By Jianbo Sun
If you're looking for something to glue Terraform ecosystem with the Kubernetes world, congratulations! You're getting exactly what you want in this blog.
We will introduce how to integrate terraform modules into KubeVela by fixing a real world problem -- "Fixing the Developer Experience of Kubernetes Port Forwarding" inspired by article from Alex Ellis.
In general, this article will be divided into two parts:
OK, let's go!
In general, KubeVela is a modern software delivery control plane, you may ask: "What benefit from doing this":
1. The power of gluing Terraform with Kubernetes ecosystem including Helm Charts in one unified solution, that helps you to do GitOps, CI/CD integration and application lifecycle management.
2. Declarative model for all the resources, KubeVela will run the reconcile loop until succeed.
3. A powerful CUE based workflow that you can define any preferred steps in the application delivery process.
If you're already a good hand of terraform, it's pretty easy for this integration.
This part can usually be skipped, if you already have a well-tested terraform module,
Before start, make sure you have:
Here's my terraform module for this demo.
git clone https://github.com/wonderflow/terraform-alicloud-ecs-instance.git
cd terraform-alicloud-ecs-instanceterraform initexport ALICLOUD_ACCESS_KEY="your-accesskey-id"
export ALICLOUD_SECRET_KEY="your-accesskey-secret"
export ALICLOUD_REGION="your-region-id"You can also create an provider.tf including the credentials instead:
provider "alicloud" {
access_key = "your-accesskey-id"
secret_key = "your-accesskey-secret"
region = "cn-hangzhou"
}terraform apply -var-file=test/test.tfvarsterraform destroy -var-file=test/test.tfvarsYou can customize this module per your needs and push to github of your own.
Before start, make sure you have installed kubevela control plane, don't worry if you don't have Kubernetes cluster, velad is enough for the quick demo.
We'll use the terraform module we have already prepared just now.
vela def init ecs --type component --provider alibaba --desc "Terraform configuration for Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service" --git https://github.com/wonderflow/terraform-alicloud-ecs-instance.git > alibaba-ecs-def.yamlChange the git url with your own if you have customized.
vela kube apply -f alibaba-ecs-def.yaml
vela kube applyworks the same withkubectl apply.
Then the extension of ECS module has been added, you can learn more details from here.
We have finished the integration, the end user can discover the capability immediately after the apply.
The end user can use following commands to check the parameters:
vela show alibaba-ecsThey can also view it from website by launching:
vela show alibaba-ecs --webThat's all of the integration needed.
In this part, we will introduce a solution that you can expose any of your Kubernetes service to public with a specific port. The solution is composed by:
1u1g) automatically by access key.Install KubeVela
curl -fsSl https://static.kubevela.net/script/install-velad.sh | bash
velad installCheck this doc to learn more details of installation.
vela addon enable terraform
vela addon enable terraform-alibabavela config create terraform-alibaba-default -t terraform-alibaba ALICLOUD_ACCESS_KEY=<"your-accesskey-id"> ALICLOUD_SECRET_KEY="your-accesskey-secret" ALICLOUD_REGION=<your-region> DANGER
Before the 1.6.0 version:vela provider add terraform-alibaba --ALICLOUD_ACCESS_KEY <"your-accesskey-id"> --ALICLOUD_SECRET_KEY "your-accesskey-secret" --ALICLOUD_REGION <your-region> --name terraform-alibaba-default
Check this doc for more details about other clouds.
frp ServerAfter the environment prepared well, you can create an application as below.
cat <<EOF | vela up -f -
# YAML begins
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: ecs-demo
spec:
components:
- name: ecs-demo
type: alibaba-ecs
properties:
providerRef:
name: terraform-alibaba-default
writeConnectionSecretToRef:
name: outputs-ecs
name: "test-terraform-vela-123"
instance_type: "ecs.n1.tiny"
host_name: "test-terraform-vela"
password: "Test-123456!"
