This topic describes how to use the Paho Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) library for Java to connect to and communicate with IoT Platform.
Usage notes
In this topic, the permissions of a common user are used to perform all operations. If you want to perform specific operations that require administrator permissions, run the sudo command.
Prerequisites
A product and a device are created in the IoT Platform console. The LightSwitch property is defined on the Define Feature tab of the Product Details page.For more information, see Create a product, Create a device and Add a TSL feature.
Prepare the development environment
In this example, the development environment consists of the following components:
Operating system: Windows 10
Java Development Kit (JDK): JDK 8
Integrated development environment (IDE): IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition
Download the Paho MQTT library for Java
Add dependencies to the Maven project based on the version of the MQTT protocol.
MQTT 3.1 and 3.1.1
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.paho</groupId> <artifactId>org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3</artifactId> <version>1.2.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>MQTT 5.0
<dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.paho</groupId> <artifactId>org.eclipse.paho.mqttv5.client</artifactId> <version>1.2.5</version> </dependency>
Connect a device to IoT Platform
Click MqttSign.java to obtain the source code provided by Alibaba Cloud. The source code is required to obtain the MQTT connection parameters.
The MqttSign.java file specifies the MqttSign class.
Syntax
class MqttSign- Description
You can use this class to obtain the following MQTT connection parameters: username, password and clientid.
Members
Type
Method
public void
calculate(String productKey, String deviceName, String deviceSecret)Obtains the username, password, and clientid parameters based on the productKey, deviceName, and deviceSecret parameters.
public String
getUsername()Obtains the username parameter.
public String
getPassword()Obtains the password parameter.
public String
getClientid()Obtains the clientid parameter.
Open IntelliJ IDEA and create a project.
Import the MqttSign.java file to the project.
In the project, add a program file that can connect a device to IoT Platform.
You must write a program to use the MqttSign class in the MqttSign.java file. This way, you can obtain the parameters that are used to establish an MQTT connection to IoT Platform.
This section provides the development instructions and sample code of establishing the connection.
Use the MqttSign class to obtain the MQTT connection parameters.
String productKey = "a1X2bEn****"; String deviceName = "example1"; String deviceSecret = "ga7XA6KdlEeiPXQPpRbAjOZXwG8y****"; // Obtain the MQTT connection parameters. MqttSign sign = new MqttSign(); sign.calculate(productKey, deviceName, deviceSecret); System.out.println("username: " + sign.getUsername()); System.out.println("password: " + sign.getPassword()); System.out.println("clientid: " + sign.getClientid());Create a Paho MQTT client to connect to IoT Platform.
// Specify the endpoint that you want to use to connect a device to IoT Platform. String port = "443"; String broker = "ssl://" + productKey + ".iot-as-mqtt.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com" + ":" + port; // Create a Paho MQTT client. MqttClient sampleClient = new MqttClient(broker, sign.getClientid(), persistence); // Configure the MQTT connection parameters. MqttConnectOptions connOpts = new MqttConnectOptions(); connOpts.setCleanSession(true); connOpts.setKeepAliveInterval(180); connOpts.setUserName(sign.getUsername()); connOpts.setPassword(sign.getPassword().toCharArray()); sampleClient.connect(connOpts); System.out.println("Broker: " + broker + " Connected");ImportantModify the endpoint in
String broker = "ssl://" + productKey + ".iot-as-mqtt.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com" + ":" + port;. The value of the broker parameter must be in the following format:"ssl://" + "${Endpoint of the IoT Platform instance to which the device wants to connect over MQTT}" + ":" + port.For more information about the endpoints of public instances and Enterprise Edition instances and the formats of the endpoints, see View the endpoint of an instance.
Publish messages.
The following code shows how to submit the LightSwitch property.
// Publish messages by using Paho MQTT. String topic = "/sys/" + productKey + "/" + deviceName + "/thing/event/property/post"; String content = "{\"id\":\"1\",\"version\":\"1.0\",\"params\":{\"LightSwitch\":1}}"; MqttMessage message = new MqttMessage(content.getBytes()); message.setQos(0); sampleClient.publish(topic, message);If you use MQTT 5.0, you can add the following sample code to publish messages that contain custom properties.
