Topik ini menjelaskan cara menggunakan Fungsi AI MaxFrame di MaxCompute dan menyediakan kasus penggunaan untuk membantu Anda memulai aplikasi inferensi offline model besar.
Ikhtisar fungsi
Fungsi AI MaxFrame adalah solusi end-to-end pada platform Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute untuk inferensi offline model besar. Fungsi ini mengintegrasikan pemrosesan data dengan kemampuan AI secara mulus, sehingga kecerdasan model besar dapat diakses di platform data besar. Integrasi ini menyederhanakan alur kerja pemrosesan data, meningkatkan kualitas hasil, menurunkan hambatan penggunaan AI dalam analitik data, serta menyederhanakan pengembangan aplikasi model besar tingkat enterprise.
Filosofi desain: "Data sebagai input, data sebagai output." Anda dapat menggunakan framework pengembangan Python MaxFrame dan API bergaya Pandas untuk menyelesaikan seluruh alur kerja dalam ekosistem MaxCompute, mencakup persiapan data, pemrosesan data, inferensi model, dan penyimpanan hasil.
Fitur inti:
Pemrosesan data skala besar: Memproses volume besar data terstruktur, seperti log untuk analisis atau data perilaku pengguna, serta data tidak terstruktur, seperti teks untuk terjemahan atau ringkasan dokumen. Anda dapat memproses data petabyte dalam satu task.
Latensi rendah dan penskalaan linear: Mencapai latensi rendah dan penskalaan linear melalui arsitektur komputasi terdistribusi.
Integrasi model besar: MaxFrame menyediakan dukungan out-of-the-box untuk rangkaian model besar seperti
Qwen 3,Qwen 2.5, danDeepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen. Model-model tersebut di-hosting secara offline di dalam platform MaxCompute, sehingga Anda tidak perlu khawatir tentang unduhan model, distribusi, atau batas konkurensi panggilan API. Anda dapat memanggil model menggunakan API, memungkinkan pemanfaatan penuh sumber daya komputasi besar MaxCompute untuk menyelesaikan tugas pemrosesan teks dengan throughput token dan konkurensi keseluruhan yang tinggi.
Skenario aplikasi: Anda dapat menggunakannya untuk berbagai tugas, seperti mengekstraksi informasi terstruktur dari teks, meringkas konten, menghasilkan abstrak, menerjemahkan bahasa, menilai kualitas teks, dan mengklasifikasikan sentimen. Hal ini sangat menyederhanakan alur kerja pemrosesan data model besar dan meningkatkan kualitas hasil.
Rangkuman keunggulan:
Dimensi
Fungsi AI MaxFrame
Kemudahan penggunaan
API Python yang familiar, pustaka model out-of-the-box, dan biaya deployment nol.
Ekstensibilitas
Mengandalkan sumber daya komputasi CU dan GU MaxCompute untuk mendukung pemrosesan paralel skala besar dan meningkatkan throughput token keseluruhan.
Integrasi data dan AI
Membaca data, memproses data, melakukan inferensi AI, dan menyimpan hasil pada satu platform terpadu. Hal ini mengurangi biaya migrasi data dan meningkatkan efisiensi pengembangan.
Cakupan skenario
Mencakup lebih dari sepuluh skenario frekuensi tinggi, seperti terjemahan, ekstraksi terstruktur, dan vektorisasi.
