Protect your public-facing website from web attacks with Web Application Firewall (WAF) 3.0. A simple DNS change routes your traffic through WAF for inspection—no infrastructure changes required. WAF filters malicious requests, forwards clean traffic to your origin server, and seamlessly protects any website, whether hosted in the cloud or on-premises.
How it works
A CNAME record routes your website's traffic through WAF for inspection. It is achieved by pointing your domain's existing DNS record to the CNAME target provided by WAF.

Origin server: The server that hosts your website. If a load balancer, such as Application Load Balancer (ALB), Classic Load Balancer (CLB), or Network Load Balancer (NLB), or a NAT Gateway is deployed in front of the server, the origin server is the next-hop device that receives traffic from WAF.
Back-to-origin: The process of WAF forwarding inspected traffic to your Origin Server. This traffic originates from WAF's public IP address range (CIDR blocks). To ensure delivery, you must add these IP addresses to the allowlist on your origin server's firewall or security group.
WAF has deployed 11 protection nodes in China (Beijing), China (Hangzhou), China (Shenzhen), China (Hong Kong), Singapore, Malaysia, US (Silicon Valley), Germany, Indonesia, Dubai, and Japan. When your service is protected by the public cluster, WAF automatically routes your traffic to the optimal protection node based on the geolocation of your origin server.
Usage notes
Before you begin, ensure you meet the following requirements:
Domain ownership: You must have permission to modify the domain's DNS records.
Domain certificate: To protect HTTPS traffic, you must have an SSL certificate for the domain.
ICP filing: If your server is in the Chinese mainland, your domain name must have an ICP filing. For more information, see How do I check the ICP filing information for a domain name?
Procedure
Go to the Web Application Firewall 3.0 console page. In the top menu bar, select a resource group and a region (Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland). In the navigation pane on the left, select Onboarding. On the CNAME Record tab, click Add.
Step 1: Configure the listener
In the Domain Name field, enter a domain name to protect, such as an exact domain name (
www.aliyundoc.com) or a wildcard domain name (*.aliyundoc.com).Wildcard domain matching rules:
Matches only subdomains at the same level. For example,
*.aliyundoc.commatcheswww.aliyundoc.comandexample.aliyundoc.com, but notwww.example.aliyundoc.com.When applied to a second-level domain such as
*.aliyundoc.com, it also matches the second-level domain itself (also known as the apex domain)aliyundoc.com.When applied to a third-level domain such as
*.example.aliyundoc.com, it does not match the third-level domain itselfexample.aliyundoc.com.
Priority rule: If both an exact domain name and a wildcard domain name are added, and a protected domain matches both, the protection rules for the exact domain name take precedence.
To confirm domain ownership, you must complete a verification. If the system prompts for verification after you enter the domain name, choose one of the following methods.
DNS validation (recommended): Manually add the TXT record provided by WAF at your domain's DNS provider.
File validation: Upload the validation file provided by WAF to a specified root directory on your origin server. This requires operational access to the origin server and a security group policy that allows public IP access, ensuring WAF can validate the file from the Internet.
DNS validation
In the validation prompt area, click the Method 1: DNS Record tab.
Add a TXT record at your domain name resolution service provider using the Record Type, Host Name, and Record Value from the WAF console.
If you use Alibaba Cloud DNS, follow these steps. If not, perform similar steps in their system.
Wait for the TXT record to take effect. A new TXT record takes effect immediately, but changes to an existing TXT record typically take effect after 10 minutes. The exact time depends on the Time to Live (TTL) configured for the domain's DNS settings, which is 10 minutes by default.
Return to the WAF console and click Verify.
Successful validation confirms your domain ownership.
If validation fails, an error message will provide details about the cause. Troubleshoot as follows:
Check the TXT record: Ensure the host record and record value you added exactly match the information provided in the WAF console. If there are discrepancies, delete the incorrect record, add it again, and vaildate again.
Wait for the DNS record to take effect: DNS records may not take effect immediately. The time that is required for a DNS record to take effect depends on the TTL cache time set on the DNS server. We recommend that you wait 10 minutes and then vaildate again.
Switch validation method: If validation repeatedly fails, we recommend using Method 2: File Verification.
File validation
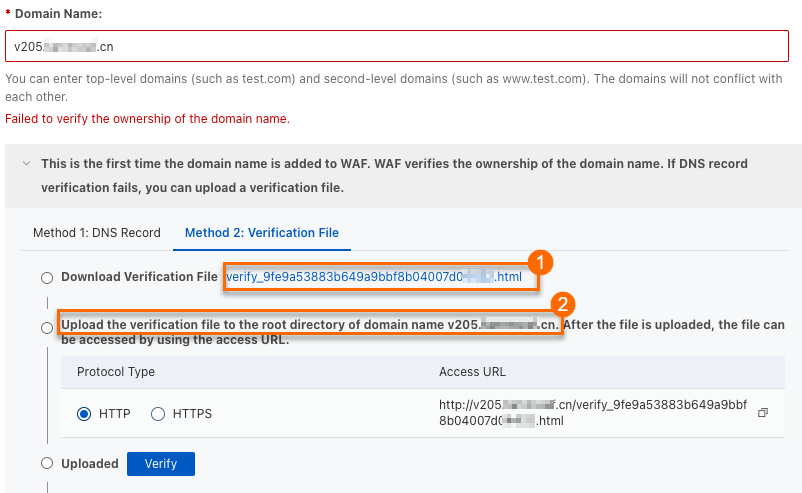
In the validation prompt area, click the Method 2: Verification File tab.
Click the link to download the validation file (① in the figure).
 Important
ImportantThe validation file is valid for only 3 days after download. If you do not complete file validation within this period, you must download it again.
Do not modify the validation file in any way, such as editing or renaming it.
