Kagent is a framework for building, deploying, and running AI applications on Kubernetes. After deployment, Kagent lets you use declarative APIs to create agents and MCP Servers. It also supports integration with various large language models.
Basic agent concepts
An agent is an application that interacts with users in natural language. It uses a large language model (LLM) to generate responses to user requests and can perform operations on the user's behalf.
Each agent consists of the following components:
LLM: Understands and responds to user requests. Examples include Qwen and ChatGPT.
Agent instruction: A set of instructions that define the agent's behavior and features. This is also called a system prompt. The instruction typically defines the agent's role, interaction guidelines, available actions, and response methods. For example: "You are a Kubernetes O&M engineer. You can help users manage their Kubernetes resources."
Tool: A function that the agent can use to interact with its environment. A tool can be an MCP Server that supports the MCP protocol, or another agent that supports the A2A protocol. For example:
An ACK MCP Server supports operations such as retrieving cluster information, running cluster diagnostics, and viewing Prometheus metrics.
A custom agent supports special tasks, such as retrieving product information.
Core features
Kagent is a Kubernetes-native framework for agent deployment and orchestration. You can use Kagent to perform the following tasks:
Quickly deploy an active agent in an ACK cluster using a YAML file.
Quickly deploy an MCP Server in an ACK cluster using a YAML file and enable interaction with an agent.
Integrate with a self-developed MCP Server to create a custom agent.
Orchestrate multiple agents using a YAML file to implement a multi-agent architecture.
Centrally orchestrate self-developed agents.
Core APIs
Kagent uses Kubernetes CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs) as its core APIs. The main resources are:
ModelConfig: Configures the call information for an AI model. This includes parameters such as the URL, model, and API key for providers such as Qwen or OpenAI.RemoteMCPServer: Registers an MCP Server that uses the HTTP protocol. After configuration, you can reference it in an agent. You can configure the URL of an MCP Server that is deployed outside the cluster or as a Service within the cluster.Agent: Represents the agent configuration. An agent is an abstraction that combines an AI model, instructions, and tools. The AI model processes calls from humans or other agents based on the configured prompt and uses its callable MCP Server to perform specific tasks. A tool can be an MCP Server or another agent that supports the A2A protocol.
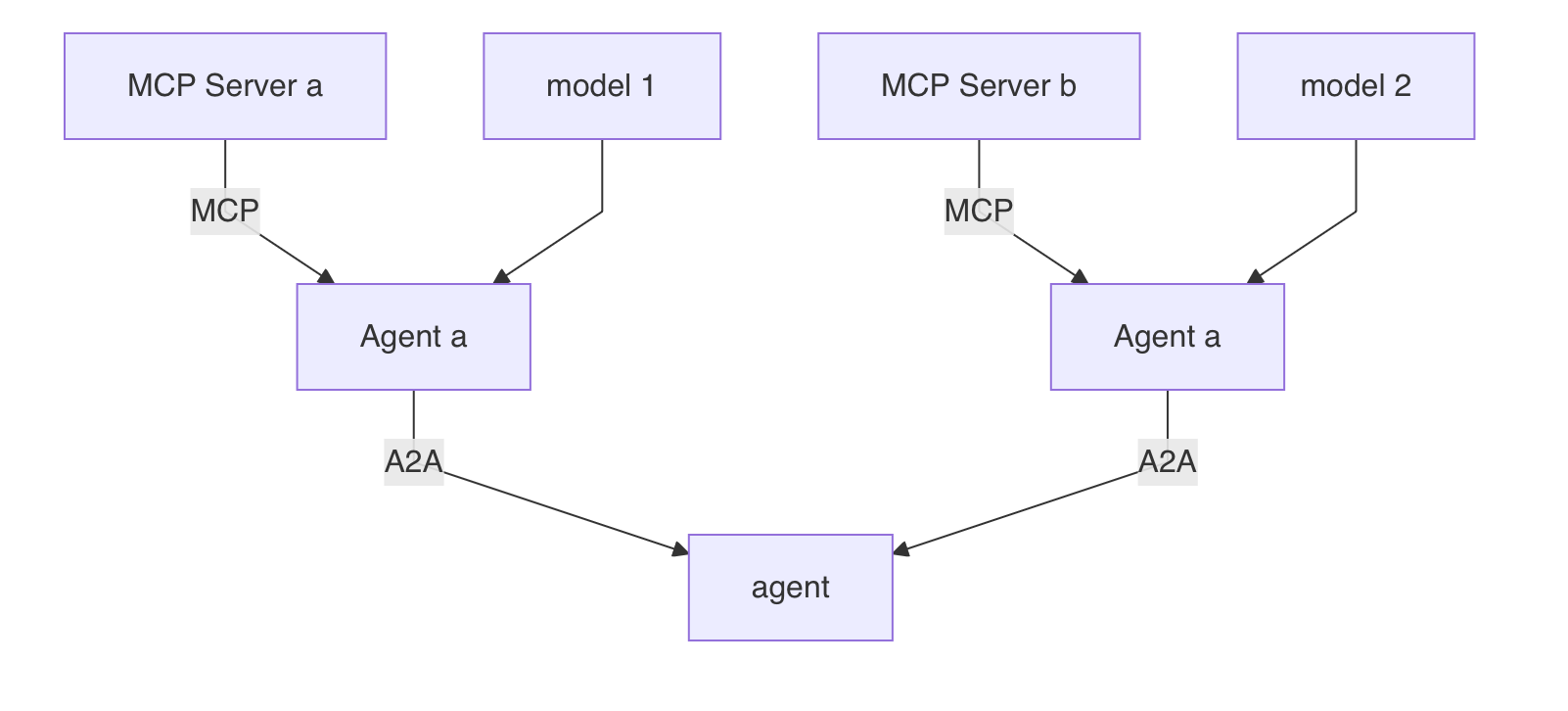
Kagent architecture
Kagent consists of three main parts:
controller: Processes Kagent-related APIs and transforms them into agent applications in the cluster.
App/Engine: The core component of Kagent. It is a Python application developed based on ADK. When an agent resource is created, the controller translates the resource into an Agent App application in real time. This application handles the conversation loop and supports the A2A protocol.
UI: Kagent provides a default web UI that you can use in a browser to create, manage, and interact with agents.
Usage notes
The default installation template provided by the Kagent community has extensive Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions. However, ACK restricts this template. By default, the template only has key permissions in the kagent namespace, such as creating and deleting Deployment and Service resources, and reading Secret resources. Therefore, you can create resources such as Agent and ModelConfig only in the kagent namespace. To create resources in other namespaces, you must add a ClusterRole resource for the Kagent-related roles.
The Kagent APIs are currently in the Alpha stage. Before you upgrade, check the corresponding version for any incompatible changes.
References
Quickly build a Q&A agent using Kagent
Use Kagent to call an MCP Server over the HTTP protocol
Quickly build a Kubernetes O&M agent using Kagent