By configuring client certificates, you can enable Transport Layer Security (TLS) mutual authentication (mTLS) on the link between clients and Edge Security Acceleration (ESA) nodes. This enhances client access security.
Client certificate issuance
You can use the Certificate Authority (CA) provided by ESA to create client certificates. You can then deploy the generated client certificates on your mobile applications. ESA generates a unique CA for each account. By default, nodes trust all client certificates issued by ESA.
Create a certificate
In the ESA console, choose Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose , and then click Create Certificate.
As needed, select a CSR Generation, Private Key Type, and Certificate Validity.
NoteThe default certificate validity period is one year.
Click OK.
ImportantIn the certificate preview dialog box, click "Copy Certificate" and "Copy Private Key" to copy the content. Then, paste the content into your client. The certificate and private key cannot be retrieved after you close this dialog box.
Bind a domain name
By binding a client certificate to a specific domain name, you can implement mutual authentication (mTLS). This ensures that only users with valid client certificates can access specific services or resources.
In the ESA console, choose Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, click .
In the domain name section, click Configure. In the domain name box, enter the domain names.
NoteYou can enter up to 50 domain names at a time.
The domain names must match the site.
Click OK.
Revoke a certificate
If you no longer need a certificate, revoke it as follows:
In the ESA console, choose Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, click .
Select , and click Revoke.
In the dialog box that appears, select the I confirm that the certificate is no longer required checkbox. Then, click Yes.
Custom certificate issuance
In addition to client certificates issued by the ESA CA, you can also use certificates that you issue from your own private channels. If you use a custom certificate, you must configure its root certificate.
Custom certificate issuance is currently supported only through OpenAPI. You can upload a maximum of five CA certificates for each plan.
Procedure
Call the Upload client mTLS CA certificate API operation to upload the CA root certificate. Record the certificate ID from the API response.
Call the Bind domain names API operation to bind a list of hosts to the CA certificate. Only the bound hosts can use the corresponding CA certificate for mTLS authentication.
The following table lists other OpenAPI operations for the custom mTLS certificate feature.
API operation name
Description
Uploads a custom-issued CA certificate.
Lists all uploaded custom-issued CA certificates.
Deletes a custom-issued CA certificate.
Queries the details of a specific custom-issued CA certificate.
Binds domain names to a custom-issued CA certificate.
Queries the domain name binding status of a custom-issued CA certificate.
Block failed authentication requests
Configure Web Application Firewall (WAF) rules to block requests that fail client certificate authentication.
Procedure
In the ESA console, choose Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose to go to the custom rule configuration page.
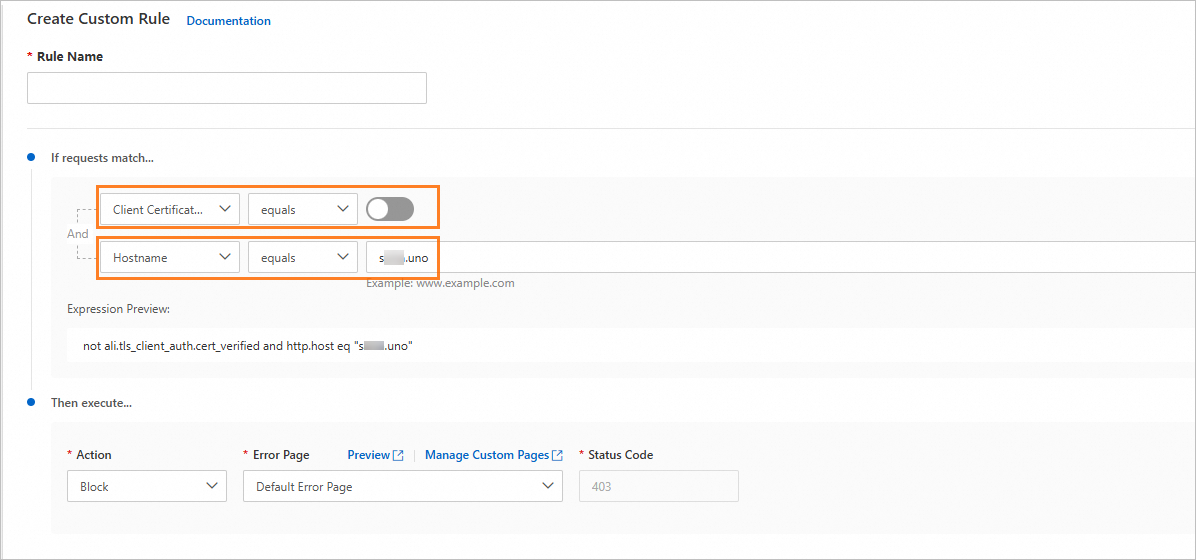
Configure a custom WAF rule.