WAF accesses the origin server based on the selected protocol type. Ensure your origin server's security group or firewall rules allow the corresponding traffic:
If you select HTTP, allow inbound TCP traffic on port 80 from 0.0.0.0/0.
If you select HTTPS, allow inbound TCP traffic on port 443 from 0.0.0.0/0.
Manually upload the validation file to the web root directory of your domain's origin server, such as an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket, a Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) instance, a Cloud Object Storage (COS) bucket, or an Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance (② in the figure).
NoteIf you add a wildcard domain name, such as
*.aliyun.com, you must upload the validation file to the root directory ofaliyun.com.After the upload is complete, you can check if the validation file was uploaded successfully by following the methods below.
Return to the WAF console and click Verify.
Successful validation confirms your domain ownership.
If validation fails, an error message will provide details about the cause. Troubleshoot the issue based on the error message:
Issue
Solution
Cannot access the domain name.
Check the domain's DNS record to ensure there is a record pointing to the origin server. For Alibaba Cloud DNS, see Add a DNS record.
Check the origin server's security group or firewall rules to ensure public access requests are allowed. For ECS security groups, see Add a security group rule.
Validation file does not exist.
Re-upload the validation file to the domain's origin server.
Incorrect file content
Go to your domain's origin server and delete the incorrect validation file.
Re-upload the correct validation file.
Because a rule allowing access from all IP addresses (
0.0.0.0/0) is a security risk, we recommend deleting this temporary rule after ownership is confirmed, unless your origin server's initial security configuration already included it.
Select the Protocol Type (HTTP or HTTPS) and enter the required configuration. You can configure both protocols at the same time.
NoteWAF Custom Edition for shared virtual hosts does not support HTTPS.
HTTP
HTTP Port
Enter the port that users use to access the website. We recommend using port 80 for the HTTP protocol. To customize the port, specify one within the port range. Press Enter after entering each port.
HTTPS
HTTPS Port
Enter the port that users use to access the website. We recommend using port 443 for the HTTPS protocol. To customize the port, specify one within the port range. Press Enter after entering each port.
HTTPS Upload Type
To allow WAF to listen for and protect your website's HTTPS traffic, you must upload the SSL certificate associated with the domain to WAF. The options are:
Upload: Use this if your certificate is not uploaded to Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
Select Existing Certificate: Select a certificate that has already been issued or uploaded in Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
Purchase Certificate: If you do not have an SSL certificate for the domain, you must purchase one and wait for it to be issued before adding the domain to WAF.
Upload
Certificate Name: Set a unique name for the certificate. It cannot be the same as an already uploaded certificate.
Certificate File: Use a text editor to open and paste the content of the certificate in PEM, CER, or CRT format.
Example format:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----......-----END CERTIFICATE-----Format conversion: If the certificate is in a format such as PFX or P7B, use the certificate tool to convert it to PEM format.
Certificate chain: If there is an intermediate certificate, concatenate the server certificate and the intermediate certificate in that order before pasting.
Private Key: Use a text editor to open and paste the content of the private key in PEM format.
RSA:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----......-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----ECC:
-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----......-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----
Select Existing Certificate
From the certificate drop-down list, select the certificate to upload to WAF.
NoteIf the WAF console displays the message "Failed to verify the integrity of the certificate chain. If you use this certificate, service access may be affected.", it means there is a problem with the certificate chain. Check the correctness and completeness of the certificate content and re-upload it in the Certificate Management Service console. For details, see Upload, sync, and share SSL certificates.
Purchase Certificate
If you have not purchased a certificate, see Purchase a commercial certificate.
ImportantIf your origin server is not configured for or does not support HTTPS (such as no SSL/TLS certificate is deployed), you must enable HTTP back-to-origin. Otherwise, back-to-origin requests will fail, and your website will be inaccessible.
To customize settings such as Enable SM-based HTTPS, HTTP2, Enable HTTPS Routing, TLS Version, HTTPS Cipher Suite, Whether Layer 7 Proxy, Such as Anti-DDoS Proxy or Alibaba Cloud CDN, Is Deployed in Front of WAF, IPv6, Exclusive IP, Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing, or Resource Group, see Advanced configurations. If no customization is needed, keep the default values for the other parameters and click Next.
Step 2: Configure forwarding
In the Server Address area, enter the IP address or domain name of the origin server according to the server type. WAF uses this configuration to forward service requests to the origin server. If you are unsure of the origin server's address, see the FAQ.
ImportantDo not confuse the Domain Name (Such as CNAME) specified here with the domain name you added in Step 1. This field is used when the origin server address is a domain name, such as a CNAME. For example, if the origin server is an ALB instance, enter its DNS name, such as
alb-xxx.cn-shanghai.alb.aliyuncsslb.com.After you determine the origin server type, complete the following configuration.
IP
Origin Port: The port that the origin server uses. Users access your website through the HTTP/HTTPS port you configured in Step 1. WAF then uses the Origin Port to access the origin server. If you are unsure which port your website uses, see the FAQ.
By default, this value is the same as the HTTP/HTTPS ports configured for the Protocol Type in the previous step. You can customize the back-to-origin port within the port range. This customization is for scenarios where you need to specify a port for WAF to use for back-to-origin requests.
Origin IP Address: Enter the IP addresses of the origin server.
It must be a publicly accessible IP address.
You can enter multiple IP addresses. Press Enter after you enter each IP address. Add up to 20 IP addresses of origin servers. If you enter multiple IP addresses, WAF forwards back-to-origin requests based on the load balancing algorithm that you select.
You can configure IPv4 and IPv6 addresses individually or simultaneously. If you want to configure an IPv6 address, first enable IPv6 protection in Configure Listener.
Domain Name (such as CNAME)
Origin Port: The port that your origin server uses. Users access your website through the HTTP/HTTPS Port configured in Step 1, and WAF uses the Origin Port to forward requests to the origin server. If you do not know which port your website uses, see the FAQ.