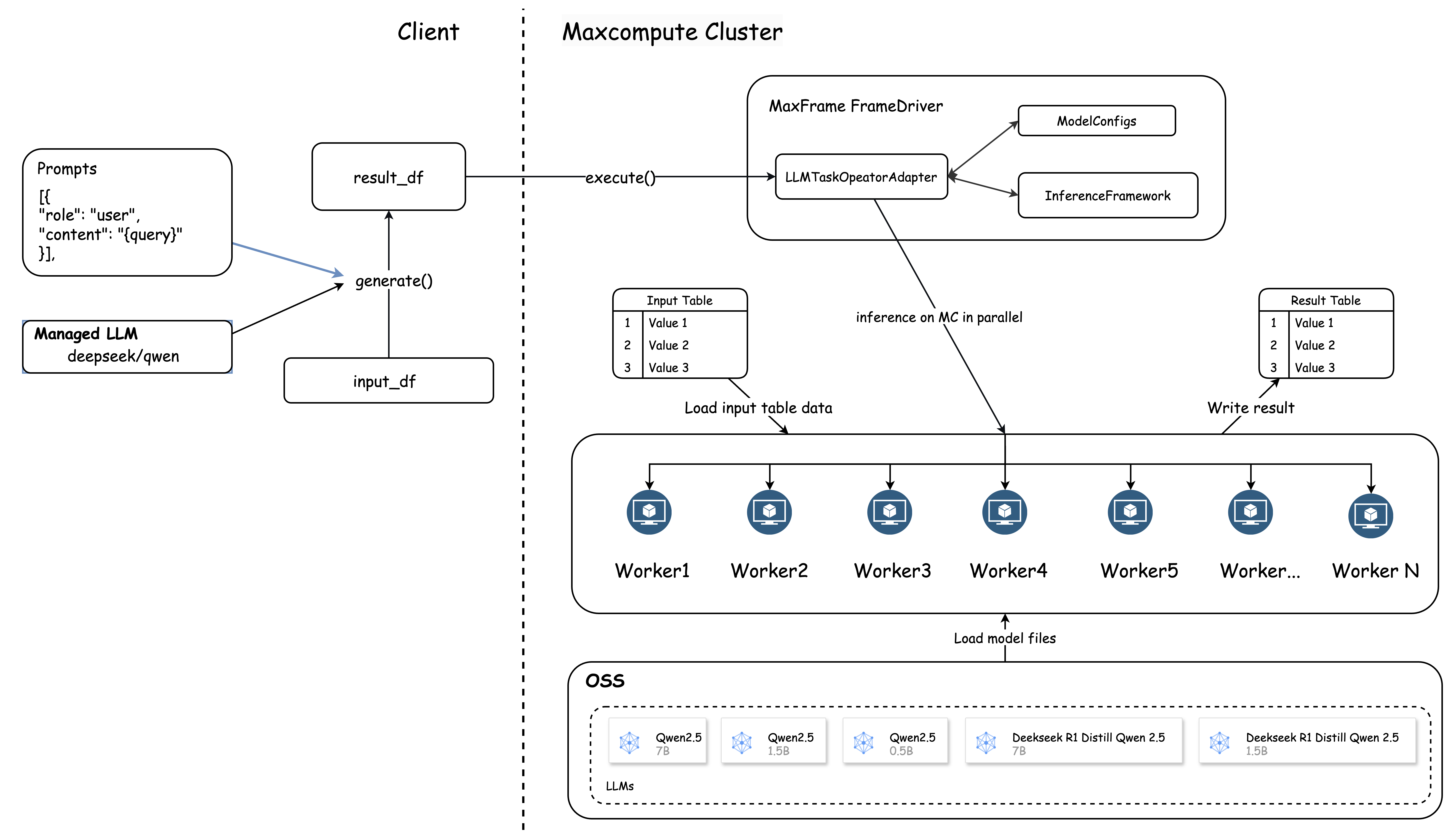
Arsitektur keseluruhan
Fungsi AI MaxFrame menyediakan antarmuka fleksibel
generate, memungkinkan Anda memilih jenis model dan menggunakan tabel MaxCompute serta Prompts sebagai parameter input.Saat antarmuka dieksekusi, MaxFrame pertama-tama membagi data tabel menjadi chunk. Kemudian, sistem menetapkan tingkat konkurensi yang sesuai berdasarkan volume data dan memulai grup pekerja untuk menjalankan tugas komputasi. Setiap pekerja menggunakan parameter prompt yang Anda berikan sebagai templat. Sistem merender baris data input untuk membangun input model. Hasil inferensi dan status keberhasilan kemudian ditulis ke MaxCompute.
Gambar berikut menunjukkan arsitektur dan proses keseluruhan.
Lingkup
Wilayah yang didukung:
Tiongkok (Hangzhou), Tiongkok (Shanghai), Tiongkok (Beijing), Tiongkok (Ulanqab), Tiongkok (Shenzhen), Tiongkok (Chengdu), Tiongkok (Hong Kong), Cloud Keuangan Tiongkok (Hangzhou), Cloud Keuangan Tiongkok (Shenzhen), Singapura, dan Indonesia (Jakarta).
Versi Python yang didukung: Python 3.11.
Versi SDK yang didukung: MaxFrame SDK V2.3.0 atau yang lebih baru. Anda dapat menjalankan perintah berikut untuk memeriksa versi Anda:
// Windows pip list | findstr maxframe // Linux pip list | grep maxframeJika versi Anda lebih lama dari yang disyaratkan, jalankan perintah berikut untuk menginstal versi terbaru:
pip install --upgrade maxframeAnda telah menginstal klien MaxFrame terbaru.
