This topic describes how to use Pktgen to test the network performance of an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
The following example demonstrates how to use Pktgen to test network performance.
Step 1: Prepare the environment
Prepare two servers: one as the sender and the other as the receiver. Add a secondary network interface card (NIC) to each server. Use one NIC for management access and the other for testing. Confirm that the two test NICs can communicate. Then, run the ifconfig command and record the IP address and MAC address of both test NICs. This information is required to configure traffic on the sender.
Step 2: Install the software
CentOS 6 reached end of life (EOL). In accordance with Linux community rules, all content was removed from the following CentOS 6 repository address: http://mirror.centos.org/centos-6/. If you continue to use the default CentOS 6 repository on Alibaba Cloud, an error is reported. To use specific installation packages of CentOS 6, change the CentOS 6 repository address. For more information, see How do I change CentOS 6 repository addresses?
Perform the following operations on both the sender and receiver instances.
Log on to the Linux ECS instance. For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following command to create the
pktgendirectory.cd /root/ mkdir pktgenRun the following command to change to the
pktgendirectory.cd pktgenRun the following command to download the Pktgen, Lua, and DPDK installation packages.
wget https://git.dpdk.org/apps/pktgen-dpdk/snapshot/pktgen-dpdk-pktgen-3.6.5.zip https://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.4.3.tar.gz https://fast.dpdk.org/rel/dpdk-18.11.11.tar.xzNoteNote: The Pktgen, Lua, and DPDK versions must be compatible to prevent compilation issues. This article uses the versions in the example command, but you can use other compatible versions.
Run the following commands in sequence to decompress the installation packages.
tar -Jxvf dpdk-18.11.11.tar.xz tar -zxvf lua-5.4.3.tar.gz unzip pktgen-dpdk-pktgen-3.6.5.zipIf any dependencies are missing during compilation, run the following commands to install the required packages.
CentOS 7
yum -y install kernel-devel.x86_64 yum -y install numactl-devel.x86_64 yum -y install elfutils-libelf-devel yum -y install libpcap-develCentOS 8
NoteThe
libpcap-develpackage is not installed by default in CentOS 8 and must be installed manually.Before you run the following commands, change the mirror repository by following the instructions in CentOS operating system. Then, from the
Centos-vault-8.5.2111.repofile, copy the[PowerTools]block and paste it into a new file namedCentOS-PowerTools.repo.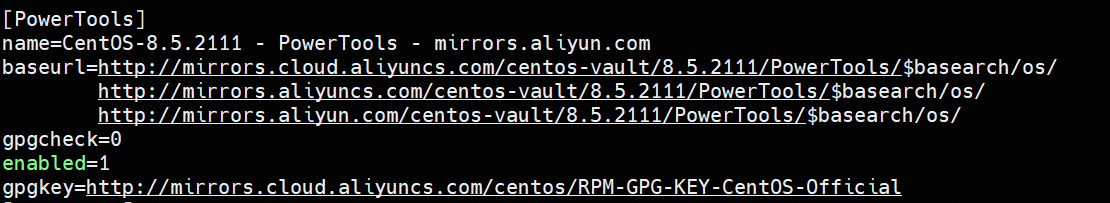
dnf config-manager --add-repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-PowerTools.repo dnf config-manager --set-enabled PowerTools dnf -y upgrade libmodulemd dnf -y install kernel-devel.x86_64 dnf -y install elfutils-libelf-devel dnf -y install numactl-devel.x86_64 dnf -y install libpcap-devel
Run the following commands in sequence to compile and install DPDK.
cd dpdk-stable-18.11.11 make config T=x86_64-native-linuxapp-gcc make all -j32 cd ..Run the following commands in sequence to compile and install Lua.
cd lua-5.4.3 make make install cd ..Run the following commands in sequence to compile and install Pktgen.
cd pktgen-dpdk-pktgen-3.6.5/ export RTE_SDK=/root/pktgen/dpdk-stable-18.11.11/ export RTE_TARGET=build make -j32
Step 3: Bind the driver to vfio
Perform the following operations on both the sender and receiver instances.
Run the following command to check the
/proc/cmdlinefile and ensure the operating system's GRUB configuration containsintel_iommu=on.cat /proc/cmdlineThe output should be similar to the following. If the parameter is missing, add it by following these steps:
BOOT_IMAGE=/boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-XXXX.19.1.el7.x86_64 root=UUID=9f2d3e15-XXXX-XXXX-8385-0165b4b67864 ro crashkernel=auto spectre_v2=retpoline rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0 console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 noibrs intel_iommu=onRun the following command to edit the
/etc/default/grubfile.vim /etc/default/grubPress
ito enter edit mode and addintel_iommu=onto the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX line. The modified content is shown in the following figure.
