Platform for AI (PAI) allows you to integrate Elasticsearch with a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)-based large language model (LLM) chatbot. This way, the accuracy and diversity of the answers generated by models are enhanced. Elasticsearch features efficient data retrieval capabilities and provides special features such as dictionary configuration and index management. This allows the RAG-based LLM chatbot to identify user requirements better and provide more appropriate and valuable feedback. This topic describes how to associate Elasticsearch with a RAG-based LLM chatbot when you deploy the RAG-based LLM chatbot. This topic also describes the basic features provided by a RAG-based LLM chatbot and the special features provided by Elasticsearch.
Background information
Introduction to EAS
Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) is a platform for online model services within Platform for AI (PAI). It supports deploying models as online inference services and AI-Web applications. EAS provides features like Auto Scaling and Blue-Green Deployment to deliver cost-effective, high-concurrency, and stable online services. EAS also provides resource group management, version control, and a comprehensive operations and maintenance monitoring system. For more information, see Overview of EAS.
Introduction to RAG
Generative AI has made remarkable strides in text and image generation. However, widely used large language models (LLMs) have several inherent limitations:
Limited domain knowledge: LLMs train on broad, general datasets. They struggle with deep, specialized tasks.
Information lag: A trained model is static. It cannot learn new information in real time.
Misleading output: Due to data bias and inherent model defects, LLMs may produce outputs that seem plausible but are incorrect, a phenomenon known as a model hallucination.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) was developed to overcome these challenges and enhance the functionality and accuracy of large models. By integrating external knowledge, RAG reduces model fabrications, improves access to recent information, and enables more personalized and accurate LLM responses.
Introduction to Elasticsearch
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch is a fully managed cloud service built on open source Elasticsearch. It is 100% compatible with open-source features and supports out-of-the-box use on a pay-as-you-go basis. It provides ready-to-use Elastic Stack components, including Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats, and offers free X-Pack (Platinum Edition advanced features) commercial plug-ins in cooperation with Elastic. These plug-ins integrate advanced features such as security, SQL, machine learning, alerting, and monitoring. It is widely used for real-time log analysis, information retrieval, and multi-dimensional data query and statistical analysis. For more information about Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch, see What is Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch?
Workflow
EAS provides a systematic RAG solution with flexible parameter configurations. You can use the RAG service through a WebUI or API calls to customize your chatbot. The core architecture of RAG consists of retrieval and generation:
Retrieval: EAS supports multiple vector databases, including open-source Faiss, Elasticsearch, Hologres, OpenSearch, and RDS for PostgreSQL.
Generation: EAS supports a rich set of open-source models, such as Qwen, Llama, Mistral, and Baichuan, and supports calls to ChatGPT.
This topic uses Elasticsearch as an example to show how to build a RAG-based chatbot using EAS and Elasticsearch. The process is as follows:
First, create an Elasticsearch instance and prepare the required configuration to connect it to the RAG service during deployment.
Deploy the RAG service on the EAS platform and connect it to the Elasticsearch instance.
You can connect to Elasticsearch in the RAG chatbot, upload your enterprise knowledge base files, and answer questions.
Prerequisites
Create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), a vSwitch, and a Security Group. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block and Create a security group.
Precautions
This solution is limited by the server resource size and the default token limit of the LLM service, which restricts the supported conversation length. This guide helps you test the basic retrieval features of a RAG chatbot.
Prepare the vector database: Elasticsearch
Step 1: Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console and create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance on the Elasticsearch Clusters page. Key parameters are described below. For more details on other configurations, see Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
Parameter | Description |
Region and Zone | Select the same region as your EAS service. |
Instance Type | The type of the cluster. Select Standard Edition. |
Password | Set the logon password and save it locally. |
Step 2: Prepare configuration items
Prepare the URL of the Elasticsearch cluster.
In the top navigation bar of the Elasticsearch Clusters page, select the region where you created the instance from the top menu bar. In the cluster list, click the ID of the created Elasticsearch instance.