Sistem pendukung model
MaxFrame menawarkan dukungan out-of-the-box untuk rangkaian model besar seperti Qwen 3, Qwen 2.5, dan Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen. Semua model di-hosting secara offline di dalam platform MaxCompute. Anda tidak perlu khawatir tentang unduhan model, distribusi, atau batas konkurensi panggilan API. Anda dapat memanggil model menggunakan API untuk menjalankan tugas inferensi offline pada model besar, memungkinkan pemanfaatan penuh sumber daya komputasi besar MaxCompute guna mencapai throughput token dan konkurensi keseluruhan yang tinggi.
Rangkaian Qwen 3: Versi yang dioptimalkan untuk inferensi berdasarkan model Qwen 3. Mendukung terjemahan multibahasa, generasi teks kompleks, dan tugas generasi kode. Cocok untuk skenario yang membutuhkan output presisi tinggi.
Model Qwen Embedding: Dirancang untuk tugas vektorisasi. Mendukung konversi teks ke vektor secara efisien dan cocok untuk skenario seperti pencarian semantik dan pencocokan kemiripan.
Rangkaian Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen: Model ringan yang dikompresi menggunakan penyulingan pengetahuan. Cocok untuk inferensi cepat di lingkungan dengan sumber daya terbatas.
Mulailah dengan model yang lebih kecil. Jika output tidak memenuhi ekspektasi Anda, beralihlah ke model yang lebih besar. Model yang lebih besar mengonsumsi lebih banyak sumber daya dan memerlukan waktu pemrosesan lebih lama. Mengutamakan model yang lebih kecil dapat meningkatkan efisiensi dan mengurangi biaya sekaligus tetap memenuhi kebutuhan output Anda.
Model yang Didukung (Terus Diperbarui)
Tipe Model | Nama Model | Jenis resource yang didukung |
Model rangkaian Qwen 3 |
| CU |
| GU | |
Model Qwen Embedding |
| CU |
| GU | |
Model seri teks Qwen 2.5 |
| CU |
Model seri Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen |
| CU |
Model Deepseek-R1-0528-Qwen3 |
| CU |
Deskripsi antarmuka
Fungsi AI MaxFrame menyediakan keseimbangan antara fleksibilitas dan kemudahan penggunaan melalui antarmuka ganda generate dan Task:
Antarmuka tujuan umum: generate
Antarmuka ini mendukung templat prompt kustom dan pengaturan parameter. Cocok untuk skenario yang memerlukan kontrol tingkat tinggi terhadap logika inferensi. Contohnya:
from maxframe.learn.contrib.llm.models.managed import ManagedTextLLM
llm = ManagedTextLLM(name="<model_name>")
# Templat prompt
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "system_messages"},
{"role": "user", "content": "user_messages"},
]
result_df = llm.generate(<df> , prompt_template=messages)
print(result_df.execute())
Parameter:
model_name: Wajib. Nama model.
df: Wajib. Teks atau data yang akan dianalisis, dibungkus dalam DataFrame.
prompt_template: Wajib. Daftar pesan yang kompatibel dengan format Chat OpenAI. Di dalam konten, Anda dapat menggunakan
f-stringuntuk mereferensikan konten kolom tabel.
Antarmuka spesifik skenario: Task - Hanya didukung oleh sumber daya komputasi GU
Antarmuka ini menyediakan antarmuka task standar yang telah ditentukan untuk menyederhanakan pengembangan pada skenario umum. Antarmuka task yang saat ini didukung termasuk translate dan extract.
from maxframe.learn.contrib.llm.models.managed import ManagedTextLLM
llm = ManagedTextLLM(name="<model_name>")
# Terjemahan teks
translated_df = llm.translate(
df["english_column"],
source_language="english",
target_language="Chinese",
examples=[("Hello", "你好"), ("Goodbye", "再见")],
)
translated_df.execute()Contoh
Jika ini pertama kalinya Anda menggunakan MaxFrame untuk pemrosesan data, lihat Memulai dengan MaxFrame untuk mempelajari fitur-fiturnya.
