With the end-to-end canary release feature provided by SAE, you can comprehensively manage traffic without changing your business code. This topic describes how to implement an end-to-end canary release by using Kubernetes Service.
Terms
Kubernetes Service: a fundamental abstraction in Kubernetes (also known as K8s) for networking, service discovery, and load balancing. A Service uses a label selector to identify the pods (application instances in SAE) to which traffic is routed. It provides a stable network address used by clients to access the pods. It also uses a load balancing mechanism to evenly distribute incoming traffic across the pods. For more information, see Service management.
Cloud-native API Gateway: a next-generation gateway product that conforms to the Kubernetes Ingress standard. The gateway combines the functionalities of traditional API gateways, traffic gateways, microservices gateways, and security gateways, supports various service discovery mechanisms, including Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) and Nacos, and provides different authentication and login methods to quickly establish a secure defense line. For more information, see What is Cloud-native API Gateway?
Lane: an isolated environment defined for applications of the same version. Only requests that match specific routing rules are routed to the corresponding tagged applications in the lane. An application can belong to multiple lanes. A lane can contain multiple applications. This lets you flexibly isolate and group applications.
Lane group: a collection of lanes. You can use a lane group to organize and isolate lanes by team or scenario.
Base environment: the default environment for untagged applications, which acts as the fallback environment when traffic fails to meet the routing rules.
Differences between Kubernetes Service-based service access and end-to-end canary release
SAE provides the following Kubernetes Service-based features:
Kubernetes Service-based service access: for inter-application communication. The backend includes only the baseline application instances.
Kubernetes Service-based service access end-to-end canary release: for an end-to-end canary release deployment. The backend includes the baseline and canary application instances. The gateway routes traffic based on the canary tags of the instances.
Examples
This topic describes how to implement an end-to-end canary release by using Kubernetes Service by simulating actual call chains. You do not need to modify business code. Instead, you only need to configure traffic rules at the entry point. If a request matches the rules, it is tagged as a canary request. When the request flows into the downstream services, the tag is propagated through the service call chain. At each service node, the tagged requests are routed to the corresponding canary application if it is available. Otherwise, the requests are routed to the baseline application.
Tested applications: backend applications A, B, and C, which can be downloaded from End-to-end canary release demo applications.zip. You can deploy these applications as baseline or canary applications.
Backend application | Baseline application | Canary application | Application port | Tag on the canary application |
A | sae-a | sae-a-a1 | 20001 | alicloud.service.tag:g1 |
sae-a-a2 | alicloud.service.tag:g2 | |||
B | sae-b | sae-b-b2 | 20002 | alicloud.service.tag:g2 |
C | sae-c | sae-c-c1 | 20003 | alicloud.service.tag:g1 |
sae-c-c2 | alicloud.service.tag:g2 |
The following figure shows traffic distribution.

Call chain for untagged traffic
Cloud-native API Gateway -> Application sae-a -> Application sae-b -> Application sae-c.
Call chain for tagged traffic
t=g1 traffic: Cloud-native API Gateway -> Application sae-a-a1 -> Application sae-b -> Application sae-c-c1.
t=g2 traffic: Cloud-native API Gateway -> Application sae-a-a2 -> Application sae-b-b2 -> Application sae-c-c2.
Prerequisites
Microservices Governance Professional Edition or Enterprise Edition is activated. For more information, see Activate Microservices Governance.
A Cloud-native API Gateway instance is created. For more information, see Create gateway instances.
The Cloud-native API Gateway instance and baseline applications can be deployed on the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) or different VPCs. If the instance and applications are on different VPCs, configure network settings to enable cross-VPC communication by using Alibaba Cloud CEN or other network products.
Limits
End-to-end canary release applies only to microservices applications created from November 8, 2023.
End-to-end canary release is available only in the new version of the SAE console.
End-to-end canary release integrates the tag-based routing feature of Microservices Governance. If you want to use the end-to-end canary release feature, do not configure canary release and tag-based routing rules for your applications.
1. Deploy baseline applications and enable related features
1.1 Deploy baseline applications
Create the following baseline applications: sae-a, sae-b, and sae-c. This section describes only the key steps. For more information, see Deploy applications.
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and then click Create Application.
In the Basic Information step, configure the parameters in the Basic Information Settings and Capacity Settings sections, and then click Create Application with One Click.
NoteIn this example, the sae-a, sae-b, and sae-c applications are deployed by uploading code packages.
