To use private IP addresses for a private zone within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), you can create an Inbound Endpoint to allocate custom service IP addresses. These addresses are created on demand and use the pay-as-you-go billing method. This topic describes how to create an Inbound Endpoint to customize private Domain Name System (DNS) service IP addresses.
Overview
An Inbound Endpoint is the nameserver address for a private zone. You can configure it as the DNS service address for cloud-based clients, such as Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances or containers. You can also configure it as the target IP address for external clients, such as on-premises hosts or external DNS servers, to access the private zone. There are two types of Inbound Endpoint: system-assigned and custom. The default system-assigned private zone IP addresses are 100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138. These addresses use anycast to provide DNS resolution services for all VPCs in all regions free of charge.
Available regions
This feature is available in the following regions:
Public cloud regions: South Korea (Seoul), Singapore, China (Hong Kong), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Hangzhou), China (Ulanqab), China (Shenzhen), Philippines (Manila), US (Virginia), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Germany (Frankfurt), Indonesia (Jakarta), and Japan (Tokyo).
Finance Cloud regions: China (Hangzhou), China (Beijing), and China (Shanghai).
Limits
Limit | Threshold | Description |
Maximum requests for a single inbound service IP address (Standard Edition) | 5,000 queries per second | A single inbound service IP address supports a peak query rate of 5,000 queries per second. DNS requests that exceed this peak are randomly discarded. The Service-Level Agreement (SLA) is not guaranteed. |
Maximum requests from a single client source IP address | 5,000 queries per second |
|
Maximum external recursive resolution requests from a single client source IP address | 600 queries per second | |
Number of service IP addresses for a single Inbound Endpoint | A minimum of 2 and a maximum of 6 | To ensure high availability (HA), a single Inbound Endpoint must have at least two service IP addresses and can have a maximum of six. |
Usage rules
The usage rules for Inbound Endpoint vary depending on the source of DNS query traffic:
Internal DNS query traffic (from ECS instances and containers)
Effective scope | Inbound Endpoint: Custom (custom IP address within a VPC) | Inbound Endpoint (system-assigned, 100.100.2.136/100.100.2.138) |