By default, the port is the same as the one specified for the Protocol Type in the previous step. If you need WAF to use a specific port for back-to-origin requests, you can customize the port within the port range.
Origin Domain Name: Enter the origin server's domain name.
WAF supports forwarding client requests only to the IPv4 address that is resolved from this domain name. For IPv6 websites, select the IP method for connection.
ImportantIf the address of the origin server changes, you must promptly update the server address here.
To customize settings such as Load Balancing Algorithm, Standby Link Back-to-origin, HTTP Back-to-Origin, Origin SNI, Request header field configuration, Traffic Tag, Back-to-origin Timeout Configuration, Retry Back-to-origin Requests, or Back-to-origin Keep-alive Requests, see Advanced configurations. If no customization is needed, keep the default values for the other configuration items and click Submit.
Step 3: Switch traffic
After completing the WAF console configuration, you must perform these steps to switch traffic to WAF. Otherwise, WAF protection will not be active.
Allow the WAF back-to-origin IP address range: If you have configured access control policies, such as security group rules or firewall rules, on your origin server, or if you use security software, such as Safedog or Yunsuo, you must add the WAF back-to-origin IP address range to the whitelist on the origin server. Otherwise, back-to-origin traffic from WAF may be blocked, which causes service interruptions.
NoteWe recommend enforcing a strict whitelist on your origin's ingress traffic, permitting connections exclusively from the WAF's back-to-origin IP address range. Anything less renders the WAF ineffective against a determined attacker.
In the upper-right corner of the Add Completed page, click WAF IP Address.
In the Back-to-origin CIDR Block dialog box, click Copy to copy all the WAF back-to-origin IP addresses to the clipboard.
NoteThe copied back-to-origin IP address ranges are separated by commas (,). They include addresses such as 2408:400a:3c:xxxx::/56, which are IPv6 address ranges.
Allow the preceding IP address ranges in your server's firewall or other locations. For example, if the origin server is an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance, add the IP ranges to the ECS security group. For more information about security group operations, see Add a security group rule.
On the ECS instance details page, click , and then select the target security group to open its details page.
On the security group details page, under , click Add Rule.
Because a single security group rule cannot contain both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, you must create separate rules for each.
Add IPv4 rule: In the Source area, paste the IP segment that you copied in the previous step and manually delete the IPv6 addresses. Set Port Range to the origin port that you configured in Step 2. Keep the remaining parameters at their default values and click Save.
Add IPv6 rule: Click Add Rule again, follow the previous step to add the IPv6 address segment, and select IPv6 in the Source area.
Locally verify the WAF configuration: Before you change the domain's DNS settings, we recommend that you verify the configuration by modifying the local
hostsfile to map the domain name. This can prevent service interruptions caused by incorrect configurations.On the Add Completed wizard page, click Copy CNAME to copy the WAF CNAME.
Go to Network Diagnostic Analysis and select Network Diagnostic Analysis, enter the copied CNAME address, such as
xxx.c.yundunwaf2.com, and click OK.Copy the IP address from the DNS service provider analysis results and add it to your local computer's
hostsfile.Windows
Use Notepad to open the
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostsfile. Add the following record to the end of the file and save it.<IP address copied in the previous step> <Domain name currently added to WAF>Open
cmdand run theping <Domain name currently added to WAF>command. If the output IP address matches the one that you added, the hosts file modification has taken effect. Otherwise, runipconfig /flushdnsto flush the DNS cache and then run the ping command again.Open a browser and enter your protected domain in the address bar.
If the website loads normally, the WAF domain configuration is correct. You can proceed to the next step of modifying the DNS resolution.
If the website access is abnormal, it may indicate an error in the WAF domain configuration. We recommend checking the above configurations, fixing any issues, and re-running the local verification.
After you complete the local verification, restore the hosts file to its original state.
macOS
Press
Command + Space barto search for and openTerminal.Enter
sudo vim /etc/hoststo open thehostsfile.Add the following line at the end of the file and save it.
<IP address copied in the previous step> <Domain name currently added to WAF>Run the
ping <Domain name currently added to WAF>command. If the output IP address matches the one that you added, the hosts file modification has taken effect. Otherwise, runsudo killall -HUP mDNSResponderto flush the DNS cache and try pinging again.Open a browser and enter your protected domain in the address bar.
If the website loads normally, the WAF domain configuration is correct. You can proceed to the next step of modifying the DNS resolution.
If the website access is abnormal, it may indicate an error in the WAF domain configuration. We recommend checking the above configurations, fixing any issues, and re-running the local verification.
After local verification is complete, remove the entry from your
hostsfile.
Modify the domain's DNS resolution: Point your domain's DNS resolution to the CNAME address provided by WAF to ensure that web requests to the domain are routed through WAF for security protection.
NoteWe recommend performing this operation during off-peak hours to minimize business impact.
On the Add Completed wizard page, click Copy CNAME to obtain the WAF CNAME address.
Set your domain's DNS resolution address to the address you copied in the previous step. If your domain's DNS is hosted by Alibaba Cloud DNS, follow these steps. If note, perform similar steps in their system.
On the Public Zone page, find the target domain and click Settings in the Actions column.
On the Settings page, locate the Hostname that you want to modify, and click Edit in the Actions column. For example, if the domain added to WAF is
www.aliyundoc.com, you need to locate and modify the entry with the host recordwwwunder the primary domainaliyundoc.com.In the Edit Record panel, set Record Type to CNAME and Record Value to the CNAME record's value provided by WAF. Keep other settings unchanged.
When modifying DNS records:
For the same host record, you can only have one CNAME record value. You need to change it to the WAF CNAME address.
A CNAME record conflicts with other record types like A, MX, and TXT for the same host record. You must delete the conflicting records before adding the new CNAME record.
WarningDuring the DNS change, some users may experience temporary service interruptions. Therefore, you must add the new CNAME record immediately after deleting the old one.