Contoh ini dijalankan dalam mode lokal. Kode berikut menunjukkan skrip lengkap dan deskripsinya:
import os
from maxframe import new_session
from odps import ODPS
import pandas as pd
import maxframe.dataframe as md
from maxframe.learn.contrib.llm.models.managed import ManagedTextLLM
o = ODPS(
os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID'),
os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'),
project='<maxcompute_project_name>',
endpoint='https://service.cn-hangzhou.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api',
)
# 1. Buat sesi menggunakan SDK MaxFrame.
session = new_session(odps_entry=o)
# Jangan potong teks kolom agar menampilkan konten lengkap.
pd.set_option("display.max_colwidth", None)
# Tampilkan semua kolom untuk mencegah kolom tengah dihilangkan.
pd.set_option("display.max_columns", None)
# 2. Impor DataFrame dan buat lima pertanyaan.
query_list = [
"What is the average distance between Earth and the sun?",
"In what year did the American Revolutionary War begin?",
"What is the boiling point of water?",
"How can I quickly relieve a headache?",
"Who is the protagonist of the Harry Potter series?",
]
df = md.DataFrame({"query": query_list})
# 3. Buat objek ManagedTextLLM dan tentukan qwen3-14b sebagai model yang digunakan.
llm = ManagedTextLLM(name="qwen3-14b")
# 4. Definisikan templat prompt yang mencakup pesan sistem dan pesan pengguna.
# Di pesan pengguna, simpan variabel {query} dalam format f-string. Placeholder ini akan diganti dengan konten dari kolom query DataFrame. Placeholder mendukung penggunaan beberapa kolom dari DataFrame, semuanya direferensikan dengan nama kolom yang sesuai.
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Please answer the following question: {query}"},
]
# 5. Panggil metode generate pada objek LLM. Berikan DataFrame dan templat prompt untuk mendapatkan jawaban untuk setiap pertanyaan.
result_df = llm.generate(df, prompt_template=messages)
# 6. Gunakan execute untuk memicu perhitungan pada DataFrame hasil.
# Semua perhitungan akan terjadi di kluster MaxCompute. DataFrame input akan secara otomatis di-shard dan diproses secara paralel berdasarkan skala komputasi.
print(result_df.execute())
Hasil berikut dikembalikan:
Nomor baris | response_json | success |
0 |
| True |
1 |
| True |
2 |
| True |
3 |
| True |
4 |
| True |
Skenario aplikasi 1: Terjemahan bahasa
Deskripsi skenario: Perusahaan multinasional perlu menerjemahkan 100.000 kontrak bahasa Inggris ke bahasa Mandarin dan menganotasi klausa utama.
Berikut adalah kode contoh:
Data sampel
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS raw_contracts ( id BIGINT, en STRING ); -- Masukkan data sampel. INSERT INTO raw_contracts VALUES (1, 'This Agreement is made and entered into as of the Effective Date by and between Party A and Party B.'), (2, 'The Contractor shall perform the Services in accordance with the terms and conditions set forth herein.'), (3, 'All payments shall be made in US Dollars within thirty (30) days of receipt of invoice.'), (4, 'Either party may terminate this Agreement upon thirty (30) days written notice to the other party.'), (5, 'Confidential Information shall not be disclosed to any third party without prior written consent.');Panggil model
from maxframe.learn.contrib.llm.models.managed import ManagedTextLLM # 1. Gunakan model Qwen3 1.7B. llm = ManagedTextLLM(name="Qwen3-1.7B") # 2. Siapkan data. Anda harus terlebih dahulu membuat tabel MaxCompute raw_contracts dan menyiapkan data yang akan diterjemahkan. df = md.read_odps_table("raw_contracts") # 3. Definisikan templat prompt. messages = [ { "role": "system", "content": "You are a document translation expert who can fluently translate the English text provided by the user into Chinese.", }, { "role": "user", "content": "Please translate the following English text into Chinese. Output only the translated text and nothing else.\n\n For example:\nInput: Hi\nOutput: Hello.\n\n Here is the text to process:\n\n{en}", }, ] # 4. Gunakan antarmuka `generate` secara langsung, definisikan prompt, dan referensikan kolom data yang sesuai. result_df = llm.generate( df, prompt_template=messages, params={ "temperature": 0.7, "top_p": 0.8, }, ).execute() # 5. Tulis data hasil ke tabel MaxCompute. result_df.to_odps_table("raw_contracts_result").execute()Hasil berikut dikembalikan:
