By configuring cache expiration time rules, you can precisely control how long resources are cached on POPs (points of presence) to balance content updates, access performance, and origin-fetch costs. This document describes how cache rules work, how to configure and verify them, and provides troubleshooting steps and best practices.
How it works
When a request reaches a POP, CDN follows this priority order to decide whether to serve a cached response or fetch the latest content from your origin server:
No-cache Headers from origin server: When the origin server responds with
pragma:no-cache,cache-control:no-cache(orno-store, ormax-age=0), the POP follows the origin's policy and does not cache the resource.Console cache rules: If you have configured rules for a specific directory or file extension in the console, and the origin server does not send the "do not cache" Headers mentioned above, the console cache rule takes precedence.
Priority logic when multiple console cache rules match:
Scenario
Priority logic
Example
Different weight
The rule with the higher Weight value (1-99) takes precedence.
If Rule A (for the
/image/directory, Weight 50) and Rule B (for the.jpgextension, Weight 90) both matchimage/a.jpg, Rule B is applied.Same weight
The rule that was created first takes precedence.
If you configure a directory rule (
/static/) and a file extension rule (.js) with the same Weight of 60, and the directory rule was created before the extension rule,/static/app.jswill match the directory rule.Once a request matches a cache rule, no other rules are checked.
By default, if the origin server responds with
Pragma: no-cacheorCache-Control: no-cache/no-store/max-age=0, the POP does not cache the resource. To force caching, select Ignore Origin No-cache Header when configuring a cache rule in the console.
Origin server cache policy: If a request does not match any console rules, or if the matched rule has Honor Origin TTL enabled, the CDN honors the HTTP response Headers from the origin server. The priority of these Headers is, from highest to lowest:
cache-control>expires>last-modified>ETag.Response Header
How it is handled
Example
Cache-Control
The
s-maxagedirective is prioritized for cache duration, followed bymax-age.s-maxage=86400, max-age=3600Expires
Specifies the expiration date and time. This is used only if no
Cache-ControlHeader is present.Expires: Wed, 21 Oct 2025 07:28:00 GMTLast-Modified
Last-Modifiedis a timestamp that indicates when the resource was last modified.
The cache duration is calculated as follows:
(Current Time -Last-Modified) * 0.1, with the resulting duration clamped to a range of 10 to 3,600 seconds.Last-Modified: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:28:00 GMTETag
An
ETagis a unique identifier generated by the server for a specific version of a resource, typically a hash value or version number.
By default, resources with anETagare cached for 10 seconds.ETag: "abc123"No-cache policy: If a request does not match any console cache rules and the origin server returns no cache-related response Headers (such as
Cache-Control), the POP does not cache the resource.
Cache policies are only applied to responses with a 200, 203, 206, 300, 301, 308, or 410 status code from the origin server. To cache responses with other status codes (such as 404), configure this on the Cache Settings page.
Procedure
By the console (recommended)
In the CDN console, navigate to the Domain Names page and click Manage in the row for your target domain.
On the page, click Add to configure a new cache rule.
