With the Gateway with Inference Extension component, after you deploy generative AI inference services by using the OpenAI API format, you can specify request routing policies based on the model name in the request, including canary releases based on traffic splitting, traffic mirroring, and traffic circuit breaking. This topic describes how to implement inference service routing based on model names by using Gateway with Inference Extension.
Before reading this topic, make sure you understand the concepts of InferencePool and InferenceModel.
The content of this topic depends on Gateway with Inference Extension 1.4.0 or later.
Background information
OpenAI-compatible APIs
OpenAI-compatible APIs refer to a type of generative large language model (LLM) inference service APIs that are highly compatible with the official OpenAI API (such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) in terms of interface, parameters, and response format. The compatibility is reflected in the following aspects:
Interface structure: Uses the same HTTP request methods (such as POST), endpoint formats, and authentication methods (such as API keys).
Parameter support: Supports parameters similar to the OpenAI API, such as model, prompt, temperature, and max_tokens.
Response format: Returns the same JSON structure as OpenAI, including fields such as choices, usage, and id.
Currently, mainstream third-party LLM services and mainstream LLM inference engines, such as vLLM and SGLang, provide OpenAI-compatible APIs to ensure consistency in user migration and experience.
Scenarios
For generative AI inference services, the model name requested by users is important metadata in the request. Specifying routing policies based on the model name in the request is a common scenario when exposing inference services through a gateway. However, for LLM inference services that provide OpenAI-compatible APIs, the model name information is located in the request body, and ordinary routing policies do not support routing based on the request body.
Gateway with Inference Extension supports specifying routing policies based on model names under OpenAI-compatible APIs. By parsing and extracting the model name from the request body and attaching it to the request header, Gateway with Inference Extension provides the out-of-the-box model name-based routing feature. To use this feature, you only need to match the X-Gateway-Model-Name request header in the HTTPRoute resource to implement model name-based routing capabilities without requiring client modifications.
This example demonstrates how to route the Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B inference services on the same gateway instance based on the model name in the request. When a request for the Qwen model is made, route the request to the Qwen inference service. When a request for the DeepSeek-R1 model is made, route the request to the DeepSeek-R1 service. The following is the main flow of routing:
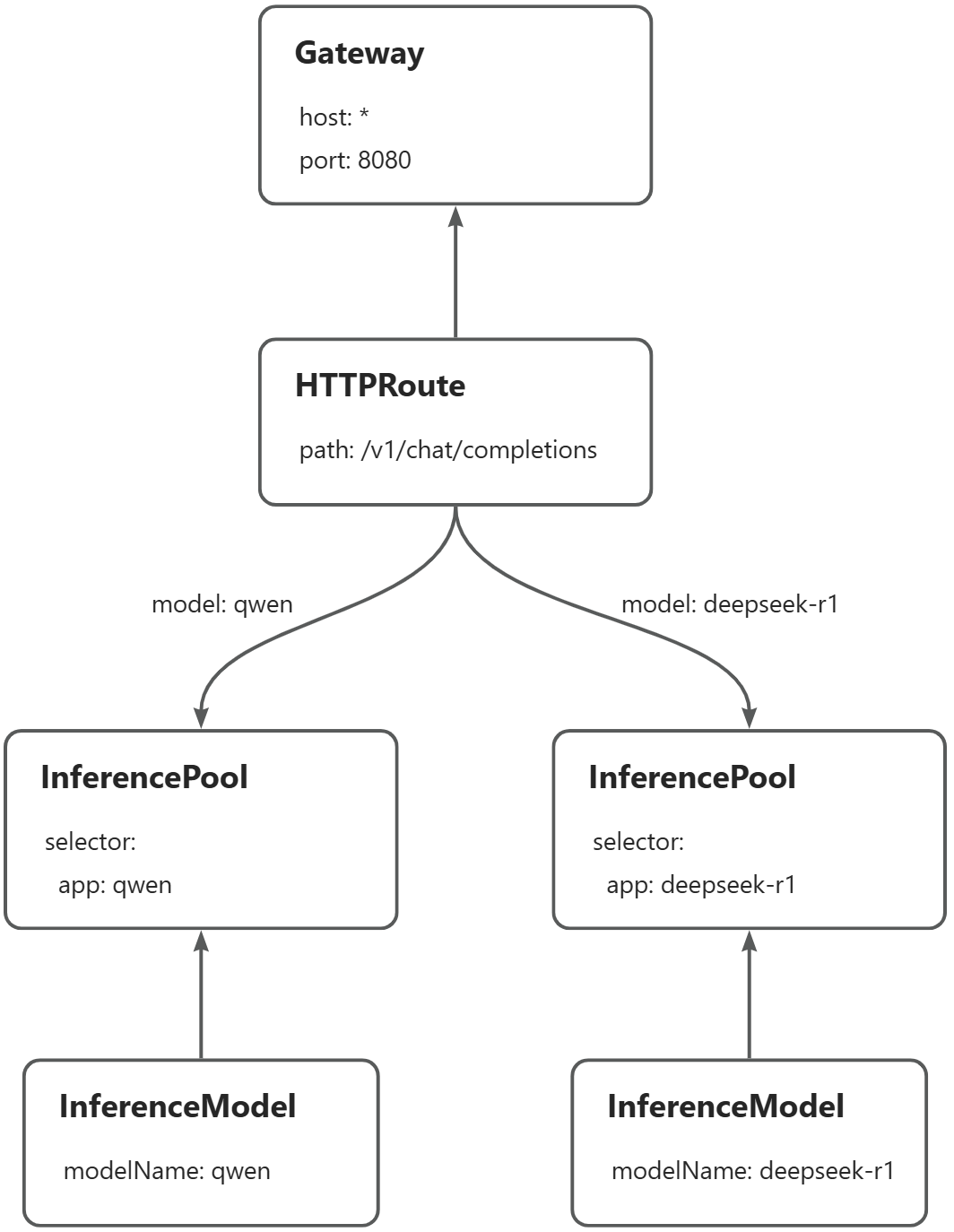
Prerequisites
An ACK managed cluster with GPU node pools is created. You can also install the ACK Virtual Node component in the ACK managed cluster to use ACS GPU computing power.
