Managed Service for OpenTelemetry allows you to create alert rules. If an alert is triggered, the system sends alert notifications to a contact group based on the notification methods specified in the alert rule. This way, you can handle the alert at the earliest opportunity.
Prerequisites
Contacts are created. Only contact groups can be set as the notification receiver of an alert.
Background information
By default, alert notifications are sent based on the following rules:
To prevent you from receiving a large number of alert notifications in a short period of time, the system sends only one message for repeated alerts within 24 hours.
If no repeated alerts are generated within 5 minutes, the system sends a recovery email to notify you that the alert is cleared.
After a recovery email is sent, the system resets the alert status. If this alert is triggered again, it is treated as a new one.
An alert control is a method to display data in datasets. When you create an alert control, a dataset is also created to store the underlying data of the alert control.
New alerts take effect within 10 minutes. The alert check may require 1 to 3 minutes.
Create an alert rule
To create an alert for an application monitoring task on Java Virtual Machine-Garbage Collection (JVM-GC) times in period-over-period comparison, perform the following steps:
Log on to the Managed Service for OpenTelemetry console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Alarm Policies page, click Create Alerm in the upper-right corner.
In the Create Alarm dialog box, configure the required parameters and click Save.
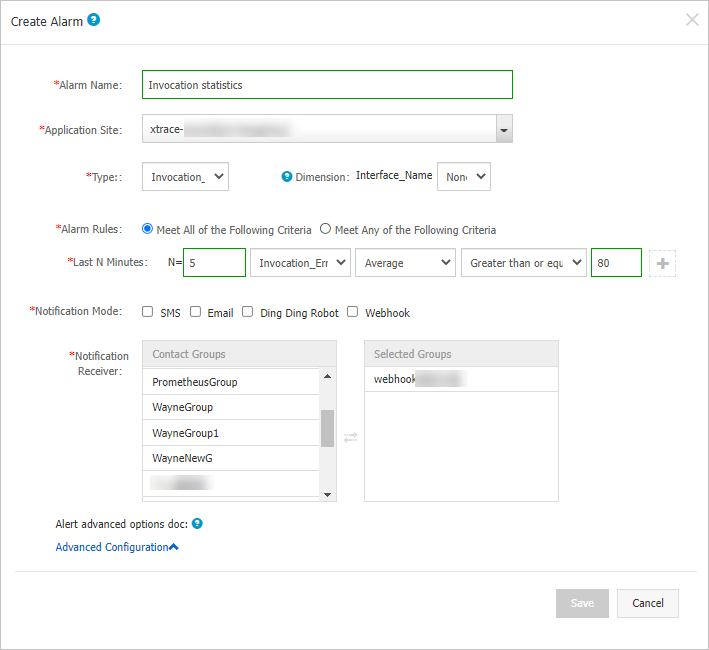
Specify the Alarm Name parameter. In this example, Application Call Statistics is entered.
Select an application from the Application Site drop-down list.
Select a metric type from the Type drop-down list. For example, you can select Invocation_Statistic.
Set the Dimension parameter to Traverse.
Set the Alarm Rules parameter to Meet All of the Following Criteria.
Specify the Last N Minutes parameter to configure alert rules. For example, if the average error rate in the last 5 minutes is greater than or equal to 100%, an alert is triggered.
NoteTo add more alert rules, click the
 icon next to the Last N Minutes parameter.
icon next to the Last N Minutes parameter. Configure the Notification Mode parameter. For example, you can select Email.
Specify the Notification Receiver parameter. In the Contact Groups list, click the name of a contact group. If the contact group appears in the Selected Groups list, the setting is successful.
Parameter description
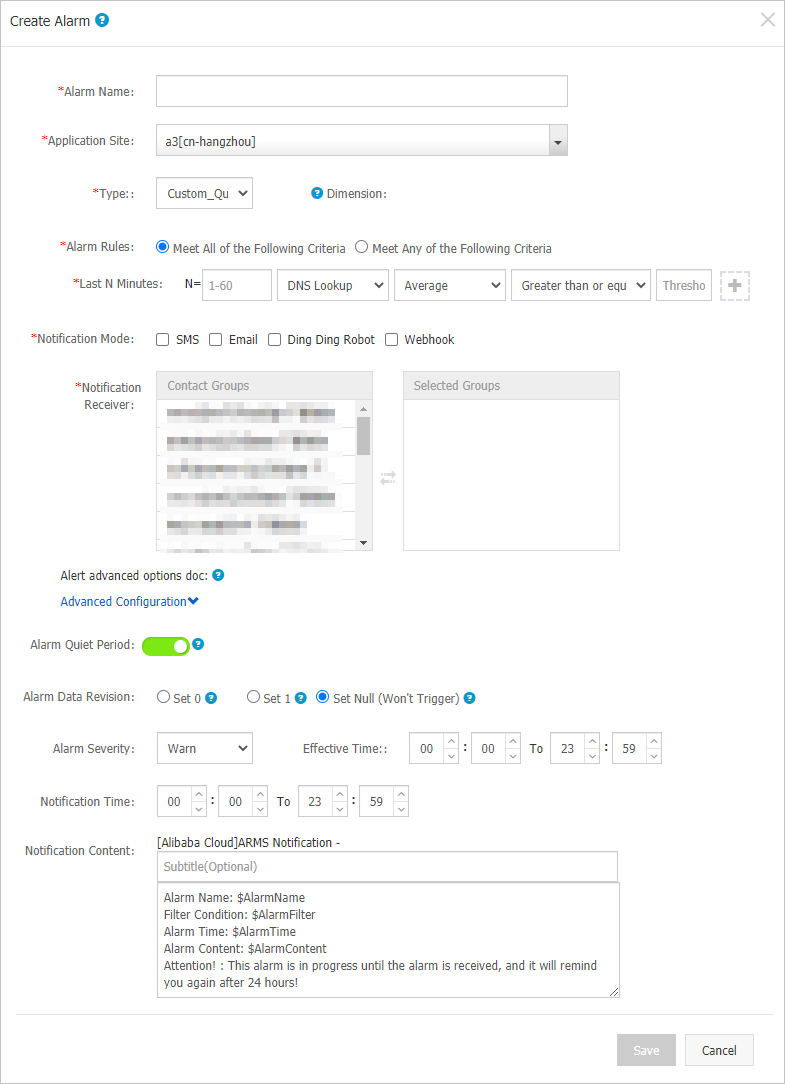
The following table describes the parameters in the Create Alarm dialog box.