+------------+------------+---------+ | index | response | success | +------------+------------+---------+ | 0 | {"id": "chatcmpl-1765195462", "object": "chat.completion", "created": 1765195462, "model": "qwen3-1.7b", "choices": [{"index": 0, "message": {"role": "assistant", "content": "This agreement is made and entered into by and between Party A and Party B as of the effective date.", "reasoning_content": "Okay, I need to translate the English sentence provided by the user into Chinese. First, let's look at the sentence structure: 'This Agreement is made and entered into as of the Effective Date by and between Party A and Party B.'\n\nFirst, 'This Agreement' translates to '本协议' (this agreement), which is appropriate. 'is made and entered into' has two verbs. 'made' usually refers to making an agreement, while 'entered into' might mean formal signing. But according to legal terminology, '签订' (to sign) or '达成协议' (to reach an agreement) might be more common. However, 'entered into' is often used in legal documents for formal signing, so an adjustment might be needed. For example, '本协议经双方于有效日期签订' (This agreement is signed by both parties on the effective date).\n\nThen, 'as of the Effective Date' translates to '自生效日期起' (from the effective date) or '自有效日期起' (from the valid date). Here, 'Effective Date' is usually translated as '生效日期' (effective date), so the whole sentence structure might need adjustment, like '本协议由双方于生效日期签订' (This agreement is signed by both parties on the effective date).\n\nFinally, 'by and between Party A and Party B' translates to '由当事人A和B之间签订' (signed between Party A and Party B) or '由当事人A和B签署' (signed by Party A and Party B). According to legal terminology, '由当事人A和B签署' or '由A和B之间签订' might be more common.\n\nPutting it all together, a possible translation is: '本协议由当事人A和B于生效日期签署。' (This agreement is signed by Party A and Party B on the effective date.) or '本协议由双方于生效日期签订。' (This agreement is signed by both parties on the effective date.) But I need to ensure the verb usage is correct. For example, 'entered into' might be more accurately '签订' (to sign) rather than '进入' (to enter), so an adjustment might be needed.\n\nLet's double-check. The user's example is 'Hi' translated to '你好' (hello), so a direct translation is fine. It might be necessary to maintain formal legal terminology, like '签订' (to sign) instead of '进入' (to enter)."}, "finish_reason": "stop"}], "usage": {"prompt_tokens": 90, "completion_tokens": 356, "total_tokens": 446}} | true | | 1 | {"id": "chatcmpl-1765195487", "object": "chat.completion", "created": 1765195487, "model": "qwen3-1.7b", "choices": [{"index": 0, "message": {"role": "assistant", "content": "The Contractor shall provide the services in accordance with the terms and conditions set forth in this agreement.", "reasoning_content": "Okay, I need to translate the English sentence provided by the user into Chinese. First, let's look at the sentence structure. The original sentence is: 'The Contractor shall perform the Services in accordance with the terms and conditions set forth herein.'\n\nFirst, let's identify the proper nouns. 'Contractor' here should be translated as '承包商' (contractor) or '承包人' (contractor), and a more specific term might be needed depending on the context, but '承包商' is probably more appropriate here. 'Services' is '服务' (services) or '工作' (work), but a more accurate translation might be needed depending on the context, like '服务' or '工作'. 'in accordance with' translates to '按照' (according to) or '依照' (in accordance with). 'terms and conditions' is '条款和条件'. 'set forth herein' is '此处列出' (listed here) or '此处规定' (stipulated here).\n\nSo the general meaning of the sentence is: 'The contractor shall provide the services in accordance with the terms and conditions listed in this agreement.'\n\nI need to check if there's a more natural way to express this. For example, in 'perform the Services,' 'Services' might refer to specific tasks or work, so '提供服务' (provide services) is appropriate. Also, 'set forth herein' might be more naturally translated as '此处列明' (listed here) or '此处规定' (stipulated here).\n\nPutting it all together, the translation should be: '承包商应按照本协议中列明的条款和条件提供服务。' (The contractor shall provide the services in accordance with the terms and conditions listed in this agreement.)\n\nI'll confirm there are no omissions or mistranslations and ensure the professional terms are accurate, for example, whether 'Contractor' needs a more specific job title, but based on common usage, '承包商' is fine here. Finally, I'll keep the sentence concise and fluent."