To save and close the file, press
Esc, enter:wq, and pressEnter.Run the following command to update the configuration.
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfgRun the following command to restart the server.
reboot
Run the following commands in sequence to load the
vfioandvfio-pcidrivers.modprobe vfio modprobe vfio-pciRun the following command to configure
noniommu_mode.echo 1 > /sys/module/vfio/parameters/enable_unsafe_noiommu_modeRun the following command to view and record the
bus-infovalue of the NIC.ethtool -i eth1NoteNote: This example uses the
eth1NIC. Use the actual NIC name for your environment.The system displays output similar to the following.
driver: virtio_net version: 1.0.0 firmware-version: expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:00:08.0 supports-statistics: no supports-test: no supports-eeprom-access: no supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: noRun the following command to unbind the virtio driver from the
eth1NIC.ImportantThis example unbinds the virtio driver from the
eth1NIC. This action interrupts network connectivity on the NIC. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.echo "[$Bus-info]" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/virtio-pci/unbindNoteNote: Replace
[$Bus-info]with thebus-infovalue you recorded in step 4.Run the following command to bind the
bus-infoto thevfio-pcidriver./root/pktgen/dpdk-stable-18.11.11/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci [$Bus-info]NoteReplace
[$Bus-info]with thebus-infovalue you recorded in step 4. In a CentOS 8.3 (Python 3.6.8) environment, you must use thepython3interpreter to run the script. Modify the command as follows:python3 /root/pktgen/dpdk-stable-18.11.11/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci [$Bus-info]
Step 4: Configure huge pages
Perform the following operations on both the Sender and Receiver instances. Check the number of NUMA nodes on your system and run the corresponding command.
For a dual-node system
echo 8000 > /sys/devices/system/node/node1/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages echo 8000 > /sys/devices/system/node/node0/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepagesFor a single-node system
echo 8000 > /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
Step 5: Start Pktgen
Perform the following operations on both the sender and receiver instances.
In the
pktgen-dpdk-pktgen-3.6.5directory, run the following command to start Pktgen, launching the Pktgen terminal../app/build/pktgen -c 0x1ffff -n 4 --socket-mem 16000 -w [$Bus-info] -- -P -m "[1-16:1-16].0"Note0x1ffff: Specifies the CPU core mask for the process. The lowest-bit core is reserved for shell control, and the other cores are used for sending and receiving packets on the port.
"[1-16:1-16].0": Specifies the CPU cores for packet processing. This range must be a subset of the cores defined in the CPU core mask.
1-16 (before the colon) is for receiving packets.
1-16 (after the colon) is for sending packets.
.0 specifies port 0.
If the sending performance is insufficient, you can adjust the CPU core range. Note that using more cores for sending packets requires more Huge Pages. Insufficient Huge Pages causes Pktgen to fail to start.
The system displays output similar to the following.
Copyright (c) <2010-2019>, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Powered by DPDK EAL: Detected 64 lcore(s) EAL: Detected 1 NUMA nodes EAL: Multi-process socket /var/run/dpdk/rte/mp_socket EAL: No free hugepages reported in hugepages-1048576kB EAL: Probing VFIO support... EAL: VFIO support initialized EAL: PCI device 0000:00:08.0 on NUMA socket -1 EAL: Invalid NUMA socket, default to 0 EAL: probe driver: 1af4:1000 net_virtio EAL: using IOMMU type 8 (No-IOMMU) Lua 5.4.3 Copyright (C) 1994-2021 Lua.org, PUC-Rio *** Copyright (c) <2010-2019>, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. *** Pktgen created by: Keith Wiles -- >>> Powered by DPDK <<< Initialize Port 0 -- TxQ 16, RxQ 16, Src MAC 00:16:3e:24:9b:a4 Port 0: Link Up - speed 10000 Mbps - full-duplex <Enable promiscuous mode> RX/TX processing lcore: 1 rx: 1 tx: 1 RX/TX processing lcore: 2 rx: 1 tx: 1 RX/TX processing lcore: 3 rx: 1 tx: 1 RX/TX processing lcore: 4 rx: 1 tx: 1 - Ports 0-0 of 1 <Main Page> Copyright (c) <2010-2019>, Intel Corporation Flags:Port : P-----R--------:0 Link State : <UP-10000-FD> ----TotalRate---- Pkts/s Max/Rx : 1/0 1/0 Max/Tx : 0/0 0/0 MBits/s Rx/Tx : 0/0 0/0 Broadcast : 0 Multicast : 0 Sizes 64 : 0 65-127 : 0 128-255 : 0 256-511 : 0 512-1023 : 0 1024-1518 : 0 Runts/Jumbos : 2/0 ARP/ICMP Pkts : 2/0 Errors Rx/Tx : 0/0 Total Rx Pkts : 2 Tx Pkts : 0 Rx MBs : 0 Tx MBs : 0 : Pattern Type : abcd... Tx Count/% Rate : Forever /100% Pkt Size/Tx Burst : 64 / 64 Port Src/Dest : 1234 / 5678 Pkt Type:VLAN ID : IPv4 / UDP:0001 802.1p CoS/DSCP/IPP : 0/ 0/ 0 VxLAN Flg/Grp/vid : 0000/ 0/ 0 IP Destination : 192.168.X.X Source : 192.168.X.X/24 MAC Destination : 00:00:00:00:00:00 Source : 00:XX:XX:24:9b:a4 PCI Vendor/Addr : 1af4:1000/00:08.0 -- Pktgen Ver: 3.6.5 (DPDK 18.11.11) Powered by DPDK (pid:4873) ------------- Pktgen:/>In the Pktgen terminal, run the following commands in sequence on the sender to configure the traffic stream.