Gateway with Inference Extension 1.4.0 is installed and Enable Gateway API Inference Extension is selected. For more information about the operation entry, see Step 2: Install the Gateway with Inference Extension component.
For the image used in this topic, we recommend that you use A10 cards for ACK clusters and GN8IS (8th-gen GPU B) cards for Alibaba Cloud Container Compute Service (ACS) GPU computing power.
Due to the large size of the LLM image, we recommend that you transfer it to Container Registry in advance and pull it using the internal network address. The speed of pulling from the public network depends on the bandwidth configuration of the cluster elastic IP address (EIP), which may result in longer wait times.
Procedure
Step 1: Deploy a sample inference service
Create vllm-service.yaml.
Deploy the sample inference service.
kubectl apply -f vllm-service.yaml
Step 2: Deploy inference routing
In this step, you create InferencePool resources and InferenceModel resources.
Create inference-pool.yaml.
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferencePool metadata: name: qwen-pool namespace: default spec: extensionRef: group: "" kind: Service name: qwen-ext-proc selector: app: qwen targetPortNumber: 8000 --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: qwen spec: criticality: Critical modelName: qwen poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: qwen-pool targetModels: - name: qwen weight: 100 --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferencePool metadata: name: deepseek-pool namespace: default spec: extensionRef: group: "" kind: Service name: deepseek-ext-proc selector: app: deepseek-r1 targetPortNumber: 8000 --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: deepseek-r1 spec: criticality: Critical modelName: deepseek-r1 poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: deepseek-pool targetModels: - name: deepseek-r1 weight: 100Deploy the inference routing.
kubectl apply -f inference-pool.yaml
Step 3: Deploy gateway and gateway routing rules
Create inference-gateway.yaml.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: GatewayClass metadata: name: inference-gateway spec: controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: inference-gateway spec: gatewayClassName: inference-gateway listeners: - name: llm-gw protocol: HTTP port: 8080 --- apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1 kind: ClientTrafficPolicy metadata: name: client-buffer-limit spec: connection: bufferLimit: 20Mi targetRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway --- apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1 kind: BackendTrafficPolicy metadata: name: backend-timeout spec: timeout: http: requestTimeout: 24h targetRef: group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gatewayCreate inference-route.yaml
In the routing rules specified in
HTTPRoute, the model name in the request body is automatically parsed into theX-Gateway-Model-Namerequest header.apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: inference-route spec: parentRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway sectionName: llm-gw rules: - backendRefs: - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: qwen-pool weight: 1 matches: - headers: - type: Exact name: X-Gateway-Model-Name value: qwen - backendRefs: - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: deepseek-pool weight: 1 matches: - headers: - type: Exact name: X-Gateway-Model-Name value: deepseek-r1Deploy the gateway and gateway rules.
kubectl apply -f inference-gateway.yaml kubectl apply -f inference-route.yaml
Step 4: Verify the effect
Obtain the gateway IP address.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get gateway/inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')Request the qwen model.
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "qwen", "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "who are you?" } ] }'Expected output:
{"id":"chatcmpl-475bc88d-b71d-453f-8f8e-0601338e11a9","object":"chat.completion","created":1748311216,"model":"qwen","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"I am Qwen, a large language model created by Alibaba Cloud. I am here to assist you with any questions or conversations you might have! How can I help you today?","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":33,"total_tokens":70,"completion_tokens":37,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}Request the deepseek-r1 model.
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "deepseek-r1", "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "who are you?" } ] }'Expected output:
{"id":"chatcmpl-9a143fc5-8826-46bc-96aa-c677d130aef9","object":"chat.completion","created":1748312185,"model":"deepseek-r1","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"Alright, someone just asked, \"who are you?\" Hmm, I need to explain who I am in a clear and friendly way. Let's see, I'm an AI created by DeepSeek, right? I don't have a physical form, so I don't have a \"name\" like you do. My purpose is to help with answering questions and providing information. I'm here to assist with a wide range of topics, from general knowledge to more specific inquiries. I understand that I can't do things like think or feel, but I'm here to make your day easier by offering helpful responses. So, I'll keep it simple and approachable, making sure to convey that I'm here to help with whatever they need.\n</think>\n\nI'm DeepSeek-R1-Lite-Preview, an AI assistant created by the Chinese company DeepSeek. I'm here to help you with answering questions, providing information, and offering suggestions. I don't have personal experiences or emotions, but I'm designed to make your interactions with me as helpful and pleasant as possible. How can I assist you today?","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":9,"total_tokens":232,"completion_tokens":223,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}As you can see, both inference services are providing services externally, and external requests can be routed to different inference services based on the model name in the request.