By Max Meiden Dasuki, Solutions Architect
With the massive growth of internet and mobile phone adoption, many games nowadays target people from around the world as their users. These games have millions if not tens of millions (or potentially hundreds of millions) of players globally playing their game. Obviously at such a scale, game developers require a platform that can provide a reliable and highly available solution. Therefore, it is not uncommon to see game developers migrating their platform to the cloud.
In this article, we will look at a relatively simple problem – creating a leaderboard for a game. If you're using a traditional relational database that is built on-premises, this problem can be challenging. You would have to devise an efficient solution to produce real-time results while considering millions of users from around the world.
The answer? Using a Redis database deployed on the cloud. Redis has a sorted set API that can help you to achieve that. Coupled with Alibaba Cloud's ability to manage Redis clusters, your needs will be covered in the best possible way. In this how to guide, we will be using Python programming language to achieve this.
The main idea of this demonstration is to use caching layer (Redis) instead of hitting the database to generate leaderboards in gaming applications. This approach is suitable for massive databases that require real-time responses.
While it's not compulsory, the basic understanding of Python is an added advantage (the sample code is in Python). Since we're utilizing Redis, it's also good to read up about it to get a better idea of what Redis is as well.
I will not go through creating Redis cluster in Alibaba Cloud, since you can read and follow the step-by-step command separately in this guide. It's easy and straight forward to set it up.
ssh -i root@rm /usr/bin/python # Change python into version 3
ln -s /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python
apt-get update # Update Ubuntu
export LC_ALL=C # Set Locale
apt-get install python3-pip # Install pip
pip install redis # Install python-redis
apt-get install apache2 # Install apache
mkdir /var/www/python # Set Environment
a2dismod mpm_event
a2enmod mpm_prefork cgi-----
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot /var/www/python
<Directory /var/www/python>
Options +ExecCGI
DirectoryIndex leaderboards.py
</Directory>
AddHandler cgi-script .py
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
-----chmod 755 /var/www/python/leaderboards.pyservice apache2 restartBelow is the code sample in Python, which I'll explain further:
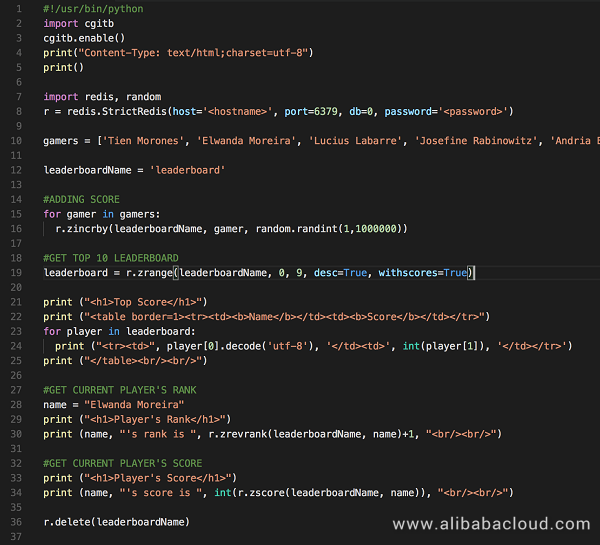
Code explanation:
r = redis.StrictRedis(host='', port=6379, db=0, password='') 
r.zincrby(leaderboardName, gamer, random.randint(1,1000000)) r.zrange(leaderboardName, 0, 9, desc=True, withscores=True)r.zrevrank(leaderboardName, gamer)+1r.zscore(leaderboardName, gamer) Below is the expected response of the code when you run it on a webserver.
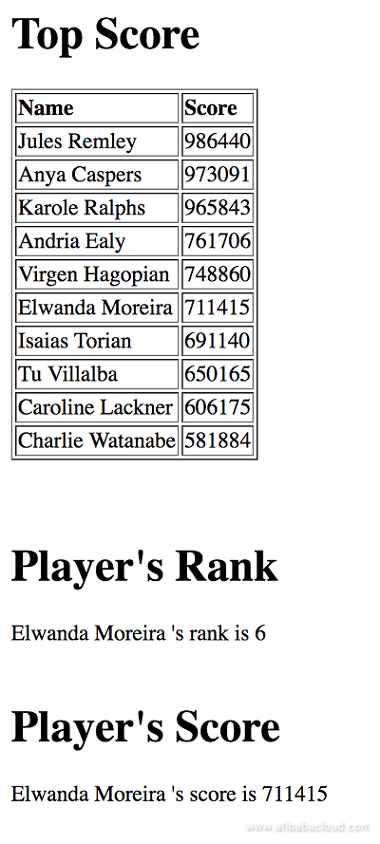
Redis stores data in-memory, and the maturity of the product makes it able to reach performance of millions of requests per second. This makes it the perfect database for this use case and other caching needs.
To learn more about Redis on Alibaba Cloud, visit the ApsaraDB for Redis page.

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - May 5, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - February 10, 2017
ApsaraDB - December 15, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - May 6, 2021
ApsaraDB - September 9, 2021
JJ Lim - December 6, 2021

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow Tair (Redis® OSS-Compatible)
Tair (Redis® OSS-Compatible)
A key value database service that offers in-memory caching and high-speed access to applications hosted on the cloud
Learn More ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
Elastic and secure virtual cloud servers to cater all your cloud hosting needs.
Learn MoreLearn More
More Posts by Alibaba Clouder
testa December 17, 2018 at 8:54 am
代码没有给啊,只有代码的图