set 0 proto udp range 0 src mac start [$MAC] range 0 src mac min [$MAC] range 0 src mac inc 00:00:00:00:00:00 range 0 dst mac start ee:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff range 0 dst mac min ee:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff range 0 dst mac inc 00:00:00:00:00:00 range 0 src port start 10000 range 0 src port min 10000 range 0 src port max 10000 range 0 src port inc 0 range 0 dst port start 2000 range 0 dst port min 2000 range 0 dst port max 2255 range 0 dst port inc 1 range 0 proto udp range 0 src ip start [$Local_IP] range 0 src ip min [$Local_IP] range 0 src ip inc 0.0.0.0 range 0 size start 64 range 0 size min 64 range 0 size max 64 range 0 size inc 0 range 0 dst ip start [$Receive_IP] range 0 dst ip min [$Receive_IP] range 0 dst ip inc 0.0.0.0 enable all rangeNoteReplace
[$MAC]with the MAC address of the sender.Replace
[$Local_IP]with the IP address of the sender.Replace
[$Receive_IP]with the IP address of the receiver.
In the Pktgen terminal, run the following command on the sender to start sending traffic.
start 0Observe the traffic data:
Sender
-iPorts 0-0 of 1 <Main Page> Copyright (c) <2010-2019>, Intel Corporation Flags:Port : P-----R--------:0 1/0 Link State : <UP-10000-FD> ----TotalRate---- Pkts/s Max/Rx : 1/0 1/0 Max/Tx : 14906304/14904704 14906304/14904704 MBits/s Rx/Tx : 0/10015 0/10015 Broadcast : 0 Multicast : 0 Sizes 64 : 0 65-127 : 0 128-255 : 0 256-511 : 0 512-1023 : 0 1024-1518 : 0 Runts/Jumbos : 16/0 ARP/ICMP Pkts : 16/0 Errors Rx/Tx : 0/0 Total Rx Pkts : 16 Tx Pkts : 1655962864Receiver
- Ports 0-0 of 1 <Main Page> Copyright (c) <2010-2019>, Intel Corporation Flags:Port : P--------------:0 Link State : <UP-10000-FD> ----TotalRate---- Pkts/s Max/Rx : 14911585/14910795 14911585/14910795 Max/Tx : 0/0 0/0 MBits/s Rx/Tx : 10020/0 10020/0 Broadcast : 0 Multicast : 0 Sizes 64 : 1862740038 65-127 : 0 128-255 : 0 256-511 : 0 512-1023 : 0 1024-1518 : 0 Runts/Jumbos : 6/0 ARP/ICMP Pkts : 6/0 Errors Rx/Tx : 0/0 Total Rx Pkts : 2298743466 Tx Pkts : 0 Rx MBs : 1544755 Tx MBs : 0 : Pattern Type : abcd... Tx Count/% Rate : Forever /100% Pkt Size/Tx Burst : 64 / 64 Port Src/Dest : 1234 / 5678 Pkt Type:VLAN ID : IPv4 / TCP:0001 802.1p CoS/DSCP/IPP : 0/ 0/ 0 VxLAN Flg/Grp/vid : 0000/ 0/ 0 IP Destination : 192.168.X.1 Source : 192.168.X.X/24 MAC Destination : 00:00:00:00:00:00 Source : 00:XX:XX:24:2d:55 PCI Vendor/Addr : 1af4:1000/00:08.0 -- Pktgen Ver: 3.6.5 (DPDK 18.11.11) Powered by DPDK (pid:4072) -------------
Run the following command on the sender to stop the traffic.
stop 0