To configure advanced settings, click Next: Advanced Settings. Then, click Create Application. For information about how to configure advanced settings, see Advanced settings.
The Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release feature is compatible with all service registration and discovery mechanisms in the SAE console. In this example, SAE built-in Nacos registry is selected as the registry.
1.2 Enable Microservices Governance for baseline applications
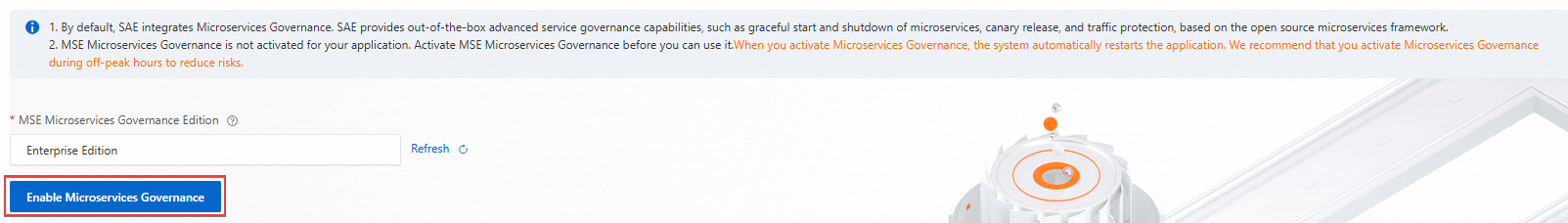
The end-to-end canary release feature is provided by MSE Microservices Governance Professional Edition. If you want to use the feature for applications, you must enable Microservices Governance for the applications.
On the Application List page, click the application name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Enable Microservices Governance.
The Microservices Governance version enabled for the application must be the same as the MSE version.
If your application is not integrated with MSE Commercial Edition, upgrade Microservices Governance for the application, For more information, see Scenario 2: Upgrade the microservices governance feature with one click for applications not integrated with the MSE Commercial Edition.
The enabling process triggers a restart of all instances of the application. We recommend that you perform the operation during off-peak hours.
1 to 2 minutes are required to enable Microservices Governance.
1.3 Enable Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release for baseline applications
The Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release feature relies on Microservices Governance. Before you enable the Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release feature for a baseline application, make sure that the Microservices Governance feature is enabled for the application. Otherwise, you cannot use the Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release feature for the application. For information about how to enable the Microservices Governance feature, see the "Enable Microservices Governance for baseline applications" section of this topic.
Enable Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release for the first baseline application in the traffic flow chain after traffic flows to the API gateway. In this example, the first baseline application is sae-a. Perform the following steps:
On the Basic Information page of the baseline application, click Deploy Application.
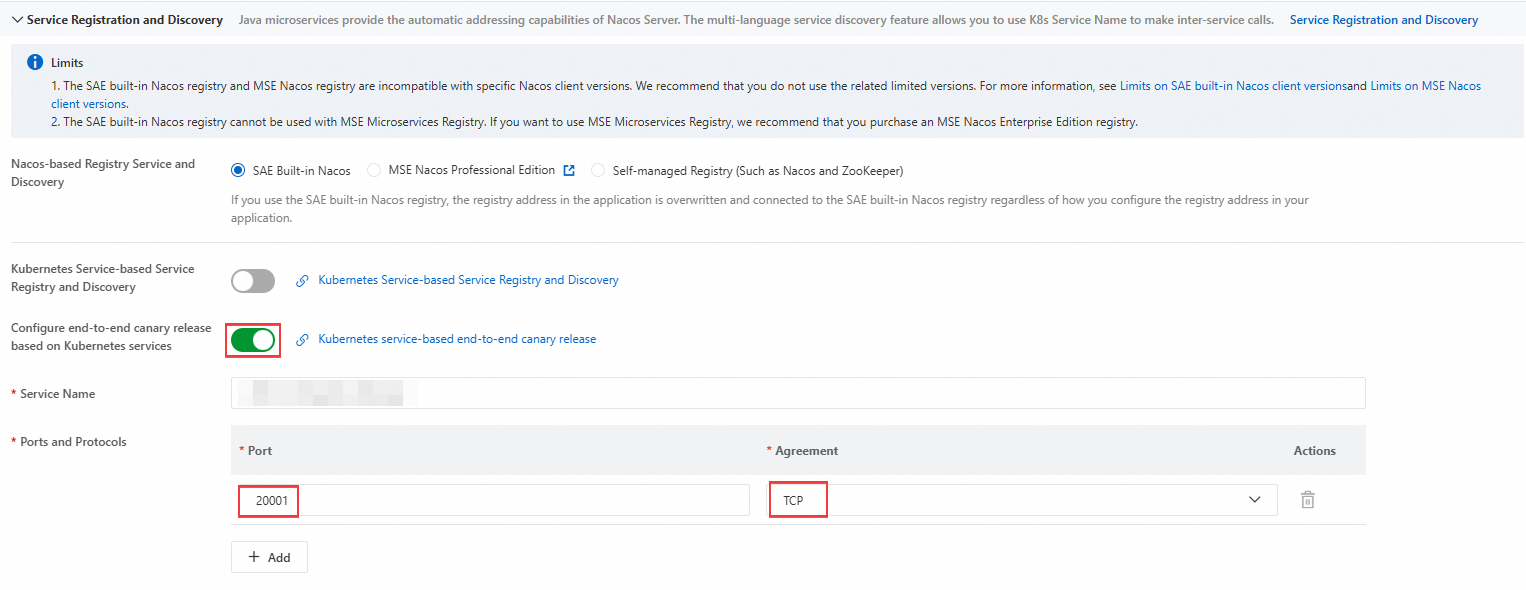
In the Service Registration and Discovery section of the Deploy Application page, enable Kubernetes Service-based Service Registry and Discovery.