In the Basic Information section, get the internal endpoint and its corresponding port number, then combine them to form the Elasticsearch URL.
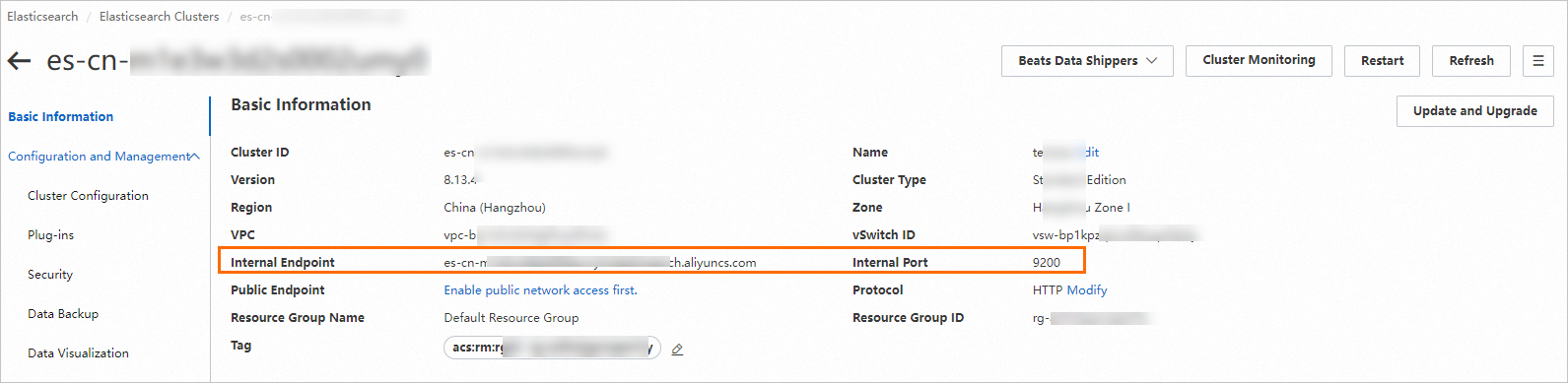
The format is:
http://<Internal endpoint>:<Port number>.ImportantWhen using an internal endpoint, ensure that the Elasticsearch instance and the PAI-RAG service are in the same VPC. Otherwise, the connection will fail.
Prepare the index name.
On the Elasticsearch instance's page, click Modify Configuration. In the upper-right corner of the YML File Configuration section. In the YML file configuration, set Auto Indexing to Enable. For more information, see Configure Elasticsearch cluster settings via YML file.
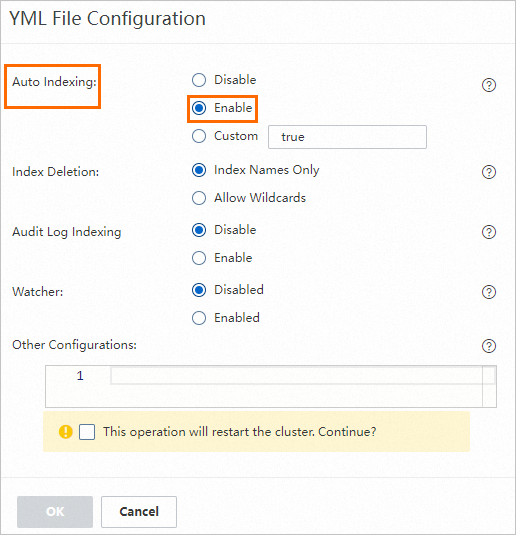
After enabling this setting, you can specify a custom index name, such as
es-test, when you deploy the PAI-RAG service.Prepare the ES user and password.
The ES user is elastic by default. The ES password is the logon password you set when creating the ES instance. If you forget the password, you can reset it. For more information, see Reset the elastic password.
Deploy the RAG service and connect it to Elasticsearch
Log on to the PAI console. In the upper part of the page, select the region in which you want to create a workspace. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Model Training > Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS). On the page that appears, select the desired workspace and click Enter Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS).