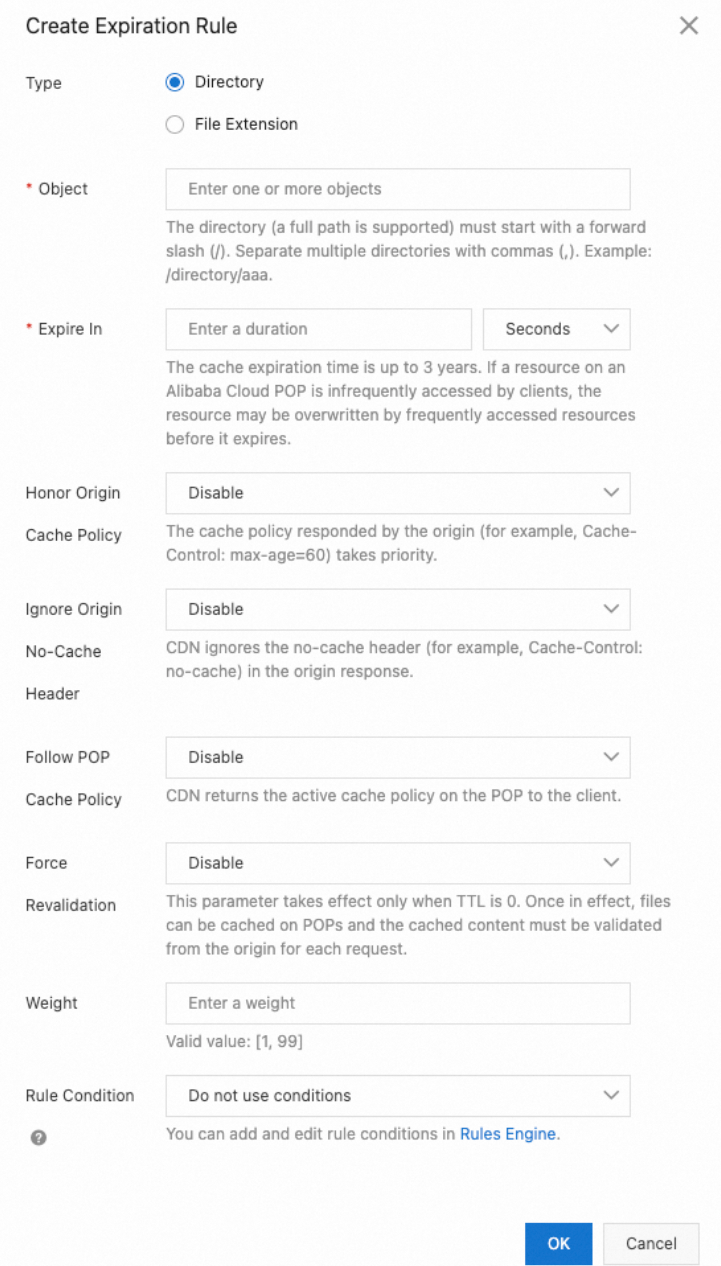
Parameter | Description |
Type | Specify the scope of the rule by Directory or File Extension. |
Object | Enter content based on the selected type: |
Expire In | The duration a resource is cached on CDN POPs. The maximum is 3 years. |
Honor Origin TTL | When enabled, the origin server's cache setting takes precedence and overrides this rule. |
Ignore Origin No-Cache Header | When enabled, the CDN ignores the following |
Follow POP Cache Policy | When enabled, the CDN sends its effective cache policy (e.g., |
Force Revalidation | This setting is effective only when the expiration time is set to 0 seconds.
|
Weight | The priority of the rule. The value can be from 1 to 99. A higher value means higher priority. |
Rule Condition | You can refine the rule's scope based on request parameters (e.g., Header, URL parameters). |
By API
Call the BatchSetCdnDomainConfig operation to configure domains in batches. See cache-related parameters in Cache configuration.
Apply rule changes immediately
New or modified rules apply only to newly cached resources. Resources that were cached before the change will continue to use the old cache policy until they expire.
To apply new rules across the entire network immediately, manually clear the existing cache. If you change a rule, purge the cached content by using the Purge resource feature. If you add a new rule, pre-populate the cache by using the Prefetch resource feature.
Verify the configuration
After configuration, you can use the curl command or browser developer tools to inspect the HTTP response Headers of a resource to verify that caching is working as expected.
1. Run the verification command
Run the following command in your terminal to test the configuration.
curl -I "https://your.domain.com/path/to/file.jpg"2. Interpret key response Headers
Response Header | Common values and interpretation |
| Indicates if the request was a cache hit.
|
| If Client Follows CDN Cache Policy is enabled, this Header shows the cache directive sent to the browser, such as |
| The total configured cache duration for the resource on the CDN POP, in seconds. |
Best practices
Use versioned filenames (recommended): When updating a static resource like
style.css, use a new filename with a version or hash value, such asstyle-v2.cssorstyle-a1b2c3d.css, and update the reference in your HTML. This method does not require a manual cache refresh and ensures users get the latest content immediately. This is the recommended way to manage cache updates.Separate dynamic and static assets: Use different domains or directory paths for dynamic and static resources. Configure separate, high-weight cache rules for each resource type to avoid policy conflicts. For example, set a long cache duration for all resources under the
/static/directory and set no-cache for resources under the/api/directory.Use the browser cache: Enable Follow POP Cache Policy to reduce repeated requests to POPs, which improves loading speed and saves traffic.
Avoid setting the cache duration too short: An overly short cache duration leads to frequent origin requests, which negates the benefits of acceleration and increases your origin server's traffic and costs.
Avoid setting the cache duration too long: An overly long cache duration can prevent clients from receiving timely data updates. For content that needs frequent updates, use the cache refresh feature or versioned filenames.
HTTP cache-control mechanisms
The HTTP protocol defines three types of Headers to implement cache control.