If you deploy the baseline application by using a code package, change the version number of the application in the Basic Information Settings section. If you deploy the application by using an image, you do not need to modify the version number. In this example, the baseline application is deployed by using a code package. Therefore, you must modify the version number.
To modify other parameters, see Advanced settings.
To configure a release policy, see Set a release policy.
 Note
NoteAfter you enable the Kubernetes Service-based end-to-end canary release feature, configure the Port and Protocol parameters. In this example, set Protocol to TCP. For information about how to configure the port, see the "Examples" section of this topic.
Click OK.
2. Deploy canary applications
Deploy canary applications based on baseline applications:
Deploy canary applications sae-a-a1 and sae-a-a2 based on the baseline application sae-a.
Deploy the canary application sae-b-b1 based on the baseline application sae-b.
Deploy canary applications sae-c-c1 and sae-c-c2 based on the baseline application sae-c.
To deploy a canary application, perform the following steps:
On the Application List page, find the desired baseline application, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and then click Create Canary Application.Note
icon in the Actions column, and then click Create Canary Application.NoteIf the Microservice Governance feature is disabled for a baseline application, you cannot create a canary application based on the baseline application. For information about how to enable the Microservice Governance feature for a baseline application, see the "Enable Microservices Governance for baseline applications" section of this topic.
In the Basic information step, configure the parameters and click Next: Advanced Settings.
In the Basic Information Settings section, specify a name for the canary application and select an image or a code package to deploy the application. For more information, see Deploy applications.
NoteThe Namespace parameter of the canary application automatically inherits the setting of the baseline application. You do not need to modify the parameter.
The Application Deployment Method parameter also automatically inherits the settings of the baseline application. In this example, you do not need to re-upload the code package for deployment. However, in the actual production environment, you need to carefully review and adjust the settings based on business requirements.
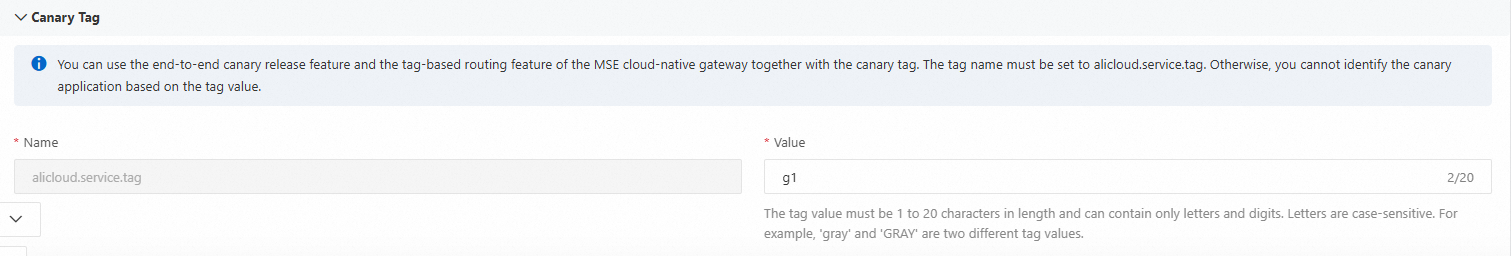
In the Canary Tag section, configure the Value parameter. For information about the tag settings used in this example, see the "Examples" section of this topic.