On the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page, click Deploy Service. Under Scenario-based Model Deployment, click RAG-based Smart Dialogue Deployment.
On the RAG-based LLM Chatbot Deployment page, configure the following key parameters. For information about other parameters, see Step 1: Deploy the RAG-based chatbot.
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Version
Select LLM-Integrated Deployment.
Model Type
Select Qwen1.5-1.8b
Resource Information
Deployment Resources
The system automatically recommends a suitable resource specification based on the selected model type. Changing to a different specification may cause the model service to fail at startup.
Vector Database Settings
Vector Database Type
Select Elasticsearch.
Private Endpoint and Port
Enter the Elasticsearch URL you obtained in Step 2, in the format
http://<Internal-Endpoint>:<Port-Number>.Index Name
Enter a new index name or an existing index name. If you use an existing index name, its structure must comply with the PAI-RAG requirements—for example, you can specify an index that was automatically created when you previously deployed a RAG service via EAS.
Account
Enter elastic.
Password
Enter the logon password you set in Step 2.
VPC (Optional)
VPC
Ensure that the configured VPC is the same as the one used by your Elasticsearch instance.
vSwitch
Security Group Name
After you configure the parameters, click Deploy.
Use the RAG-based LLM chatbot
The following section describes how to use a RAG-based LLM chatbot. For more information, see RAG chatbot for LLM.
1. Check Vector Database Configuration
Click the name of your target RAG service, then click View Web App in the upper-right corner.
Verify the Elasticsearch vector database configuration.
The system automatically configures a default knowledge base and applies the vector database settings you provided during deployment. In the Vector Database Settings area, check if the Elasticsearch configuration is correct. You can modify the settings if needed and then click Connect ElasticSearch.
2. Upload enterprise knowledge base files
On the Knowledge Base tab, go to the File Management tab to upload your knowledge base files.
After the upload is complete, the system automatically stores the files in the vector database in the PAI-RAG format. If a file with the same name is uploaded, it overwrites the existing file in all vector databases except FAISS. Supported file types include .html, .htm, .txt, .pdf, .pptx, .md, Excel (.xlsx or .xls), .jsonl, .jpeg, .jpg, .png, .csv, and Word (.docx). For example, rag_chatbot_test_doc.txt.

3. Perform knowledge Q&A
On the Chat tab, select a knowledge base name and a Retrieval Mode to start asking questions.
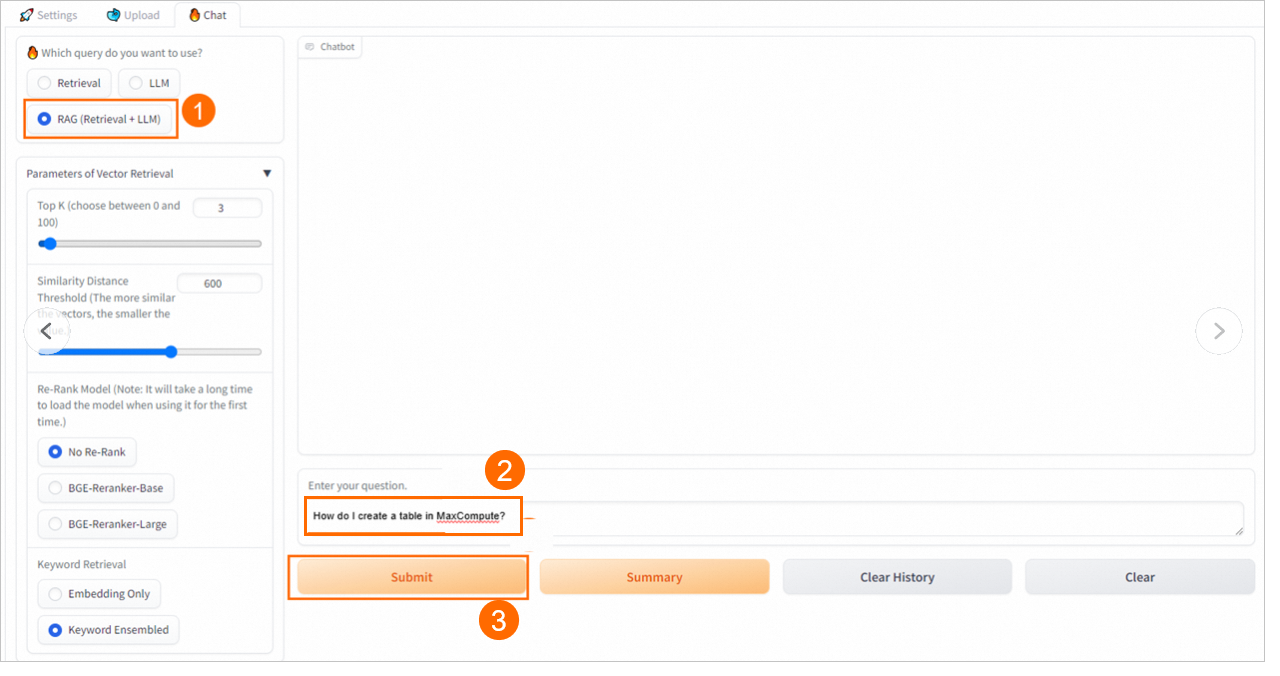
Special features provided by Elasticsearch
Customize tokenization and stopword dictionaries