Click OK to save the DNS settings. The updated DNS record will then take effect.
NoteIt takes some time for DNS records to propagate. If the website is inaccessible after the change, wait 10 minutes and refresh the page to try again.
Step 4: Verify the protection
After completing the setup, follow these steps to verify that the domain has been successfully added.
Enter the added website domain in your browser. If it loads normally, the domain has been added successfully.
NoteAccess your website domain, not the CNAME provided by WAF. The CNAME is only for DNS resolution and cannot be accessed directly.
In your browser, enter the added website domain name and a web attack code, for example,
<protected domain name>/alert(xss), wherealert(xss)is a test cross-site scripting attack). If a 405 block page appears, it means WAF intercepted the attack and is working correctly.
After completing the CNAME setup, also pay attention to the following:
Custom protection rules: WAF enables a set of default protection rules for added domains. You can view these rules on the page. If the default rules do not meet your business requirements (for example, to add a specific IP address to the whitelist to allow all requests from that address), you can create or modify protection rules. For more information, see Mitigation Settings Overview.
Obtain client IP on the origin server: By default, all requests received by the origin server appear to originate from WAF's IP addresses. To obtain the real IP address of the client on the origin server, see Obtain the originating IP address of a client.
Advanced configurations
While following the Procedure, you can set the following advanced configurations to enhance security, improve performance, and simplify management. You can also modify the settings after the integration is complete. On the CNAME Record tab, find the target domain and click Edit in the Actions column.
Enhance security protection level (HTTPS)
Parameter | Description |
Supports the SM2 algorithm to meet specific security and compliance requirements. Currently, only SM encryption from the client to WAF is supported. SM back-to-origin is not supported. You need to provide an SM certificate and private key in PEM format. | |
Uses the HTTP/2 protocol to improve webpage loading speed, reduce latency, and enhance user experience. If your website supports HTTP/2, enable this feature. After enabling, HTTP/2 and HTTPS use the same port. | |
Forces all HTTP access to be redirected to HTTPS and enables HSTS by default, ensuring that clients always access through a secure connection. This is available only when HTTP is not selected as the listener protocol. | |
Defines the allowed TLS versions between the client and WAF. Higher versions offer stronger security but have lower compatibility with older clients. For high-security scenarios, we recommend selecting TLS 1.2 and later versions. | |
Defines the allowed encryption algorithms between the client and WAF. Strong cipher suites offer high security but have low compatibility with older clients. For high-security scenarios, we recommend selecting a strong cipher suite. | |
Allows WAF to connect to the origin via HTTP when the origin server does not support HTTPS. You must enable this if your origin server does not have an SSL certificate; otherwise, your website will be inaccessible. | |
When the origin server hosts HTTPS services for multiple domain names on the same IP address, you must enable this feature to ensure correct routing. |
Enable SM-based HTTPS
On the Configure Listener page, you can turn on the Enable SM-based HTTPS switch.
In the SM Certificate Upload Mode area, select an appropriate upload method:
Manual upload: Select a local SM certificate in PEM format. The certificate must include four files: SM Certificate (such as
server_enc.pem), Encryption Private Key (such asserver_enc.key), SM Signing Certificate (such asserver_sign.pem), and Signing Private Key (such asserver_sign.key). If the certificate is in another format, such as PFX or P7B, transform it to PEM format.Select Existing Certificate: Select a certificate that has been issued or uploaded in Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
Apply for a New Certificate: If you do not have an SSL certificate for the domain name, you must first purchase a certificate. Wait for the certificate to be issued before you add it to WAF.
Optional: If you want to allow only SM clients to access your website, you can turn on the Allow Access Only from SM Certificate-based Clients switch.
HTTP/2
On the Configure Listener page, select HTTP2.
Enable HTTPS Routing
On the Configure Listener page, expand Advanced Settings and click Enable HTTPS Routing.
TLS Version
On the Configure Listener page, expand Advanced Settings, and select the desired TLS Version:
TLS 1.0 and Later (Best Compatibility and Low Security): Supports all legacy clients.
TLS 1.1 and Later (High Compatibility and High Security): Prevents clients that only support TLS 1.0 from accessing the website.
TLS 1.2 and Later (High Compatibility and Best Security): Meets the latest security compliance requirements but will cause legacy clients using TLS 1.0 and 1.1 to be unable to access the website.
Support TLS 1.3: Select this if your website supports the TLS 1.3 protocol. WAF does not listen for TLS 1.3 client requests by default.
HTTPS Cipher Suite
On the Configure Listener page, expand Advanced Settings and select the desired HTTPS Cipher Suite:
All Cipher Suites (High Compatibility and Low Security)
Custom Cipher Suite (Select It based on protocol version. Proceed with caution.): If your website supports only specific cipher suites, select this option and choose from the list of supported suites.
Strong cipher suites
Weak cipher suites
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
AES128-GCM-SHA256
AES256-GCM-SHA384
AES128-SHA256
AES256-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
AES128-SHA
AES256-SHA
DES-CBC3-SHA
NoteCipher suite security recommendation: The ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 and ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384 cipher suites use ECDHE for key exchange and RSA for authentication, with AES-CBC for encryption. Their security and performance are lower than suites that use authenticated encryption modes such as AES-GCM. Some security scanners may identify them as weak. If this occurs, select a custom cipher suite and manually exclude these two suites.
Cipher suite naming standards: Naming standards for cipher suites vary. WAF displays them in OpenSSL format, while some scanners may use the IANA standard. For example, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384 in OpenSSL corresponds to TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 in IANA. To quickly find the correspondence, visit ciphersuite.info or use other TLS query tools.
Enable HTTP Routing
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Advanced HTTPS Settings and click Enable HTTP Routing. The back-to-origin port defaults to 80. Change this port if needed.