In the Capacity Settings section, configure the Single Instance Type and Instances parameters.
In the Advanced Settings step, configure the advanced settings based on business requirements. For more information, see Advanced settings.
A canary application inherits the Nacos registry and Kubernetes Service registry and discovery configurations from the baseline application. You do not need to modify the configurations.
Click Create Application.
3. Create a Cloud-native API Gateway route
3.1 Create a Cloud-native API Gateway route
After you create the canary application, return to the Application List page. In the left-side navigation pane, click Namespaces. On the Namespaces page, select the namespace of the baseline and canary applications.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Gateway Routing. On the page that appears, click Create Gateway Route.
On the Create Route page, create a Cloud-native API Gateway route. This section describes only the key steps. For more information, see Create and manage a route for an application (API Gateway).
The configurations in this section apply only to this example. In the production environment, adjust the settings based on your business requirements.
Set Gateway Type to Cloud-native API Gateway.
Select the gateway instance that you created for the task.
Set the Path matching rule to Prefix
/.Set Service Source to K8S Service.
Set Scenario to Single Service.
In the Backend Services section, set Application Name to sae-a, Service Name to
sae-a-****-gray, Terms of Service to HTTP, and Port to20001.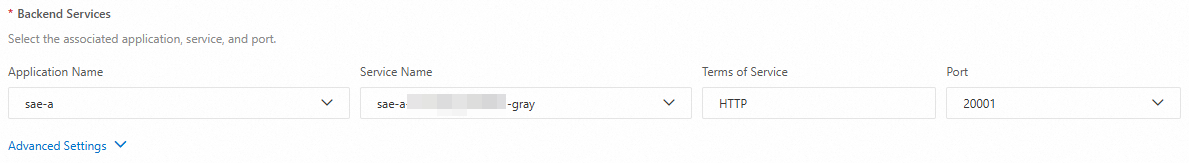 Note
NoteIf your baseline application uses Kubernetes Service for service access, two service name prefixes are in the Service Name drop-down list. Select the name prefix of the end-to-end canary release service. Differences between the two name prefixes:
Baseline application service name prefix: uses the
Baseline application name--Namespace IDformat. Example:sae-a-beijing-test.End-to-end canary release service name prefix: uses the
Baseline application name-Namespace ID-grayformat. Example:sae-a-beijing-test-gray.
Click Save.
3.2 Check whether the service is created
After you create the cloud-native API gateway route, an SAE Kubernetes Service is automatically created in the configured cloud-native API gateway instance. For information about how to query services, see View a service.
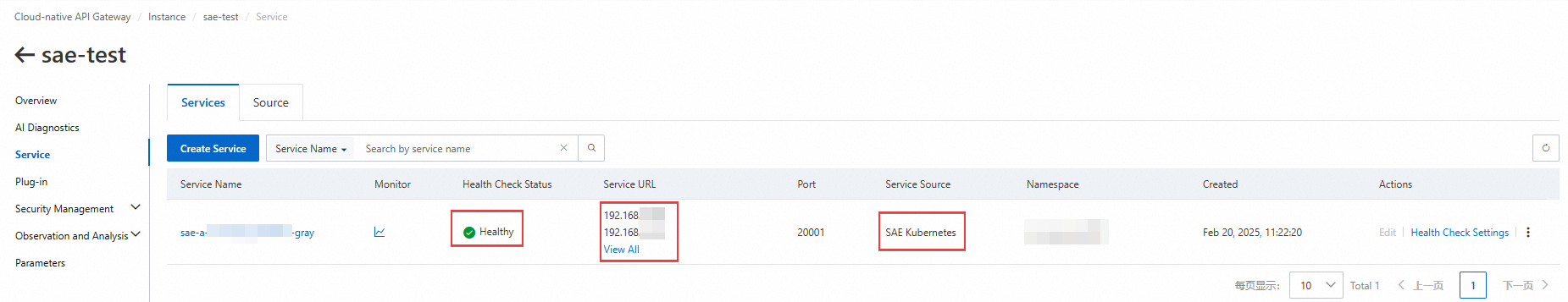
Take note of the following points:
Check whether the health check status is Healthy. If not, move the pointer over the anomaly and troubleshoot it based on the error message.