Set Client Certificate Verified to
 .
.For Hostname, enter the domain names for which you want to block requests.
ImportantYou must configure the hostname condition. Otherwise, all requests that fail client certificate authentication are blocked.
Set Action to Block, or another action as needed.
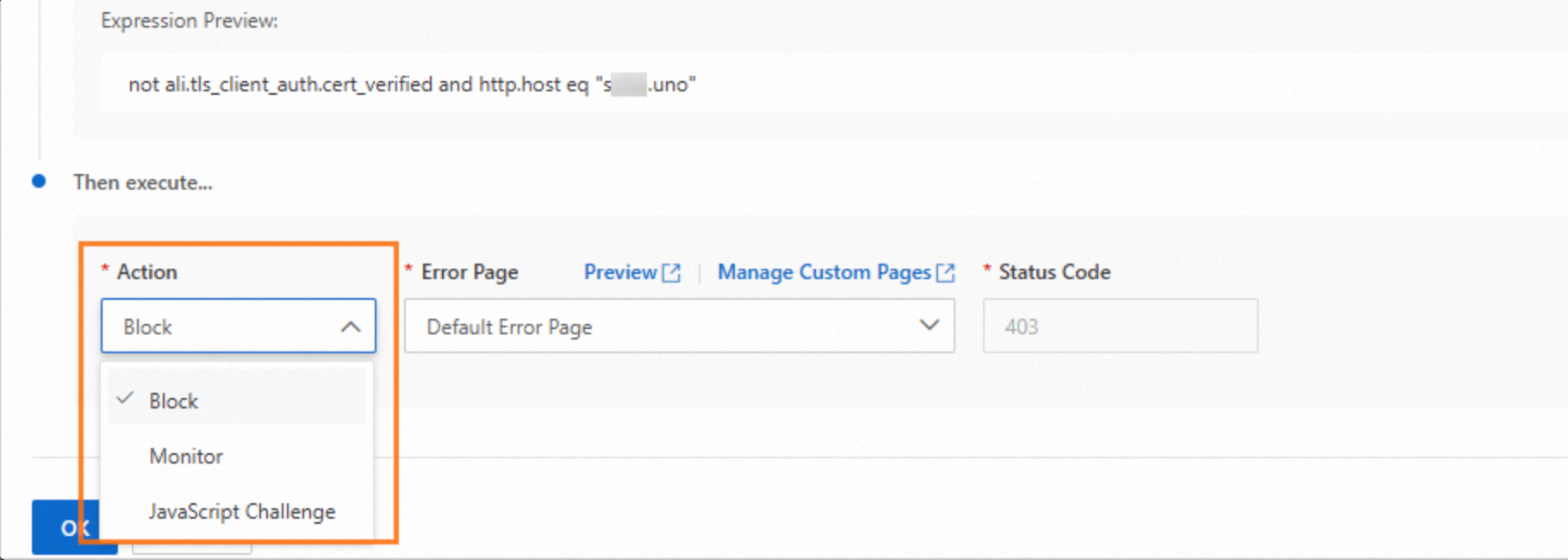
Click OK to add the rule.
After the rule is added, any request to a domain name in the rule that fails client certificate authentication is blocked and returns a 403 status code.
Verification
If a client makes a request without a certificate, WAF blocks the request and returns a 403 status code.

If a client makes a request with a client certificate issued by ESA, the request is processed normally.
curl -v "https://example.com" --cert ./example.crt --key ./example.key * Trying 10.10.10.10... * TCP_NODELAY set * Connected to 1.zhouwei.queniuwk.cn (10.10.10.10) port 443 (#0) * Cipher selection: ALL:!EXPORT:!EXPORT40:!EXPORT56:!aNULL:!LOW:!RC4:@STRENGTH * successfully set certificate verify locations: * CAfile: /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt CApath: none * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS Unknown, Certificate Status (22): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2): * NPN, negotiated HTTP1.1 * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Request CERT (13): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Certificate (11): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Change cipher spec (1): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Next protocol (67): * TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Change cipher spec (1): * TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20): * SSL connection using TLSv1.2 / ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 * Server certificate: * subject: CN=1.zhouwei.queniuwk.cn * start date: Jul 31 00:00:00 2024 GMT * expire date: Jul 31 23:59:59 2025 GMT * subjectAltName: host "1.zhouwei.queniuwk.cn" matched cert's "1.zhouwei.queniuwk.cn" * issuer: C=US; O=DigiCert Inc; OU=www.digicert.com; CN=Encryption Everywhere DV TLS CA - G2 * SSL certificate verify ok. > GET / HTTP/1.1 > Host: 1.zhouwei.queniuwk.cn > User-Agent: curl/7.74.0 > Accept: */*