Effective Scope of Inbound Service IP Addresses | The inbound VPC. Other VPCs that require access must establish network connectivity with the inbound VPC through Express Connect or Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN). | Accessible from all VPCs |
Set by associated VPCs (for example, for Private Zone domain names, cache reserve domain names, or forwarding rules) | Supported. However, the domain name's effective scope must be the inbound VPC for the resolution settings to take effect. | Supported. The effective scope can be set to the inbound VPC or other VPCs. The resolution settings take effect within the associated VPC. |
Implementing line-based intelligent resolution | Configure a custom resolution line | Set a custom line or the effective scope of the domain name. |
External DNS query traffic (traffic entering through an inbound VPC)
Effective scope | Inbound Endpoint: Custom (custom IP address within a VPC) | Inbound Endpoint (100.100.2.136/100.100.2.138) |
Inbound service IP addresses | The inbound VPC. On-premises data centers that require access must establish network connectivity with the inbound VPC through a leased line, VPN, or SWAN. | The inbound VPC. On-premises data centers that require access must establish network connectivity with the inbound VPC through a leased line, VPN, or SWAN. |
Set by associated VPCs (for example, for Private Zone domain names, cache reserve domain names, or forwarding rules) | Supported. However, the domain name's effective scope must be the inbound VPC for the resolution settings to take effect. | Supported. However, the domain name's effective scope must be the inbound VPC for the resolution settings to take effect. |
How Split-Line Intelligent Resolution Works | Set a custom line. |
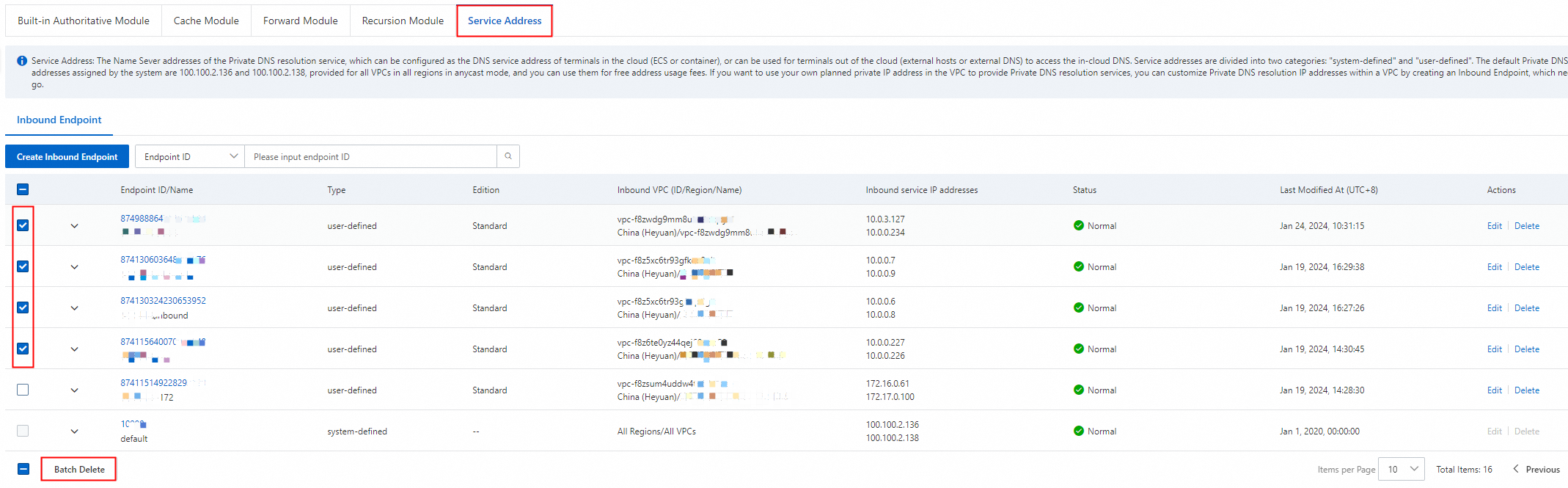
Add Inbound Endpoint
On the Inbound Endpoint tab, click Add Inbound Endpoint and fill out the form.
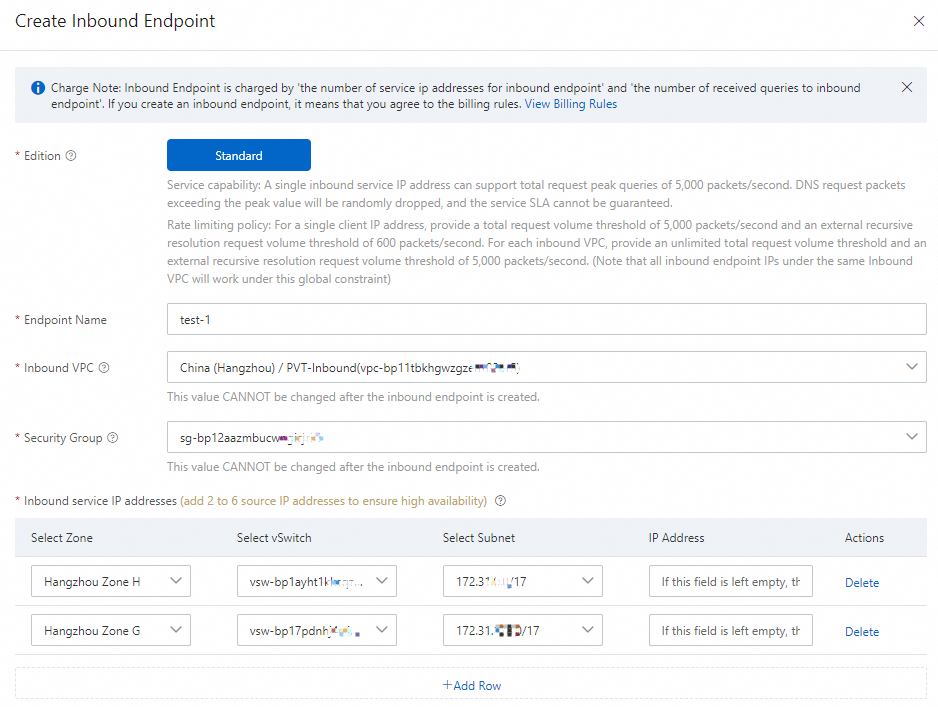
Form Item
Description
Edition
The edition of the Inbound Endpoint. Only the Standard Edition is currently available.
Endpoint Name
You can name it according to your business needs.
Inbound VPC
All inbound DNS query traffic is routed through this VPC.
ImportantYou cannot change the inbound VPC after an Inbound Endpoint is created. This prevents accidental traffic interruptions.
For information about the regions where this feature is available, see the "Available regions" section. We are collecting feedback to prioritize the release in other regions. To request this feature in another region, submit a ticket and specify the region.
Security Group
The rules in the security group are applied to the inbound VPC. For more information, see Create a security group.