Check whether the service URL is the IP addresses of the associated baseline and canary applications.
Check whether the service source is SAE Kubernetes.
4. Create a lane group and lanes
4.1 Create a lane group
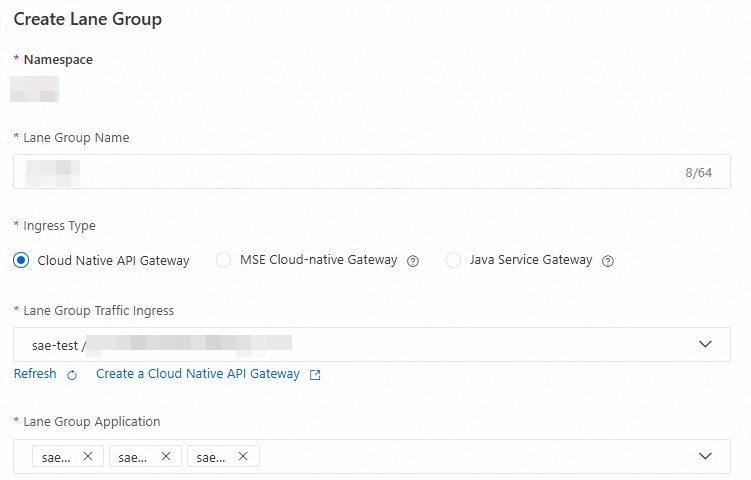
After you create the Cloud-native API Gateway, return to the Namespaces page. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the End-to-end Canary Release page, select the namespace and click Create Lane Group and Lane.
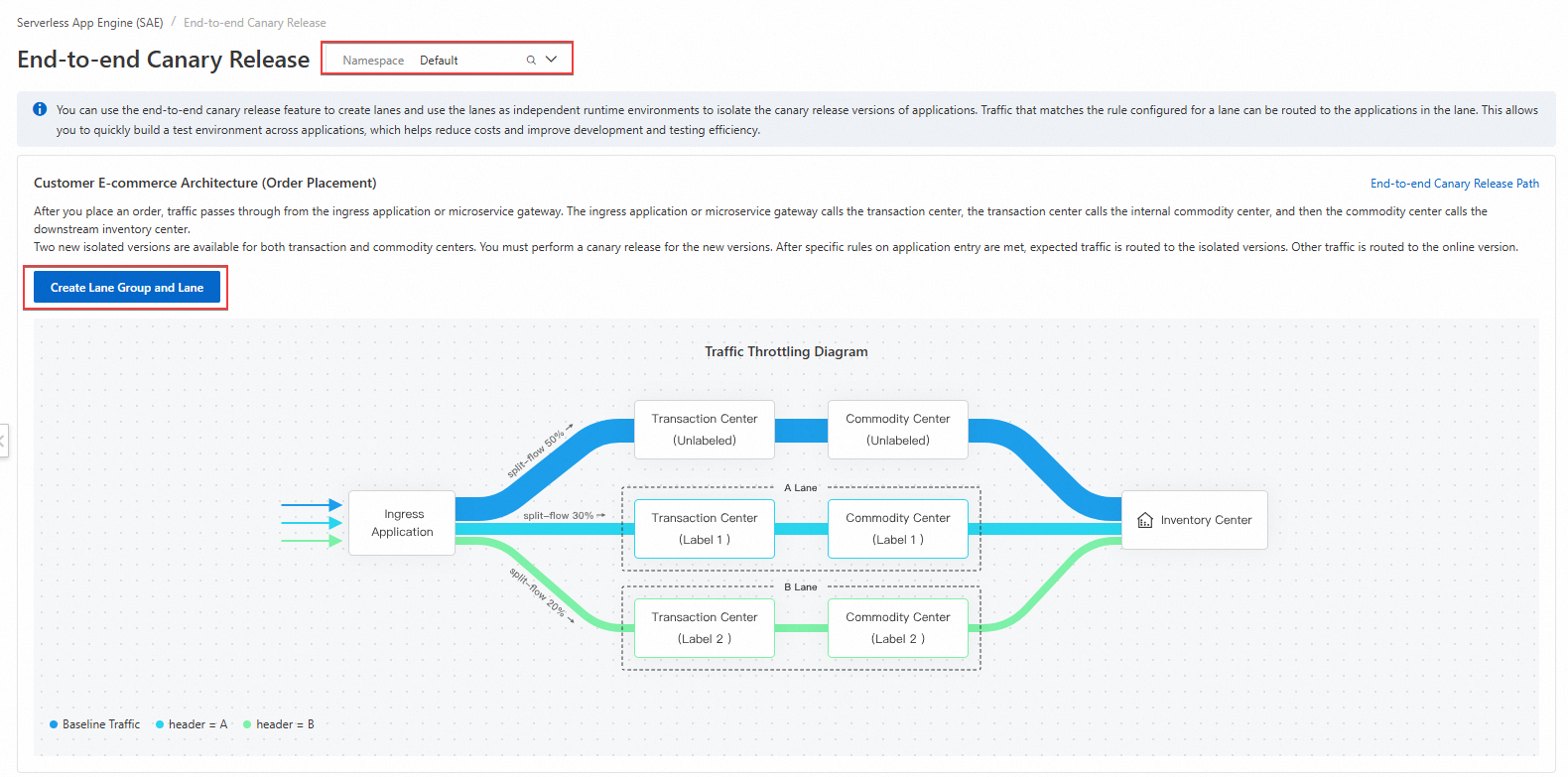
In the Create Lane Group panel, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Specify a lane group name.
Set Ingress Type to Cloud-native API Gateway.
Set Lane Group Traffic Ingress to the created Cloud-native API Gateway instance.
Select all baseline applications for Lane Group Application.
4.2 Create lanes
You can create lanes by content or ratio in a lane group. After you create the first lane, you cannot change the canary release mode for subsequent lanes.
The configuration examples in the following table apply only to the scenario in this topic. In the actual production environment, adjust the configurations based on business requirements.
Create lanes based on the canary release by content mode
Perform the following steps to create two lanes:
On the End-to-end Canary Release page, click Create First Split Lane.
ImportantAfter the first lane is created, click Create Lane to create a second lane.
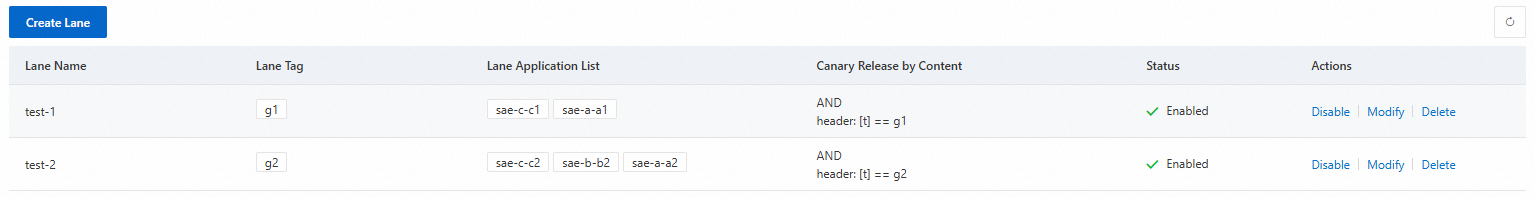