}, "finish_reason": "stop"}], "usage": {"prompt_tokens": 86, "completion_tokens": 325, "total_tokens": 411}} | true | | 2 | {"id": "chatcmpl-1765195505", "object": "chat.completion", "created": 1765195505, "model": "qwen3-1.7b", "choices": [{"index": 0, "message": {"role": "assistant", "content": "All payments shall be made in US dollars within 30 days of receipt of the invoice.", "reasoning_content": "Okay, I need to translate the English sentence provided by the user into Chinese. First, let's look at the sentence structure: 'All payments shall be made in US Dollars within thirty (30) days of receipt of invoice.'\n\nFirst, 'All payments' translates to '所有付款' (all payments), which is appropriate. 'shall be made' is '将被作出' (will be made) or '将被支付' (will be paid), where '将被支付' might be more formal. 'in US Dollars' is '以美元计付' (paid in US dollars) or '以美元支付' (paid in US dollars), but 'US Dollars' is usually translated as '美元' (dollars), so '以' (in) is not needed. 'within thirty (30) days' is '在收到发票后的30天内' (within 30 days of receiving the invoice). 'of receipt of invoice' is '收到发票之日' (the day the invoice is received).\n\nSo the whole sentence can be translated as: '所有付款应在收到发票后30天内以美元支付。' (All payments shall be made in US dollars within 30 days of receipt of the invoice.)\n\nI need to check if there's a more natural expression, for example, if '收到发票后30天内' (within 30 days after receiving the invoice) is accurate, or if the word order needs to be adjusted. For example, 'within thirty days of receipt of invoice' might be more naturally expressed as '收到发票后30天内'.\n\nAfter confirming there are no errors, I'll output the translation directly."}, "finish_reason": "stop"}], "usage": {"prompt_tokens": 89, "completion_tokens": 256, "total_tokens": 345}} | true | | 3 | {"id": "chatcmpl-1765195538", "object": "chat.completion", "created": 1765195538, "model": "qwen3-1.7b", "choices": [{"index": 0, "message": {"role": "assistant", "content": "Either party has the right to terminate this Agreement upon thirty days' written notice.", "reasoning_content": "Okay, I need to translate the English sentence provided by the user into Chinese. First, let's look at the sentence structure: 'Either party may terminate this Agreement upon thirty (30) days written notice to the other party.'\n\nFirst, let's break down the sentence components. 'Either party' refers to any party, 'may terminate' means can terminate, 'this Agreement' is this agreement, 'upon thirty (30) days written notice' is thirty days' written notice, and 'to the other party' is to notify the other party.\n\nWhen translating, I need to be accurate with legal terms. For example, 'Either party' is usually translated as '任何一方' (any party) or '任一方' (either party). 'may terminate' is '有权终止' (has the right to terminate) or '可以终止' (can terminate). 'this Agreement' is '本协议' (this agreement). 'upon thirty (30) days written notice' needs to accurately express 'thirty days' written notice'. 'to the other party' is '通知另一方' (notify the other party).\n\nThen, I'll consider the fluency of the sentence. The original sentence is a compound sentence, so I need to ensure the Chinese translation has a reasonable structure. For example, 'Either party may terminate this Agreement upon thirty (30) days written notice to the other party.' can be translated as '任何一方有权在书面通知另一方三十天后终止本协议。' (Either party has the right to terminate this agreement thirty days after written notice to the other party.) or more concisely '任何一方有权在三十天书面通知后终止本协议。' (Either party has the right to terminate this agreement after thirty days' written notice.)\n\nLet's check for a more natural expression. For example, 'upon' here might be better translated as '在……之后' (after...). Also, 'written notice' is '书面通知' (written notice), and 'days' is '天数' (number of days).\n\nFinally, I'll settle on the translation: '任何一方有权在三十天书面通知后终止本协议。' (Either party has the right to terminate this agreement after thirty days' written notice.) or more concisely '任何一方有权在三十天书面通知后终止本协议。' I need to ensure no information is lost, for example, 'terminate' is '终止' (terminate) and not '终止或解除' (terminate or rescind).\n\nAfter confirming it's correct, I'll output the translation directly."