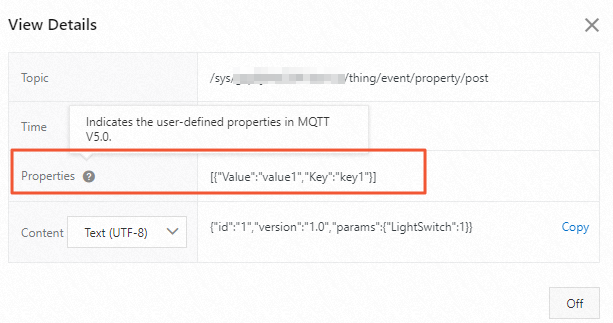
// New feature in MQTT 5.0: Create custom properties. MqttProperties properties = new MqttProperties(); List<UserProperty> userPropertys = new ArrayList<>(); userPropertys.add(new UserProperty("key1","value1")); properties.setUserProperties(userPropertys); // New feature in MQTT 5.0: Specify the request and response mode. properties.setCorrelationData("requestId12345".getBytes()); properties.setResponseTopic("/" + productKey + "/" + deviceName + "/user/get"); message.setProperties(properties); // By default, Paho SDK that supports MQTT 5.0 uses topic aliases. sampleClient.publish(topic, message);For information about the formats of TSL data, see Device properties, events, and services.
For information about how to use custom topics for communication, see Topics.
Subscribe to a topic to obtain messages from IoT Platform.
The following code shows how to subscribe to a topic. IoT Platform returns a response message to the topic after the property is submitted.
class MqttPostPropertyMessageListener implements IMqttMessageListener { @Override public void messageArrived(String var1, MqttMessage var2) throws Exception { System.out.println("reply topic : " + var1); System.out.println("reply payload: " + var2.toString()); } } ... // Subscribe to a topic by using Paho MQTT. String topicReply = "/sys/" + productKey + "/" + deviceName + "/thing/event/property/post_reply"; sampleClient.subscribe(topicReply, new MqttPostPropertyMessageListener());
For more information about the communication methods of devices, servers, and IoT Platform, see Overview.
Click the Build Project button whose icon is
 to compile the project.
to compile the project.
Sample code
You can run the sample code to connect a device to IoT Platform.
Download a demo package from v3.1.1 Demo or v5.0 Demo and decompress the package.
Open IntelliJ IDEA and import the sample project aiot-java-demo in the demo package.
In the src/main/java/com.aliyun.iot directory, replace the sample device information with your device information in the App or Mqtt5App file.
NoteIf you use MQTT 3.1 or 3.1.1, replace the sample device information in the App file with your device information. If you use MQTT 5.0, replace the sample device information in the Mqtt5App file with your device information.
Replace the sample values of the productKey, deviceName, and deviceSecret parameters with your device certificate information.
String productKey = "${ProductKey}"; String deviceName = "${DeviceName}"; String deviceSecret = "${DeviceSecret}";Modify the endpoint in
String broker = "ssl://" + productKey + ".iot-as-mqtt.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com" + ":" + port;. For more information, see Step 4 in the "Connect a device to IoT Platform" section of this topic.
Run the App or Mqtt5App program.
The following figure shows the success logs.
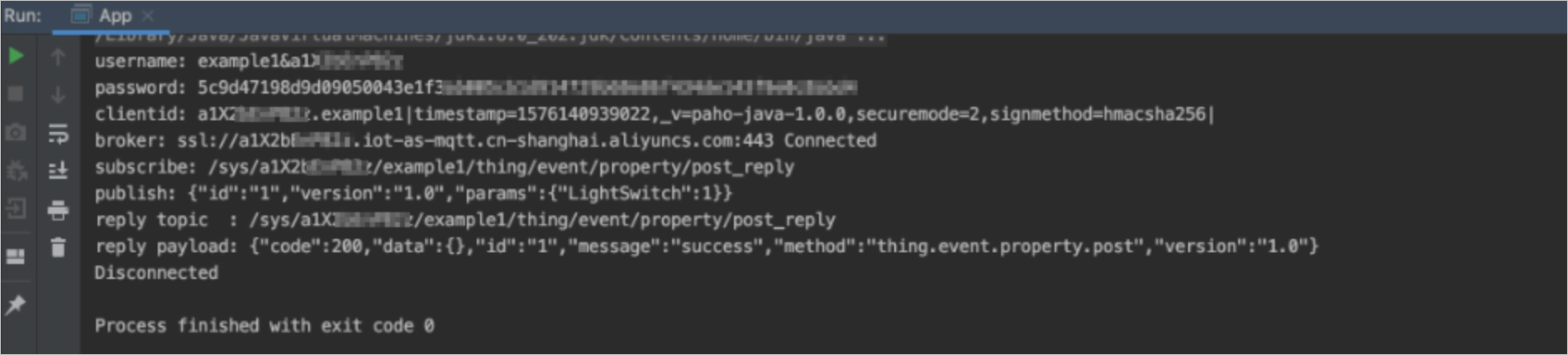
In the IoT Platform console, you can view the device status and logs.
Choose . The Devices page shows that the device is in Online state.
Choose . Then, click the Cloud run log or Device local log tab to view logs. For more information, see IoT Platform logs and Local device logs.
If you run the Mqtt5App program, you can view the custom properties that the device submitted in logs.
Error codes
If a device fails to establish an MQTT connection to IoT Platform, you can troubleshoot the issue based on the error code. For more information, see Troubleshooting.