In the Create Lane panel, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Example
Description
Lane Name
First lane: test-1
Second lane: test-2
Specify the unique name of the lane.
Lane Tag
First lane: g1
Second lane: g2
From the drop-down list, select the tag you configured when you created the canary application.
Lane Status
Enabled
By default, a lane is enabled.
Canary Release Mode
Canary Release By Content
Click Canary Release By Content. For more information about the canary release mode, go to the SAE console.
Canary Condition
First lane:
Meet All Conditions
Parameter Type:
HeaderParameter:
tCondition:
==Value:
g1
Second lane:
Meet All Conditions
Parameter Type:
HeaderParameter:
tCondition:
==Value:
g2
If a request meets all the conditions, it is tagged with the specified lane tag.
Two filter conditions are supported:
Meet All Conditions: If requests meet all conditions, they are tagged with the lane tag.
Meet Any Conditions: If requests meet any of the conditions, they are tagged with the lane tag.
You can use the following parameters for condition filtering:
Parameter Type: You can select Header, Cookie, or Parameter.
Parameter: You can customize a parameter.
Condition: You can select
==,!=,in, Percentage, Regular Expression Match, or Prefix Match.Value: You can customize the value.
Create lanes based on the canary release by ratio mode
Perform the following steps to create two lanes:
On the End-to-end Canary Release page, click Create First Split Lane.
