This topic introduces the system architecture of ApsaraDB for Memcache.
Introduction
ApsaraDB for Memcache adopts a cluster architecture. ApsaraDB for Memcache has built-in data sharding and read algorithms. The entire procedure is transparent to users, eliminating the need for user development and operation and maintenance concerns. Each shard node adopts a primary-backup architecture to ensure high availability of the service.
System architecture
ApsaraDB for Memcache consists of three components: Proxy server (service proxy), partitioning server, and configuration server.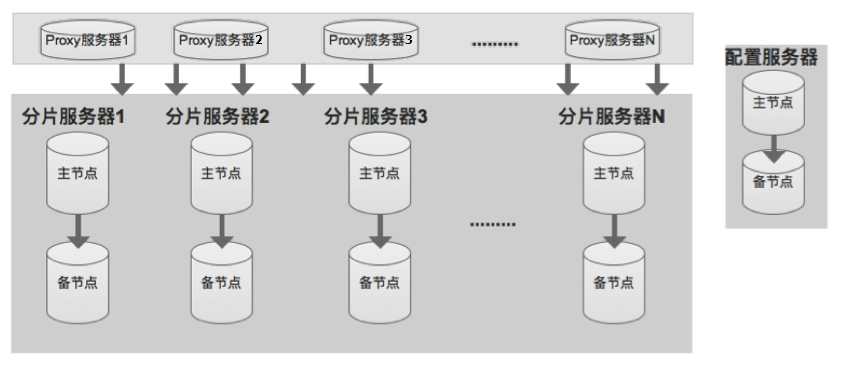
Proxy server
Single node configuration. In the cluster architecture, multiple Proxies are formed, and the system automatically implements load balancing and failover for them.
Partitioning server
Each partitioning server is a dual-replica high availability architecture. After a primary node failure, the system automatically performs primary-backup switch to ensure high availability of the service.
Configuration server
Used to store cluster configuration information and partition policy. Currently, a dual-replica high availability architecture is adopted to ensure high availability.
Precautions
The number and configuration of the three components are fixed by the system when purchasing the corresponding specifications of the cluster version. Users cannot flexibly choose at the moment. The specification details are as follows:
Specification | Number of proxies | Number of partitioning servers | Memory size of a single partitioning server |
|---|---|---|---|
1 GB | 1 | 1 | 1 GB |
2 GB | 1 | 1 | 2 GB |
4 GB | 1 | 1 | 4 GB |
8 GB | 1 | 1 | 8 GB |
16 GB | 2 | 2 | 8 GB |
32 GB | 4 | 4 | 8 GB |
64 GB | 8 | 8 | 8 GB |
128 GB | 16 | 16 | 8 GB |
256 GB | 16 | 16 | 16 GB |
512 GB | 32 | 32 | 16 GB |
The Memcache cluster uniformly exposes an endpoint. Users access this endpoint for normal Memcache access and data operations. The proxy server, partitioning server, and configuration server do not provide domain name access. Users cannot directly connect to perform operations on them.