ImportantIn the security group of the inbound VPC, allow inbound traffic on port 53 from the source CIDR block for DNS queries.
If inbound traffic originates from other VPCs within Alibaba Cloud, allow outbound traffic on port 53 in the security groups of those VPCs.
Inbound service IP addresses
The IP addresses must be available in subnets within a zone and not be in use by Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. To ensure high availability, you must add at least two inbound IP addresses, preferably in different zones. An Inbound Endpoint supports a maximum of 6 inbound IP addresses.
ImportantYou cannot add or modify the service IP address of an Inbound Endpoint if that address is the same as the target IP address of a forwarding rule and the outbound endpoint for that rule is in the same VPC as the Inbound Endpoint. This restriction does not apply if the endpoints are in different VPCs. If a resolution loop occurs because VPCs are connected through CEN, a SERVFAIL error is returned.
If you do not specify IP addresses, the system automatically assigns them.
Submit the form to create the Inbound Endpoint.
The Inbound Endpoint list displays the inbound endpoints that you have created. The status of an Inbound Endpoint can be Normal, Creating, Create failed., Modifying, Modify failed., or Abnormal.
ImportantCreating an Inbound Endpoint takes 5 to 10 minutes. If the status is Creating, wait for the process to complete.
You cannot modify or delete endpoints with a status of Creating or Modifying. If an endpoint's status is Abnormal or Modify failed., you can submit a ticket to request troubleshooting and resolution.
Modify Inbound Endpoint
On the Inbound Endpoint tab, click Edit in the Actions column for the target endpoint.
In the dialog box, you can modify the Endpoint Name and Inbound service IP addresses.
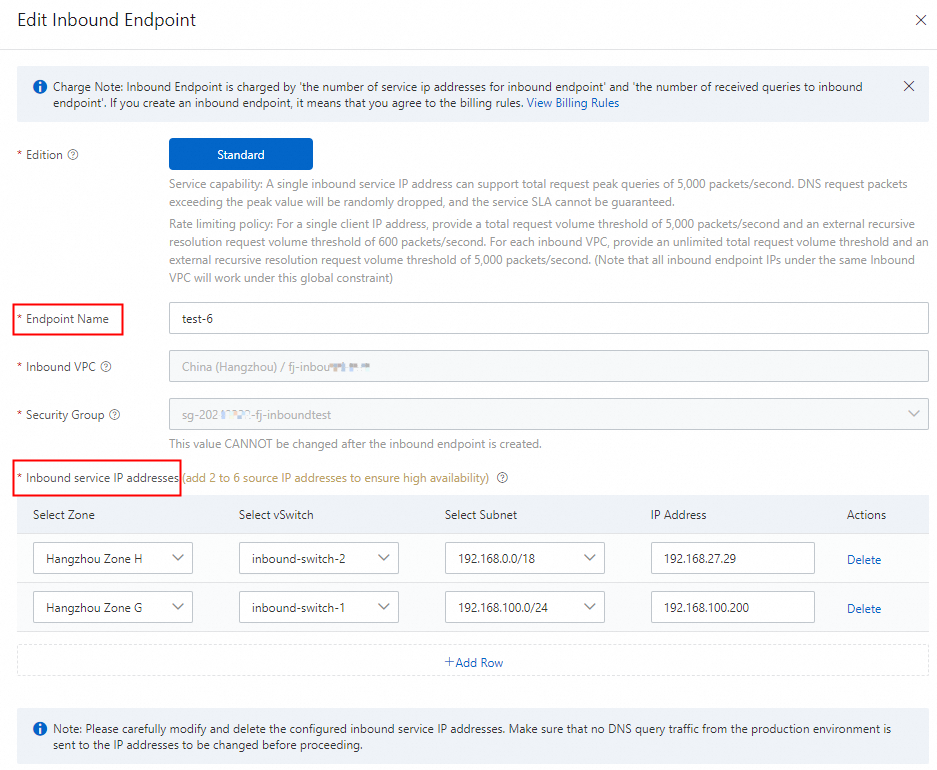
After you submit the form, the status of the endpoint in the list changes to Modifying. While the endpoint is in this state, you cannot perform any other operations.
Delete Inbound Endpoint
Delete a single Inbound Endpoint
On the Inbound Endpoint tab, click the Delete button in the Actions column for the target endpoint, and confirm the operation in the dialog box to delete the node.
Batch delete Inbound Endpoint
On the Inbound Endpoint tab, select the Inbound Endpoint that you want to delete and click the Batch Delete button at the bottom of the page. After you confirm the operation in the dialog box, the nodes are deleted.