Parameter | Meaning | Description |
Application Site | The monitoring task for which the alert rule is created. | Select a monitoring task from the drop-down list. |
Dimension | The dimension for the specified metric (dataset). You can select None, =, or Traverse. |
|
Last N Minutes | The system checks whether the metric value in the last N minutes meets the trigger condition. | Valid values of N: 1 to 60. |
Notification Mode | Valid values: Email, SMS, Ding Ding Robot, and Webhook. | You can select multiple notification methods. For more information about how to configure a DingTalk chatbot alert, see Obtain the webhook URL of a DingTalk chatbot. |
Alarm Quiet Period | You can turn on or turn off Alarm Quiet Period. By default, Alarm Quiet Period is turned on. |
|
Alarm Severity | Valid values: Warn, Error, and Fatal. | N/A |
Notification Time | The time range during which alert notifications can be sent. No alert notifications are sent outside of this time range, but alert events are recorded. | For more information about how to view alert event records, see Manage alerts. |
Notification Content | The custom content of the alert notification. | You can edit the default template. In the template, you must specify the $AlarmName, $AlarmFilter, $AlarmTime, and $AlarmContent variables. The rest of the content can be customized. Other variables are not supported. |
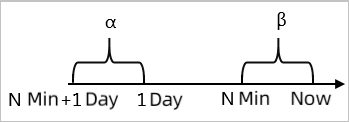
Description of complex general parameters: period-over-period comparison
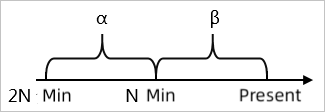
Minute-on-minute comparison: For example, β indicates the data in the last N minutes and α indicates the data generated between the last 2N and N minutes. The minute-on-minute comparison is the percentage increase or decrease when β is compared with α. The data can be the average value, sum, maximum value, or minimum value.
Minute-on-minute hourly comparison: For example, β indicates the data in the last N minutes and α indicates the data generated in the last N minutes in the previous hour. The minute-on-minute hourly comparison is the percentage increase or decrease when β is compared with α.
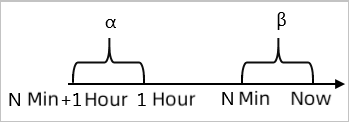
Minute-on-minute daily comparison: For example, β indicates the data in the last N minutes and α indicates the data generated in the last N minutes at the same time in the previous day. The minute-on-minute daily comparison is the percentage increase or decrease when β is compared with α.
Description of complex general parameter: Alarm Data Revision
You can set the Alarm Data Revision parameter to Set 0, Set 1, or Set Null (Won't Trigger). This parameter allows you to fix data anomalies, such as no data, abnormal composite metrics, and abnormal period-over-period comparisons.
Fill 0: fixes the checked value to 0.
Fill 1: fixes the checked value to 1.
Set Null (Won't Trigger): does not trigger the alert.
Scenarios:
Anomaly 1: no data
User A wants to use the alerting feature to monitor page views. When User A creates a browser monitoring, alert, User A specifies that an alert is triggered if the sum of page views is less than or equal to 10 in the last 5 minutes. If the page is not accessed, no data is reported, and no alert notification is sent. To resolve this issue, User A can select Fill 0 for the Alarm Data Revision Policy parameter. If no data is received, the system determines that zero data records are received. This meets the conditions specified in the alert rule, and an alert notification is sent.
Anomaly 2: abnormal period-over-period comparisons
User C wants to use the alerting feature to monitor the CPU usage of a node. When User C creates an application monitoring alert, User C specifies that an alert is triggered if the average CPU usage of the node in the last 3 minutes decreases by 100% compared with that in the previous monitoring period. If the CPU fails in the last N minutes, the system cannot obtain α, which is used to calculate the period-over-period comparison result. In this case, the comparison result does not exist. No alert notification is sent. To resolve this issue, User C can select Fill 1 for the Alarm Data Revision Policy parameter. If α is not obtained, the system determines that the period-over-period comparison result is a decrease of 100%. This meets the conditions specified in the alert rule, and an alert notification is sent.
What to do next
You can query and delete alert records in alert management.