ImportantAfter the first lane is created, click Create Lane to create a second lane.
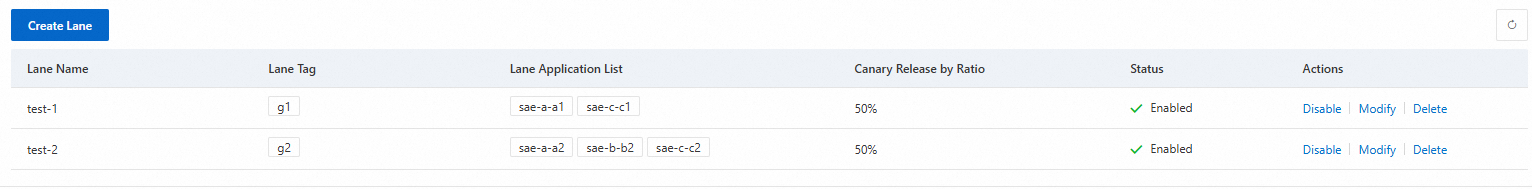
In the Create Lane panel, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Example
Description
Lane Name
First lane: test-1
Second lane: test-2
Specify the unique name of the lane.
Lane Tag
First lane: g1
Second lane: g2
From the drop-down list, select the tag you configured when you created the canary application.
Lane Status
Enabled
By default, a lane is enabled.
Canary Release Mode
Canary Release By Ratio
Select Canary Release By Ratio. For more information about this mode, go to the SAE console.
Traffic Ratio
First lane: 50%
Second lane: 50%
Configure the traffic ratio for the selected route or path. By default, all routes or paths in a lane use the same traffic ratio.
5. Verify the results
5.1 Perform access test
Log on to the Cloud-native API Gateway console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Instance. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the Cloud-native API Gateway instance that you created and click the ID of the instance.
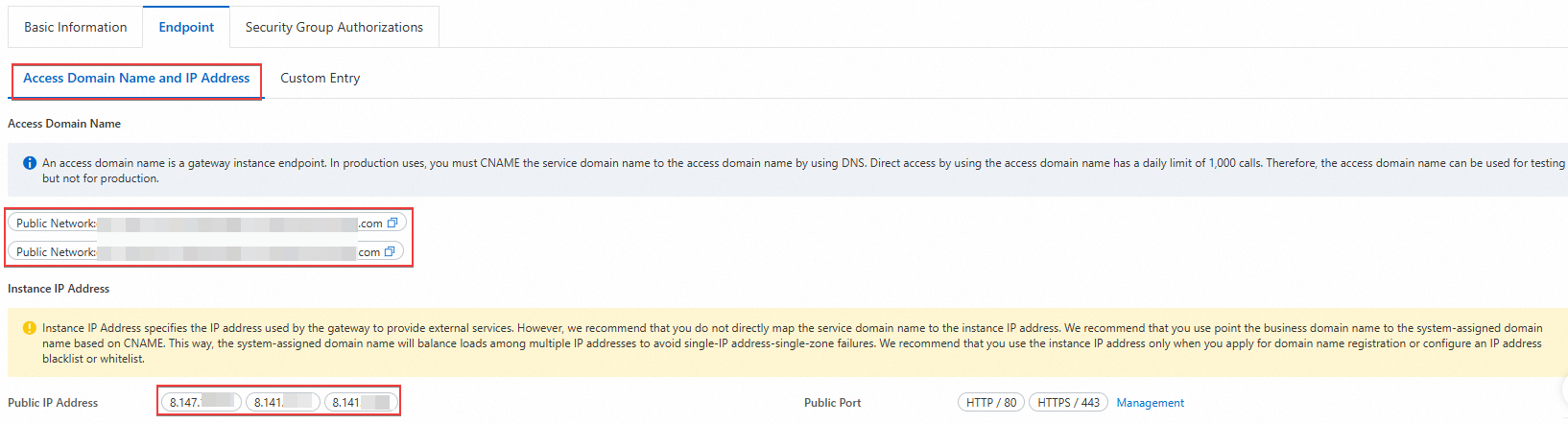
On the Overview page of the Cloud-native API Gateway instance, click the Endpoint tab. On the Access Domain Name and IP Address tab, view the access domain name and instance IP address.
