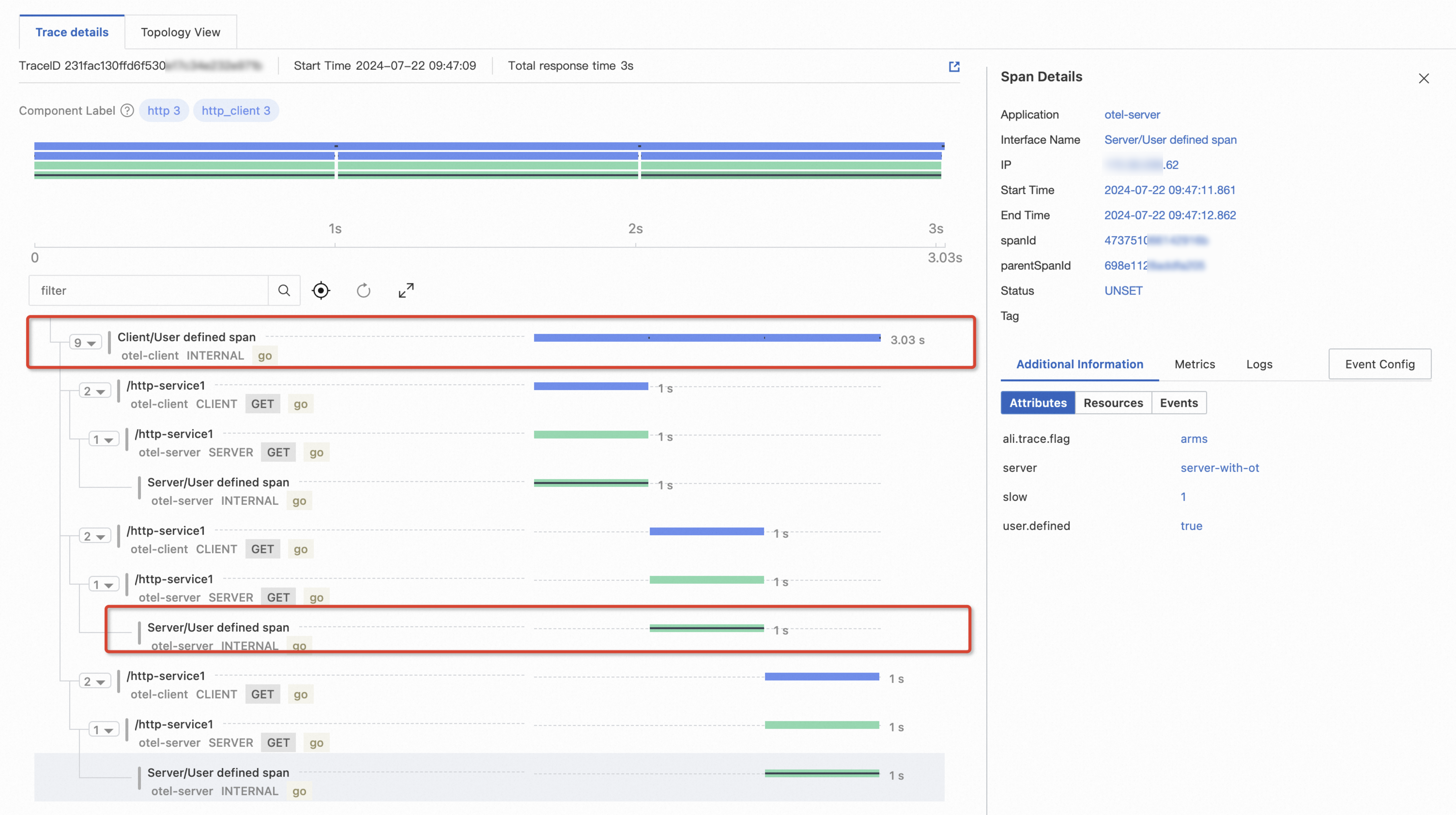
Step 3: Query the trace
On the page of the ARMS console, click the application name, and then click the Traces tab to view the details of the custom instrumentation trace. For more information, see Trace query.