}, "finish_reason": "stop"}], "usage": {"prompt_tokens": 89, "completion_tokens": 394, "total_tokens": 483}} | true | | 4 | {"id": "chatcmpl-1765195574", "object": "chat.completion", "created": 1765195574, "model": "qwen3-1.7b", "choices": [{"index": 0, "message": {"role": "assistant", "content": "Confidential Information shall not be disclosed to any third party without prior written consent.", "reasoning_content": "Okay, the user wants me to translate a piece of English into Chinese and output it directly without any other content. First, I need to confirm what the English sentence provided by the user is. The example sentence given by the user is 'Confidential Information shall not be disclosed to any third party without prior written consent.', and the user's example is input 'Hi' output '你好' (hello). Now the text provided by the user is 'Confidential Information shall not be disclosed to any third party without prior written consent.', which needs to be translated into Chinese.\n\nFirst, I need to accurately understand the meaning of this sentence. 'Confidential Information' should be '机密信息' (confidential information) or '保密信息' (secret information). 'shall not be disclosed' is '不得泄露' (shall not be disclosed). 'to any third party' is '任何第三方' (any third party). 'without prior written consent' is '未经事先书面同意' (without prior written consent). So the Chinese translation of the whole sentence should be '机密信息不得以任何第三方未经事先书面同意而泄露。' (Confidential information shall not be disclosed by any third party without prior written consent.)\n\nHowever, the user might want a more formal translation, like an expression commonly used in legal documents. For example, '机密信息不得向任何第三方披露,除非获得事先书面同意。' (Confidential information shall not be disclosed to any third party unless prior written consent is obtained.) This is more in line with legal terminology. But the user didn't specify, so I might need to stick to a direct translation but ensure accuracy.\n\nAlso, I need to pay attention to the sentence structure. 'shall not be disclosed' in the original sentence is '不得被披露' (shall not be disclosed), so I need to ensure the tense and voice of the verb are correct in the translation. At the same time, translating 'to any third party' as '任何第三方' (any third party) is correct, but sometimes '任何第三方' might need adjustment, for example, '任何第三方或任何其他个人' (any third party or any other individual)? But the example sentence provided by the user is '任何第三方', so I should probably keep it as is.\n\nLet's check for a more natural expression. For example, '机密信息不得未经事先书面同意向任何第三方披露' (Confidential information shall not be disclosed to any third party without prior written consent) might be more in line with Chinese expression habits. But the user might want a direct translation, so I need to weigh that. However, the example sentence given by the user is '机密信息不得向任何第三方泄露,除非获得事先书面同意。' (Confidential information shall not be disclosed to any third party unless prior written consent is obtained.), so I might need to maintain a similar structure.\n\nFinally, I'll ensure the translated sentence is fluent, conforms to Chinese grammar, and has no missing information. After confirming it's correct, I'll output the translation directly."}, "finish_reason": "stop"}], "usage": {"prompt_tokens": 85, "completion_tokens": 454, "total_tokens": 539}} | true | +------------+------------+---------+
Skenario aplikasi 2: Ekstraksi kata kunci
Deskripsi skenario: Skenario ini menunjukkan kemampuan Fungsi AI MaxFrame untuk memproses data tidak terstruktur. Teks dan citra, yang merupakan bagian besar dari data tidak terstruktur, menimbulkan tantangan signifikan bagi analitik data besar. Contoh berikut menunjukkan cara menggunakan Fungsi AI untuk menyederhanakan proses ini.
Kode berikut menunjukkan cara menggunakan Fungsi AI untuk mengambil pengalaman kerja kandidat dari resume dengan teks yang dihasilkan secara acak.
Berikut adalah kode contoh:
Data sampel
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS traditional_chinese_medicine ( index BIGINT, text STRING ); -- Masukkan data sampel. INSERT INTO traditional_chinese_medicine VALUES (1, 'Patient Zhang, male, 45 years old. Chief complaint: recurrent cough for 2 weeks. Current symptoms: cough with abundant white and sticky phlegm, chest tightness, shortness of breath, poor appetite, and loose stools. Tongue: white and greasy coating. Pulse: slippery. Diagnosis: Phlegm-dampness obstructing the lungs. Treatment principle: Dry dampness, resolve phlegm, regulate qi, and stop coughing. Prescription: Modified Erchen Tang.'), (2, 'Patient Li, female, 32 years old. Visited for "insomnia and excessive dreaming for 1 month." Accompanied by heart palpitations, forgetfulness, mental fatigue, and a sallow complexion. Tongue: pale with a thin white coating. Pulse: thin and weak. Diagnosis: Heart and spleen deficiency syndrome. Prescription: Modified Guipi Tang, one dose daily, decocted in water.'), (3, 'Patient Wang, 68 years old. Chief complaint: lower back and knee soreness, frequent nocturia for half a year. Accompanied by aversion to cold, cold limbs, tinnitus like cicadas, and listlessness. Tongue: pale, swollen with teeth marks, and a white, slippery coating. Pulse: deep and thin. TCM diagnosis: Kidney yang deficiency syndrome. Treatment: Warm and supplement kidney yang. Prescription: Modified Jinkui Shenqi Wan.'), (4, 'Patient Zhao, 5 years old. Fever for 3 days, highest temperature 39.5°C, slight aversion to wind and cold, nasal congestion with turbid discharge, red and swollen painful throat. Tongue: red tip with a thin yellow coating. Pulse: floating and rapid. Diagnosis: Wind-heat invading the lungs syndrome. Treatment principle: Dispel wind, clear heat, diffuse the lungs, and stop coughing. Prescription: Modified Yinqiao San.'), (5, 'Patient Liu, male, 50 years old. Recurrent epigastric bloating and pain for 3 years, worsened for 1 week. Symptoms: epigastric fullness, frequent belching, symptoms worsen with emotional fluctuations, and irregular bowel movements. Tongue: red with a thin yellow coating. Pulse: wiry. Diagnosis: Liver-stomach disharmony syndrome. Treatment principle: Soothe the liver, harmonize the stomach, regulate qi, and relieve pain. Prescription: Modified Chaihu Shugan San combined with Zuojin Wan.');Panggil model
from maxframe.learn.contrib.llm.models.managed import ManagedTextLLM from pydantic import BaseModel from typing import List, Optional # 1. Gunakan model Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507-FP8. llm = ManagedTextLLM(name="Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507-FP8") df = md.read_odps_table("traditional_chinese_medicine", index_col="index") # Empat partisi konkuren parallel_partitions = 4 df = df.mf.rebalance(num_partitions=parallel_partitions) class MedicalRecord(BaseModel): """ Skema terstruktur untuk catatan konsultasi pengobatan tradisional Tiongkok """ patient_name: Optional[str] = None # Nama pasien (misalnya, "Zhang") age: Optional[int] = None # Usia gender: Optional[str] = None # Jenis kelamin ("Male"/"Female") chief_complaint: str # Keluhan utama symptoms: List[str] # Daftar gejala tongue: str # Diagnosis lidah (misalnya, "Pale tongue with a white, greasy coating") pulse: str # Diagnosis denyut nadi (misalnya, "Wiry and slippery pulse") diagnosis: str # Diagnosis sindrom TCM treatment_principle: str # Prinsip pengobatan prescription: str # Nama resep # Gunakan antarmuka task preset extract. result_df = llm.extract( df["text"], description="Please extract structured data from the following consultation record in order. Return the result in a strict JSON format according to the schema.", schema=MedicalRecord ) result_df.execute() result_df.to_odps_table("result").execute()
Manajemen resource dan optimasi kinerja
Kebijakan penjadwalan resource heterogen
MaxFrame mendukung dua jenis resource:
CU (Compute Unit): Resource komputasi CPU tujuan umum, cocok untuk model kecil dan tugas inferensi data skala kecil.
GU (GPU Unit): Resource komputasi GPU, dioptimalkan untuk inferensi model besar dan mendukung ukuran model yang lebih besar.
Untuk model besar, seperti 8B dan lebih besar, inferensi CPU kurang efisien. Anda dapat beralih ke resource komputasi GU untuk menjalankan inferensi.
Anda dapat memilih resource secara dinamis dengan mengonfigurasi session:
# Konfigurasikan penggunaan resource CU/GU.
# Gunakan resource komputasi CU.
options.session.quota_name = "mf_cpu_quota"
# Gunakan resource komputasi GU.
options.session.gu_quota_name = "mf_gpu_quota"
Inferensi paralel
MaxFrame menggunakan mekanisme komputasi paralel untuk melakukan inferensi offline pada data skala besar:
Pemotongan data: Anda dapat menggunakan antarmuka
rebalanceuntuk mendistribusikan data tabel input secara merata ke beberapa node pekerja berdasarkan jumlah partisi yang ditentukan (num_partitions).Pemuatan model paralel: Setiap pekerja memuat dan melakukan pra-ambil model secara independen untuk menghindari latensi cold start akibat pemuatan model.
Agregasi hasil: Hasil output ditulis ke tabel MaxCompute berdasarkan partisi, mendukung analitik data selanjutnya.
Untuk pekerjaan inferensi data skala besar, Anda dapat menggunakan antarmuka rebalance untuk memotong data terlebih dahulu demi konkurensi. Hal ini memungkinkan pemrosesan data secara paralel.