Origin SNI
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Advanced HTTPS Settings and select Origin SNI. You can then set a value for the SNI extension field. Valid values:
Use Domain Name in Host Header
The SNI value of the back-to-origin request is the same as the value of the Host field in the HTTP request header. For example, if the added domain name is
*.aliyundoc.comand the client request Host iswww.aliyundoc.com, the back-to-origin SNI iswww.aliyundoc.com.Custom
Specify a fixed SNI value, which can be different from the Host field. Use this only when the origin server has special configuration requirements, such as needing to direct requests from multiple domain names to a specific backend service.
Extend network access capabilities (IPv6)
Enable IPv6
Description:
If your website supports IPv6, use this feature to direct IPv6 traffic to WAF. The system assigns an IPv6 WAF IP address to the domain name.
IPv4 client requests are forwarded to the IPv4 origin server. IPv6 client requests are preferentially forwarded to the IPv6 origin server. If no IPv6 origin server is configured, they are forwarded to the IPv4 origin server.
ImportantThis feature is available only for the pay-as-you-go, subscription Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of WAF in Chinese Mainland.
If this feature is enabled, Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing is not supported.
Steps: On the Configure Listener page, expand More Settings, and click Enable IPv6.
Improve service availability and performance
Parameter | Description |
All domain names added to the same WAF instance share a WAF IP by default. A domain name for which this feature is enabled will be assigned an independent IP address. When other domain names suffer DDoS attacks, this domain name will not be affected. For more information, see Exclusive IP address. Important Subscription Basic Edition instances do not support this feature. | |
Configure at least three protection nodes in different regions for the WAF instance. Combined with intelligent DNS resolution and the least-time back-to-origin algorithm, this ensures the shortest path and lowest latency for traffic from the protection node to the origin server. For more information, see Use the intelligent load balancing feature. Important Subscription Basic Edition instances do not support this feature. | |
When the origin server has multiple addresses, you can configure a load balancing policy to make WAF forward back-to-origin requests according to the policy, achieving traffic distribution. | |
Configure a secondary origin server to ensure high availability of the service. When all primary back-to-origin link addresses are unreachable and the request traffic is not less than 100 QPS, the system will automatically switch to the secondary link within 30 seconds. It will automatically switch back after the primary link is recovered. |
Enable Exclusive IP
ImportantPay-as-you-go instances are billed based on the number of enabled exclusive IP addresses. For more information, see Pay-as-you-go billing description.
Exclusive IP addresses are not fixed. To ensure business stability, strictly follow the steps in this topic to modify the domain's DNS settings. For more information, see Can I change the DNS record to the WAF VIP?
Enabling this feature disables Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing.
On the Configure Listener page, expand More Settings and click Exclusive IP Address. For subscription instances, if this option is unavailable, follow the prompts on the page to upgrade your instance and purchase the Exclusive IP value-added service before you can continue the configuration.
Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing
ImportantBilling for pay-as-you-go instances is determined by whether Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing is enabled. For more information, see Pay-as-you-go billing.
If enabling Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing, you cannot use IPv6 or exclusive IP addresses.
On the Configure Listener page, expand More Settings. In the Protection Resource area, select Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing to enable this feature. If you use a subscription instance and this option is unavailable, follow the on-screen instructions to upgrade and enable the Intelligent Load Balancing value-added service before you proceed with the configuration.
Load Balancing Algorithm
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, select a Load Balancing Algorithm from the following options:
Round-robin
Forwards client requests sequentially to each server in the origin server address list. This is ideal for scenarios that require even load distribution across multiple origin servers.
IP hash
Forwards requests from the same client to the same origin server. This is suitable for scenarios that require session persistence, but may result in an unbalanced load.
Least time
Uses intelligent DNS resolution and the least-time back-to-origin algorithm to ensure the shortest path and lowest latency for traffic from the protection node to the origin server.
ImportantTo use the Least time algorithm, ensure that Protection Resource is set to Shared Cluster-based Intelligent Load Balancing during Configure Listener. For more information, see Shared Cluster Intelligent Load Balancing.
Standby Link Back-to-origin
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, click Standby Link Back-to-origin. You can enter up to 20 addresses in IP or domain name format. Press Enter after you enter each address to confirm. If you enter multiple addresses, WAF forwards origin requests according to your configuration for the load balancing algorithm.
IP: Must be an accessible public IP address.
Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported, either individually or together.
Before you configure an IPv6 address, you must enable IPv6 protection during Configure Listener. For more information, see Enable IPv6.
Domain name: WAF only supports forwarding client requests to the IPv4 address resolved from this domain. For IPv6 websites, use the IP method.
ImportantIf the address of the origin server changes, you must promptly update the server address here.
Obtain real client information
Parameter | Description |
Is there a Layer 7 proxy (Anti-DDoS/CDN, etc.) in front of WAF? | If a Layer 7 proxy (such as a CDN) is deployed in front of WAF, you must set the Obtain Actual IP Address of Client to ensure that WAF can obtain the real client IP information for security analytics (for example, the Attacker IP Address in a Security Reports). |
Helps the origin server distinguish requests that have passed through WAF and obtain the originating IP address of the client or source port. | |
WAF inserts specific headers into the HTTP requests it processes by default. If your web application needs to handle these headers, you can configure them as needed. When WAF inserts a header, if the header already exists in the request, its value is overwritten. If not, WAF adds the header with the specified value. |
Is a Layer 7 proxy such as Anti-DDoS Proxy or CDN deployed in front of WAF
On the Configure Listener page, in the Is a Layer 7 proxy such as Anti-DDoS Proxy or CDN deployed in front of WAF section, configure the following settings:
No
Indicates that business requests received by WAF come directly from the client.
Yes
Indicates that business requests received by WAF are forwarded from another Layer 7 proxy service. You need to further set how to determine the client's IP.
Use the First IP Address in X-Forwarded-For Field as Actual IP Address of Client
WAF obtains the client IP address in the following order:
Reads X-Real-IP from the request header as the client IP address.