internet_max_bandwidth_out: "10"
associate_public_ip_address: "true"
instance_charge_type: "PostPaid"
user_data_url: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wonderflow/terraform-alicloud-ecs-instance/master/frp.sh"
ports:
- 8080
- 8081
- 8082
- 8083
- 9090
- 9091
- 9092
tags:
created_by: "Terraform-of-KubeVela"
created_from: "module-tf-alicloud-ecs-instance"
# YAML ends
EOFThis application will deploy an ECS instance with a public ip, explanation of some useful fields:
| Field | Usage |
| providerRef | reference to the provider credentials we added |
| writeConnectionSecretToRef | the outputs of terraform module will be written into the secret |
| name | name of the ecs instance |
| instance_type | ecs instance type |
| host_name | hostname of the ecs |
| password | password of the ecs instance, you can connect by ssh
|
| internet_max_bandwidth_out | internet bandwidth of the ecs instance |
| associate_public_ip_address | create public IP or not |
| instance_charge_type | the charge way of the resource |
| user_data_url | the installation script after the ecs instance created, we have installed the frp server in the script |
| ports | ports that will be allowd in the VPC and security group, 9090/9091 is must for frp server while others are preserved for client usage |
| tags | tags of the ECS instance |
You can learn more fields by:
vela show alibaba-ecsAfter applied, you can check the status and logs of the application by:
vela status ecs-demo
vela logs ecs-demoYou can get the secret from the terraform resource contains the output values.
You may already see the result in vela logs, you can also check the output information from Terraform by:
$ kubectl get secret outputs-ecs --template={{.data.this_public_ip}} | base64 --decode
["121.196.106.174"]KubeVela will soon support query resource like this https://github.com/kubevela/kubevela/issues/4268
As a result, you can visit the frp server admin page on port :9091, the admin password is vela123 in the script.
By now, we have finished the server part here.
The usage of frp client is very straight-forward, we can provide public IP for any of the service inside the cluster.
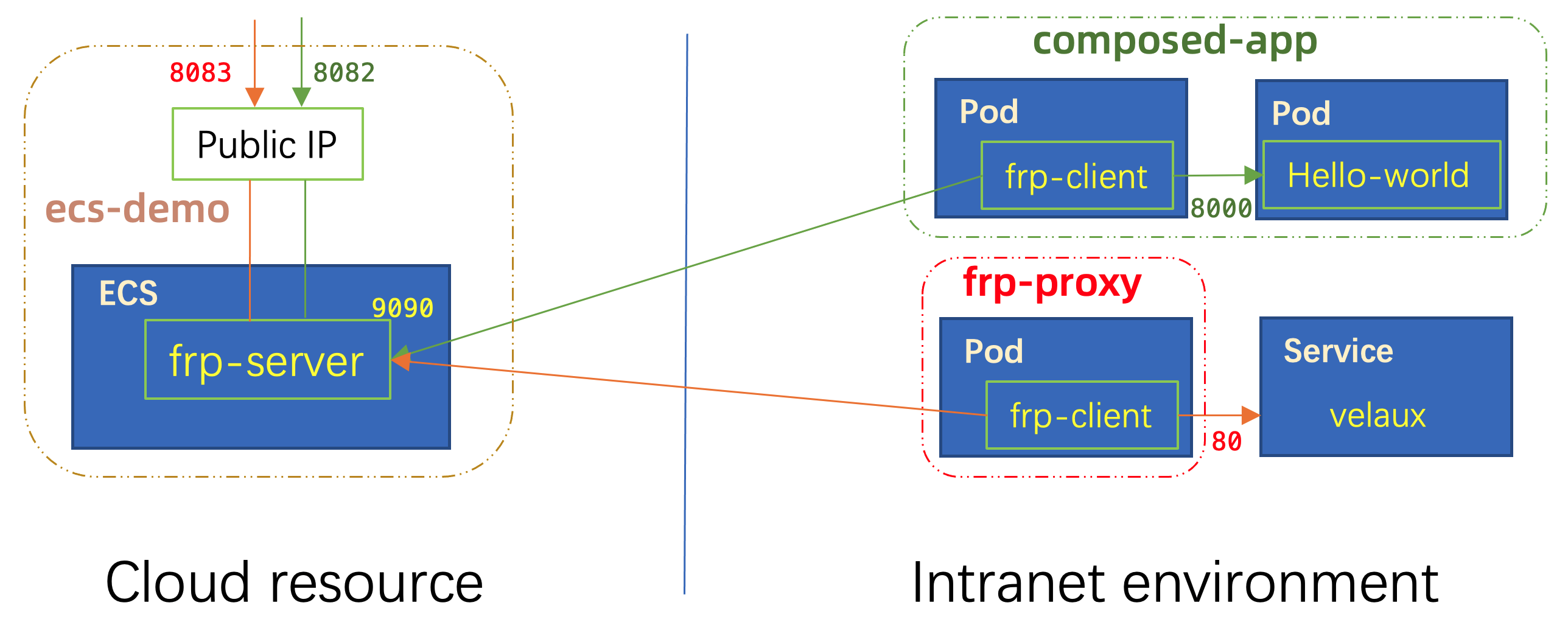
1) Deploy as standalone to proxy for any Kubernetes Service.