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch comes with the built-in IK analysis plug-in (analysis-ik). The IK analyzer tokenizes sentences into words, not just characters. It includes a main dictionary for complex Chinese text tokenization and a stopword dictionary to filter out common, low-value words (like "the", "is", "at"). Both dictionaries improve retrieval efficiency and accuracy. While the default dictionaries are powerful, specialized fields like law or medicine have extensive jargon. Your knowledge base might also contain product, company, or brand names not in the default dictionaries. You can create custom dictionaries to improve search results for your specific business needs. For more about the Elasticsearch IK analysis plug-in, see Use the analysis-ik plug-in.
1. Prepare a main dictionary or stopword dictionary
Prepare a custom main dictionary or stopword dictionary locally:
File format: The file must be a
.dicfile. The filename can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, or underscores, and must not exceed 30 characters. For example,new_word.dic.Content requirements: Add new words or stopwords to the file, one per line. For example, the built-in tokenizer might split "cloud server" into "cloud" and "server". If your business requires it to be treated as a single term, you can add "cloud server" to your main dictionary. The content of the
new_word.dicfile might look like this:
cloud server custom token
2. Upload the dictionary file
After preparing the dictionary file, you need to upload it to the specified location. The following steps show how to do this using a rolling update. For other methods of updating dictionary files, see Use the analysis-ik plug-in.
Go to the Elasticsearch instance details page.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Elasticsearch Cluster.
Navigate to the desired cluster.
In the top navigation bar, select the resource group to which the cluster belongs and the region where the cluster resides.
On the Elasticsearch Cluster page, find the cluster and click its ID.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose .
On the Built-in Plug-ins tab, find the analysis-ik plug-in and click Rolling Update in the Actions column.
In the Configure IK Dictionaries - Rolling Update panel, click Edit on the right side of the dictionary that you want to update, upload a dictionary file, and then click Save.
You can use one of the following methods to update a dictionary file:
Upload On-premises File: Click the upload area and select the file that you want to upload from your on-premises machine. Alternatively, drag the file that you want to upload from your on-premises machine to the upload area.
Upload OSS File: Configure the Bucket Name and File Name parameters, and click Add.
Make sure that the bucket that you specify resides in the same region as your Elasticsearch cluster.
The dictionary file that you specify cannot be automatically updated. If the content of the dictionary file that is stored in OSS changes, you must perform a rolling update to make the changes take effect.