If X-Real-IP does not exist, uses the first IP address in X-Forwarded-For (XFF) as the client IP address.
[Recommended] Use the First IP Address in Specified Header Field as Actual IP Address of Client to Prevent X-Forwarded-For Forgery
NoteWe recommend configuring the other proxy service to write the client's source IP address into a specified header field, such as X-Real-IP or X-Client-IP, and select this configuration to prevent attackers from bypassing WAF by forging the XFF field.
In the Header Field box, enter one or more header fields. Press Enter after you enter each field. WAF obtains the client IP from these fields in the following order:
Matches the configured Header Field sequentially.
If none of the specified headers exist, tries to read the X-Real-IP field.
If there is still no result, uses the first IP address in XFF as the client IP address.
Enable Traffic Tag
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Other Advanced Settings, select Enable Traffic Tag, and configure the following marking fields:
Custom Header: By configuring a Header Name and a Header Value, WAF adds this header to origin requests to identify requests that have passed through WAF. For example, you can configure the header as
WAF-TAG: Yes, whereWAF-TAGis the header name andYesis the header value. After configuration, your origin server can use this field to create validation or access control policies to enhance security protection and request detection.ImportantDo not enter standard HTTP header fields, such as User-Agent. Doing so will cause the standard header's content to be overwritten by your custom value.
Originating IP Address: If you specify the header field that contains the originating IP address of the client, WAF records this header field and forwards it to the origin server. For more information about how WAF determines the originating IP address of the client, see Is there a Layer 7 proxy (such as Anti-DDoS or CDN) in front of WAF.
Source Port: Specifies the header field that contains the originating port of the client. WAF records this header field and forwards it to the origin server.
Request Header Forwarding
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Other Advanced Settings. In the Request Header Forwarding area, select the header fields to insert.
Insert X-Client-IP to get the real client IP: Forwards the originating IP address of the client.
Add X-True-IP with Real Client IP: Forwards the client's IP address to the origin server.
Insert Web-Server-Type to get the server type: The first proxy typically adds this header to inform the backend server of the type of frontend web server or proxy that is processing the request.
Add WL-Proxy-Client-IP with Real Client IP: This feature is similar to X-Client-IP. WL-Proxy-Client-IP is a request header specific to Oracle WebLogic Server.
Insert X-Forwarded-Proto to get the frontend protocol: The protocol that the client uses to connect to the first proxy.
Optimize back-to-origin link quality
Parameter | Description |
When the origin server's processing time is long, leading to possible timeout issues, you can configure the timeout for WAF to establish new connections and read/write connections. | |
When a back-to-origin attempt fails, WAF will try to fetch from each origin server three times by default. If this feature is disabled, WAF will not retry if a back-to-origin attempt fails. | |
Configure the ability to maintain a long-term connection between WAF and the origin server. If you experience occasional 502 errors after integration, check the relevant parameters on the origin server. We recommend setting the value of WAF's persistent connection parameter to be less than or equal to the corresponding parameter value on the origin server. |
Set back-to-origin timeout
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Other Advanced Settings and configure the following settings:
Connection Timeout Period: The timeout period for WAF to establish a connection with the origin server. In most cases, you do not need to adjust this parameter. Increase this parameter only if connections are slow to establish due to high network latency or an extremely high load on the origin server. The default value is 5 s, and the valid range is 1 s to 3,600 s.
Read Connection Timeout Period: The timeout for receiving a response from the origin server. You can increase the value of this parameter for operations that require a long response time, such as report exports and batch data processing. Valid values: 1 to 3,600. Default value: 120. Unit: seconds.
Write Connection Timeout Period: Specifies the timeout duration for requests sent from WAF to an origin server. In most cases, you can use the default value. Increase the timeout only if the origin server is under an extremely high load and processes requests slowly. Valid values: 1 to 3,600. Default value: 120. Unit: seconds.
Retry back-to-origin requests
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Other Advanced Settings and configure the settings in the Back-to-origin Retry section.
Back-to-origin keep-alive requests
ImportantIf you disable this feature, back-to-origin keep-alive connections will not support the WebSocket protocol.
On the Configure Forwarding Rule page, expand Other Advanced Settings. Then, in the Back-to-origin Keep-alive Requests area, enable the feature and configure the following settings:
Max Requests per Connection: The default value is 1,000. The valid range is 60 to 1,000. For example, if your origin server uses Nginx, this parameter corresponds to the Nginx
keepalive_requestsparameter. For more information, see the Nginx documentation.Timeout Period of Idle Keep-alive Requests: The default value is 15 s, and the valid range is 10 s to 3,600 s. For Nginx origin servers, this parameter is equivalent to the Nginx
keepalive_timeoutparameter.
Improve resource management efficiency
Resource Group
Sescription: Simplifies resource management and permission configuration to improve management efficiency. If you do not specify a resource group, the domain is added to the Default Resource Group. For more information, see Resource groups.
Steps: On the Configure Listener page, in the Resource Group area, select the resource group for the domain name from the drop-down list.
Maintenance
Update the certificate securing a domain name
If a certificate is about to expire or changes for other reasons, such as being revoked, you must update the certificate securing the domain name.
Purchase a new certificate from Alibaba Cloud
In the Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate) console, renew the SSL certificate. For more information, see Renew an SSL certificate.
In the WAF console, find the domain name in the CNAME record list and click Edit in the Actions column.
In the HTTPS Upload Type area, select Select Existing Certificate, select the updated certificate, and then click .
Already purchased a new certificate from another platform
Download the certificate file from the original purchase platform.
In the CNAME access list of the WAF console, click Edit in the Actions column for the target domain name.
In the HTTPS Upload Type area, select Upload and enter the required information.
Certificate Name: Set a unique name for the certificate. It cannot be the same as an already uploaded certificate.
Certificate File: Use a text editor to open and paste the content of the certificate in PEM, CER, or CRT format.