 Important
ImportantAn access domain name is the entry point of a gateway instance. In production environments, you must CNAME the service domain name to the access domain name by using DNS. You can send a maximum of 1,000 requests per day for direct access to a gateway instance by using the access domain name. Therefore, you can use this access method only for testing.
The instance IP address is the one used by the gateway to provide external services. However, do not directly map the service domain name to the instance IP address. We recommend that you CNAME the business domain name to the access domain name. This way, the access domain name balances loads across multiple IP addresses to avoid single-IP-address-single-zone failures. We recommend using the instance IP address only for domain name registration or for configuring an IP address blacklist or whitelist.
Copy the access domain name or public IP address and perform an access test in a browser.
Sample URL format for access by using the domain name:
http://<Access domain name>/<Access path>. Example:http://env-cu2c******/a.Sample URL format for access by using the public IP address:
http://<Internet: 80>/<Access path>. Example:http://8.147.XX.XX:80/a.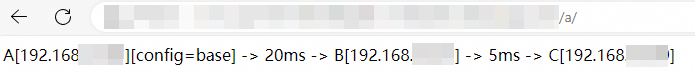
5.2 Verify traffic routed to canary applications
You can verify access by using the public IP address of the Cloud-native API Gateway. However, in the production environment, do not directly map the service domain name to the public IP address. We recommend that you CNAME the service domain name to the access domain name.
Verify traffic routed to canary applications based on content
Run the following curl command to verify traffic routed to the baseline applications:
# Test command curl 8.130.XX.XX/a # Test result A[192.168.XX.XX][config=base] -> B[192.168.XX.XX] -> C[192.168.XX.XX]Run the curl command to verify traffic routed to the canary applications. The following example shows the result when you set Parameter to Header.
# Test command curl 8.130.XX.XX/a -H "tag: ${tag}" # Test result A${tag}[192.168.XX.XX][config=base] -> B[192.168.XX.XX] -> C${tag}[192.168.XX.XX]NoteIf requests contain the
tag: ${tag}tag, the requests match the rule and the tag is passed to subsequent applications.
Verify traffic routed to canary applications based on traffic ratio
Run the following curl command for verification:
#Test command
curl 8.130.XX.XX/a
# Test result
A[192.168.XX.XX][config=base] -> B[192.168.XX.XX] -> C[192.168.XX.XX]
A${tag}[192.168.XX.XX][config=base] -> B[192.168.XX.XX] -> C${tag}[192.168.XX.XX]5.3 Microservices Governance observability
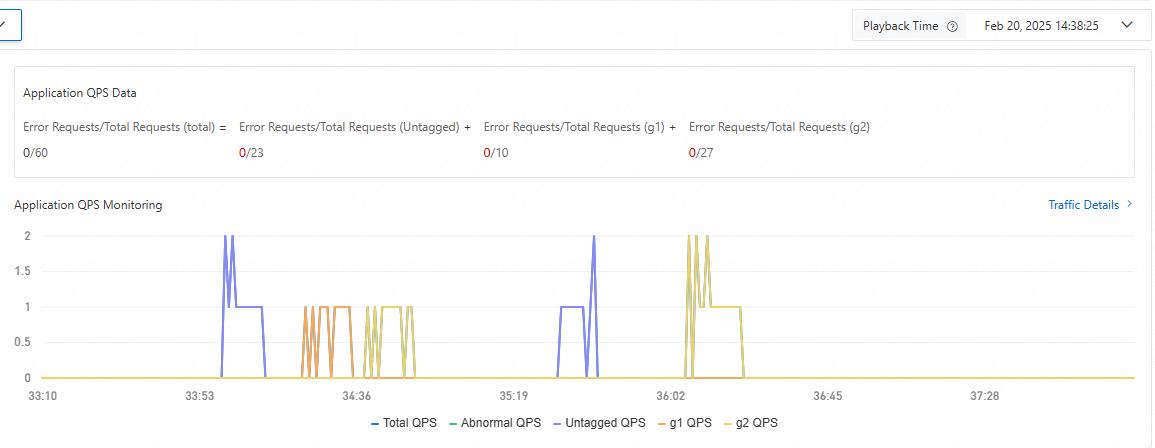
Go to the End-to-end Canary Release page in the SAE console. In the Lane Groups and Involved Applications section, click the application name. In the Application QPS Monitoring section, you can view the traffic information of the baseline and canary applications of the lane. Select a playback time to display the corresponding metric data.
You can also click Traffic Details in the Application QPS Monitoring section to view more information.