NoteYou can upload multiple dictionary files. The files must have a
.dicextension. Filenames can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and underscores, and must not exceed 30 characters.To modify the content of an uploaded dictionary, click the
 icon next to the target dictionary file to download and edit it. Then, delete the original file from the console and re-upload the modified version. You must click Save after deleting the original file; otherwise, the system will report a duplicate file name when you try to upload the new one.
icon next to the target dictionary file to download and edit it. Then, delete the original file from the console and re-upload the modified version. You must click Save after deleting the original file; otherwise, the system will report a duplicate file name when you try to upload the new one.
Click OK. After the dictionary file is updated, reconnect the RAG-based LLM chatbot to the Elasticsearch cluster on the web UI. For more information, see Connect to a vector database.
After reconnecting, you can ask questions in the WebUI. When the Retrieval Mode is set to Keyword Only or Hybrid (Vector Search + Keyword Search), Elasticsearch will use the updated dictionary for full-text search.
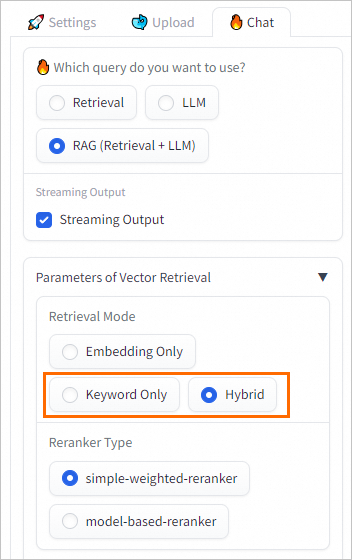
Index management
Elasticsearch provides the index management feature. Effective index management can allow a RAG-based LLM chatbot to efficiently and accurately retrieve valuable information from vast datasets and generate high-quality answers. To manage indexes, perform the following steps:
Go to the details page of an Elasticsearch cluster.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left navigation menu, choose Elasticsearch Clusters.
Navigate to the target cluster.
In the top navigation bar, select the resource group to which the cluster belongs and the region where the cluster resides.
On the Elasticsearch Clusters page, find the cluster and click its ID.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose .
In the Kibana section of the page that appears, click Modify Configuration. On the Kibana Configuration page, configure a private or public IP address whitelist for Kibana.
For more information, see Configure a public or private IP address whitelist for Kibana.
Log on to the Kibana console.
Click the Back icon in the upper-left corner of the page to return to the Data Visualization page.
In the Kibana section, click Access over Internet or Access over Internal Network.
NoteThe Access over Internet or Access over Internal Network entry is displayed only after the Public Network Access or Private Network Access switch is turned on for Kibana.
On the Kibana logon page, enter the username and password.
Username: The default username of an Elasticsearch cluster is elastic.
You can also customize a username. For more information, see Use the RBAC mechanism provided by Elasticsearch X-Pack to implement access control.
Password: the password that corresponds to the elastic username. The password of the elastic account is specified when you create the Elasticsearch cluster. If you forget the password, you can reset it.
For more information about the procedure and precautions for resetting the password, see Reset the access password of an Elasticsearch cluster.
Click Log In. The page shown in the following figure appears.

View and manage indexes.
In the top navigation bar, click the
 icon and choose .
icon and choose . In the left-side navigation pane, choose Data > Index Management.
On the Index tab of the page that appears, view the index that you want to manage and perform management operations such as disabling the index, refreshing the index, clearing the index, or deleting the index. The following figure shows an example on how to manage an index named es_test.
References
EAS simplifies deployment for AIGC and LLM scenarios. You can easily launch services with a single click. For more information, see Scenario-based deployment.
The RAG service WebUI offers a wide range of inference parameters. The RAG service also supports API calls. For more information about implementation details and parameter settings, see RAG chatbot for LLM.
The RAG chatbot can also be connected to other vector databases, such as OpenSearch or RDS for PostgreSQL. For details, see Use EAS and OpenSearch to deploy a RAG-based chatbot or Use EAS and RDS PostgreSQL to deploy a RAG chatbot.