Example format:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----......-----END CERTIFICATE-----Certificate chain: If an intermediate certificate is included, paste it after the server certificate in the order of server certificate and then intermediate certificate.
Format conversion: If the certificate is in a format such as PFX or P7B, use the certificate tool to convert it to the PEM format.
Private Key: Use a text editor to open and paste the content of the private key in PEM format.
Example format:
RSA:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----......-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----ECC:
-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----......-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----
When a certificate has less than 30 calendar days of validity remaining, WAF displays an
 icon in the connection list to indicate that the certificate is about to expire. We recommend updating it promptly to avoid affecting normal business operations.
icon in the connection list to indicate that the certificate is about to expire. We recommend updating it promptly to avoid affecting normal business operations.You can set up SSL certificate message reminders to receive notifications by email, text message, and other methods before the certificate expires. For more information, see Set up message notifications for SSL certificates.
To avoid business interruptions caused by an expired certificate, we recommend enabling the certificate hosting service of Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate). This service automatically requests certificates before they expire. For more information, see What is Certificate Hosting Service?
Re-add a domain after ICP filing expiration
After a domain is added via CNAME, WAF periodically checks its ICP filing status. If the filing expires, WAF will automatically stop forwarding traffic for that domain. After the filing expires, you need to re-apply for it. Once successful, return to the CNAME onboarding page and click Add Again.
Disable or remove WAF protection
Temporarily disable WAF protection: If you encounter issues after onboarding, such as a high number of false positives, and need to temporarily disable WAF protection, turn off the WAF Protection Status switch on the Protected Objects page in the WAF console. For more information, see Disable WAF protection with one click.
Remove the instance: If you no longer want to use WAF to protect an ECS instance, follow these steps to remove it.
Change the domain's DNS record back to the origin server address. For example, set it to the IP address of the origin server.
In the WAF console, click Delete in the Actions column for the target domain name.
Business impact: Before deleting the domain, you must change the domain's DNS record back to the origin server address. Otherwise, the CNAME address pointed to by the domain will become invalid, causing your website to become inaccessible.
Billing reminder: For a pay-as-you-go WAF instance, in addition to request processing fees, you are also charged for features, including the instance itself and protection rules. If you want to stop using WAF and stop billing, see Disable WAF.
Manage WAF domains in bulk via API
When you have multiple domains to manage in WAF, you can use the API to quickly view or add them.
To add a domain to a WAF instance, see CreateDomain.
To query the configuration details of a CNAME domain, see DescribeDomain.
Apply in production
To ensure security and stability in a production environment, follow these best practices when onboarding production ECS instances.
HTTPS configuration: Deploy certificates on your ECS instances and use the following configurations for efficient certificate management.
Upload your certificate files to Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
When adding the ECS instance to WAF, configure a traffic forwarding port of the HTTPS type. In the TLS Version Control section, configure TLS 1.2 or later.
Set up notifications for SSL certificates to update them promptly before they expire.
Phased rollout: First, add a non-production ECS instance during off-peak hours. After running it for a period to confirm that services are normal, proceed to add the production ECS instance.
Check services: After onboarding is complete, confirm that your services are normal in the following ways:
Check logs: Check for significant fluctuations in the percentage of 200 status codes in your logs and look for sudden spikes or drops in QPS. If you have enabled the WAF log service, see WAF logs.
Application monitoring: Check if core application functions, such as user access and transactions, are working normally.
Maintenance: After onboarding in a production environment, continuous maintenance is required to monitor for attacks and false positive events.
Event handling: Check Security Reports and configure CloudMonitor notifications to stay informed about attacks and security events.
Rule tuning: Continuously monitor attack logs to analyze whether legitimate user requests are being mistakenly blocked and optimize protection rules accordingly.
FAQ
Onboarding
How do I view the WAF back-to-origin CIDR blocks and the WAF CNAME?
You can find the WAF back-to-origin CIDR blocks and the CNAME address provided by WAF for each added domain on the onboarding page. To allow the WAF back-to-origin IP address range, see Allow the WAF back-to-origin IP address range.

How do I check the DNS status of an added domain?
You can check the DNS status of a domain in the onboarding list to promptly identify domains at risk of DNS anomalies and adjust DNS resolution settings according to the console prompts.
DNS Status
Action
Normal DNS resolution
The domain's DNS is resolved to WAF as expected. No action is required.
Abnormal DNS resolution, using A record for connection
You need to delete the A record of the added domain name, re-add a CNAME record, and point the record value to the CNAME address that is provided by WAF. For more information, see Change the domain's DNS record.
Abnormal DNS resolution, using incorrect WAF IP
You need to delete the A record of the added domain name, re-add a CNAME record, and point the record value to the CNAME address that is provided by WAF. For more information, see Change the domain's DNS record.
Abnormal DNS resolution, using incorrect CNAME address
You need to change the record value in the CNAME record to the CNAME address that is provided by WAF. For more information, see Change the domain's DNS record.
Unknown DNS resolution, proxy enabled for the domain
A Layer 7 proxy is enabled in front of WAF. You need to check whether the origin server address that is configured in the proxy is the CNAME address that is provided by WAF. If it is correct, you can ignore this alert.
DNS check timed out
Click the
 icon to re-run the DNS status check.
icon to re-run the DNS status check.No DNS record, please connect to WAF
You need to add a CNAME record and enter the CNAME address that is provided by WAF as the record value. For more information, see Change the domain's DNS record.
DNS not resolved to WAF, please connect to WAF
You need to modify the CNAME record and enter the CNAME address that is provided by WAF as the record value. For more information, see Change the domain's DNS record.
How do I check the ICP filing information for a domain name?
In the Network Diagnostic Analysis, select Website Diagnostic Analysis and enter the domain name. Confirm that the Filing Inspection status is The website has been filed. If the message "The website has not been filed. Please consult your website server provider" is displayed, you must complete the ICP filing before adding the domain name to WAF.