cat <<EOF | vela up -f -
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: frp-proxy
spec:
components:
- name: frp-proxy
type: worker
properties:
image: oamdev/frpc:0.43.0
env:
- name: server_addr
value: "121.196.106.174"
- name: server_port
value: "9090"
- name: local_port
value: "80"
- name: connect_name
value: "velaux-service"
- name: local_ip
value: "velaux.vela-system"
- name: remote_port
value: "8083"
EOFIn this case, we specify the local_ip by velaux.vela-system, which means we're visiting the Kubernetes Service with name velaux in the namespace vela-system.
As a result, you can visit velaux service from the public IP 121.196.106.174:8083.
2) Compose two components together for the same lifecycle.
cat <<EOF | vela up -f -
# YAML begins
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: composed-app
spec:
components:
- name: web-new
type: webservice
properties:
image: oamdev/hello-world:v2
ports:
- port: 8000
expose: true
- name: frp-web
type: worker
properties:
image: oamdev/frpc:0.43.0
env:
- name: server_addr
value: "121.196.106.174"
- name: server_port
value: "9090"
- name: local_port
value: "8000"
- name: connect_name
value: "composed-app"
- name: local_ip
value: "web-new.default"
- name: remote_port
value: "8082"
EOFWow! Then you can visiting the hello-world by:
curl 121.196.106.174:8082The webservice type component will generate a service with the name of the component automatically. The frp-web component will proxy the traffic to the service web-new in the default namespace which is exactly the service generated.
When the application deleted, all of the resources defined in the same app are deleted together.
You can also compose the database together with them, then you can deliver all components needed in one time.
You can clean up all the applications in the demo by vela delete:
vela delete composed-app -y
vela delete frp-proxy -y
vela delete ecs-demo -yI think you've learned how to use KubeVela in this scenario now, just try it in your environment!
In this blog, we have introduced the way to integrate Terraform module with KubeVela. It provides interesting use case that allow you to expose any of inner service to public.
While KubeVela can do more things than that, go and discover it at kubevela.io!
Trace and Visualize the Relationships Between the Kubernetes Resources with KubeVela
Alibaba Cloud's Jianfeng Zhang: Core Cloud Products Are Fully Serverless

672 posts | 56 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - November 18, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 27, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - July 12, 2022
Aliware - July 27, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 16, 2023
Alibaba Developer - January 14, 2020

672 posts | 56 followers
Follow Apsara Stack
Apsara Stack
Apsara Stack is a full-stack cloud solution created by Alibaba Cloud for medium- and large-size enterprise-class customers.
Learn More ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
Elastic and secure virtual cloud servers to cater all your cloud hosting needs.
Learn More Super Computing Cluster
Super Computing Cluster
Super Computing Service provides ultimate computing performance and parallel computing cluster services for high-performance computing through high-speed RDMA network and heterogeneous accelerators such as GPU.
Learn More Elastic High Performance Computing
Elastic High Performance Computing
A HPCaaS cloud platform providing an all-in-one high-performance public computing service
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community