If you are using an Alibaba Cloud server, go to the Alibaba Cloud ICP Filing System to file for your website. For more information, see ICP filing process.
If you are not using an Alibaba Cloud server, go to your server provider's filing system or the MIIT ICP Filing official website to file.
How do I find the public IP or domain name of my origin server?
In the section, if you are unsure about the origin server address, go to the Network Diagnostic Analysis page, enter the domain name of the website you are adding, and check the DNS Provider Resolution Results area. If an IP record, such as an A record or AAAA record, is returned, enter the corresponding IP in WAF. If a domain name record, such as a CNAME record, is returned, enter the corresponding Domain Name (Such as CNAME).
How do I determine the port my website uses?
In the section, configure the back-to-origin port that the website uses. You can use the following information to confirm the port.
Standard ports (default): Web services use standard ports by default. Therefore, you do not need to specify them in the domain name when you access the web services.
HTTP: For example,
http://yourdomain.commeans that port 80 is used.HTTPS: For example,
https://yourdomain.commeans that port 443 is used.
Non-standard ports: If the website uses a non-standard port, the port number is displayed directly after the domain name in the format
domain:port number.HTTP: For example,
http://yourdomain.com:8080means that port 8080 is used.HTTPS: For example,
https://yourdomain.com:8443means that port 8443 is used.
NoteTo ensure accuracy, we recommend checking the configuration file of your web server, such as Nginx or Apache, such as
nginx.conf, to obtain the most accurate port information.
WAF VIP
What is a WAF VIP and how can I view it?
After a domain name is added to WAF, the system assigns an independent virtual IP address (VIP) to receive business requests. This VIP is not shared with other tenants. Alibaba Cloud WAF instances provide a high-availability protection service. This VIP is not attached to any specific physical device but belongs to the Alibaba Cloud WAF cluster resources. Within the same WAF instance:
If domain exclusive IP or intelligent load balancing is not enabled, all domain names share one VIP.
If domain exclusive IP is enabled, each domain name is assigned an independent VIP.
If intelligent load balancing is configured, all domain names share multiple VIPs.
The WAF VIP cannot be directly viewed in the console. You need to use the
pingornslookupcommand on a client to query the domain name that has been added to WAF.ping example.com #Replace with the domain name added to WAFImportantThis VIP is the WAF ingress IP address, not the WAF back-to-origin IP address range. The origin server must be configured in strict accordance with the steps in Allow the WAF back-to-origin IP address range.
How do I set a default SSL or TLS policy to make the VIP compliant?
To meet HTTPS communication requirements in compliance scenarios, WAF supports customizing SSL certificates and TLS policies for VIPs. Before you perform a compliance scan on the WAF VIP, follow these steps to upload a compliant HTTPS certificate and enable or disable specific versions of TLS protocols and cipher suites.
NoteIf you enable Exclusive IP Address, this configuration also applies to the exclusive IP address.
Click Default SSL/TLS Settings above the CNAME records.

In the Default SSL/TLS Settings dialog box, configure the following settings and click OK.
Parameter
Description
HTTPS Upload Type
Upload an SSL certificate. The operation is the same as for uploading a domain certificate. See Upload a certificate.
TLS Version
The options are:
TLS 1.0 and Later (Best Compatibility and Low Security)
TLS 1.1 and Later (High Compatibility and High Security): Legacy clients that use the TLS 1.0 protocol cannot access the website.
TLS 1.2 and Later (High Compatibility and Best Security): Meets the latest security compliance requirements, but prevents older clients that use the TLS 1.0 or TLS 1.1 protocol from accessing the website.
Support TLS 1.3: If your website supports the TLS 1.3 protocol, select this option.
HTTPS Cipher Suite
Select the cipher suites to enable. The options are:
All Cipher Suites (High Compatibility and Low Security)
Custom Cipher Suite (Select It based on protocol version. Proceed with caution.): If your website supports only specific cipher suites, select this option. For more information about supported custom cipher suites, see WAF-supported cipher suites.
When I scan my domain's ports, why does it show open high-risk ports that I didn't open? Is there a risk?
When using tools such as Nmap to scan a domain added to WAF via CNAME, you might see open ports that are not open on your origin server. This is because the domain's DNS points to WAF's VIP, so you are actually scanning the VIP's ports. This is normal.
WAF only forwards traffic for ports configured in the console. For unconfigured ports, WAF sends an RST packet to terminate the connection immediately after the TCP three-way handshake and does not forward any data. Therefore, there is no security risk for unconfigured ports, and the VIP ports cannot be manually closed. For more information, see WAF non-standard port opening instructions.
Can I change the DNS record to the WAF VIP?
No. When adding a domain to WAF via CNAME, you must point the DNS resolution to the CNAME provided by WAF, not to WAF's VIP address. This is because the VIP address may change, for example, when enabling or disabling exclusive IP address or intelligent load balancing, or in extreme cases of WAF failure. Pointing directly to the VIP could lead to service interruptions. Using a CNAME ensures that the system switches the backend IP address automatically, which guarantees business continuity.
Product capabilities
Can I use WAF with other services, such as a CDN or NAT Gateway?
Yes. If there is a Layer 7 Proxy like CDN or Anti-DDoS in front of WAF, you need to pay attention to the Is a Layer 7 proxy (such as Anti-DDoS or CDN) deployed in front of WAF? setting when adding to WAF. For more information, see Provide WAF security protection for domain names with CDN content acceleration enabled.
The origin server address for WAF connection is the next-hop device for traffic after WAF protection. It supports resources such as NAT Gateway, Server Load Balancer, servers, and OSS.
What cipher suites does WAF support?
In CNAME record mode, you can use custom cipher suites to control which client requests WAF responds to based on the supported suites. For a list of supported cipher suites, see HTTPS cipher suite.


