VPN Gateway is integrated with Network Intelligence Service (NIS). NIS can help you diagnose VPN gateways and provide suggestions based on the issues that are detected. This way, you can troubleshoot the issues that you encounter when you use VPN Gateway. The issues include IPsec negotiation issues, route configuration issues, and issues that are related to VPN gateway status. The diagnostic process does not affect your business.
Diagnostic items
The following table describes the diagnostic items of VPN Gateway.
Category | Diagnostic item | Description |
Configurations | Instance configurations | Checks whether a VPN gateway is being configured. If a VPN gateway is being configured, wait until its status changes to Available before you perform an operation on the VPN gateway. |
Version | Checks whether the VPN gateway is of the latest version. We recommend that you upgrade your VPN gateway to the latest version. For more information, see Upgrade a VPN gateway. | |
IPsec negotiations | Checks the status of Phase 1 and Phase 2 negotiations for each IPsec-VPN connection on the VPN gateway. If an exception occurs during the negotiations, see the solution displayed in the console or relevant topics for troubleshooting. For more information, see Troubleshoot IPsec-VPN connection issues. | |
VPN tunnel configurations | Checks whether the IPsec-VPN connections configured on the VPN gateway. If the system detects that the required configuration items of a IPsec-VPN connection are missing, you need to configure the IPsec-VPN connection based on your network requirements. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in single-tunnel mode or Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode. | |
CIDR block conflicts | Checks whether the destination CIDR blocks of the policy-based routes, destination-based routes, and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routes on the VPN gateway conflict with 100.64.0.0/10. 100.64.0.0/10 is reserved by Alibaba Cloud. Make sure that the destination CIDR blocks of the policy-based routes, destination-based routes, and BGP routes on the VPN gateway do not conflict with 100.64.0.0/10 or its subnets. Otherwise, the VPN gateway cannot work as expected. If such conflicts exist, modify the conflicted CIDR blocks or use NAT Gateway for address translation. For more information, see Use a VPC NAT gateway and a VPN gateway to connect a data center and a VPC. | |
BGP consistency | Checks whether Phase 2 negotiations succeed but BGP negotiations failed. If Phase 2 negotiations succeed but BGP negotiations fail, check the BGP configurations and transmission of BGP packets. For more information, see the "What do I do if the system prompts that Phase 2 negotiations succeeded but the BGP negotiation is in the Abnormal state?" section of the FAQ about IPsec-VPN connections topic. | |
Shared Phase 1 IPsec negotiations | Checks whether the configurations of multiple IPsec-VPN connections are the same if the IPsec-VPN connections share Phase 1 negotiations. If multiple IPsec-VPN connections are associated with the same VPN gateway and customer gateway, and use the same Internet Key Exchange (IKE) version, the IPsec-VPN connections share the same Phase 1 negotiation. In scenarios in which multiple IPsec-VPN connections share the same Phase 1 negotiation, the IPsec-VPN connections must have the same Pre-Shared Key and IKE settings, including the version, negotiation mode, encryption algorithm, authentication algorithm, DH group, and SA lifetime (in seconds). This ensures that the IKE settings of each IPsec-VPN connection can be shared during IPsec negotiations. Modify the IPsec-VPN connection configurations based on your business requirements to ensure that the IPsec-VPN connections use the same configurations. For more information, see the "Modify an IPsec-VPN connection" section of the Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in single-tunnel mode topic. | |
Quotas | VPN gateway bandwidth usage | Checks whether the bandwidth usage of the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit. If the bandwidth usage of the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit, you can upgrade the bandwidth of the VPN gateway based on your network requirements. For more information, see Upgrade or downgrade a VPN gateway. |
Fees | Overdue payments | Checks whether the VPN gateway has overdue payments. If the VPN gateway has overdue payments, add funds to your account. |
Overdue payment alert | Checks whether the VPN gateway expires within seven days. | |
Routes | Unadvertised routes | Checks whether the VPN gateway has unadvertised policy-based or destination-based routes. If unadvertised policy-based or destination-based routes exist, delete or advertise the routes based on your network communication requirements. For more information, see the Advertise a policy-based route and Delete a policy-based route sections of the "Configure policy-based routes" topic, or the Advertise a destination-based route and Delete a destination-based route sections of the "Manage destination-based routes" topic. |
Improper BGP configurations | Checks whether the VPN gateway uses proper BGP configurations if an IPsec-VPN connection uses BGP.
| |
VPN route configurations |
| |
Destination-based route conflicts | Checks whether the destination CIDR blocks of destination-based routes on the VPN gateway overlap with each other. If such conflicts exist, delete the conflicted destination-based routes and create new ones. Make sure that the destination CIDR blocks of destination-based routes do not overlap with each other. For more information, see Manage destination-based routes. You can also use BGP for networking. For more information, see Connect a VPC to a data center in dual-tunnel and BGP routing mode. | |
Policy-based route conflicts | Checks whether the destination CIDR blocks of policy-based routes on the VPN gateway overlap with each other. If such conflicts exist, delete the conflicted policy-based routes and create new ones. Make sure that the destination CIDR blocks of policy-based routes do not overlap with each other. For more information, see Configure policy-based routes. You can also use BGP for networking. For more information, see Connect a VPC to a data center in dual-tunnel and BGP routing mode. | |
BGP route conflicts |
If such conflicts exist, troubleshoot the issues by following the on-screen instructions displayed in the console. | |
Match between VPC routes and VPN routes | Checks whether the destination CIDR block of the route in a VPC route table that points to the VPN gateway overlaps with the destination CIDR block of the policy-based route on the VPN gateway. Make sure that the destination CIDR block of the policy-based route contains the destination CIDR block of the route in the VPC route table that points to the VPN gateway. If the preceding condition is not met, you need to modify the destination CIDR block of the policy-based route. You must delete the policy-based route and create a new one that meets the condition. For more information, see Configure policy-based routes. |
Start a diagnostics
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the VPN gateway is deployed.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the VPN gateway that you want to manage and choose in the Diagnose column.
In the Instance Diagnostics panel, view the diagnostic details.
NoteIf NIS is not activated, select Terms of Service for Standard Edition NIS and click Activate NIS free of charge to diagnose instances.
If you activate NIS as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user and a message appears indicating that you do not have the permission, grant the AliyunNISFullAccess permission to the RAM user by using your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
Ifyou diagnose a VPN gateway for the first time, the system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForNis. For more information, see Service-linked roles.
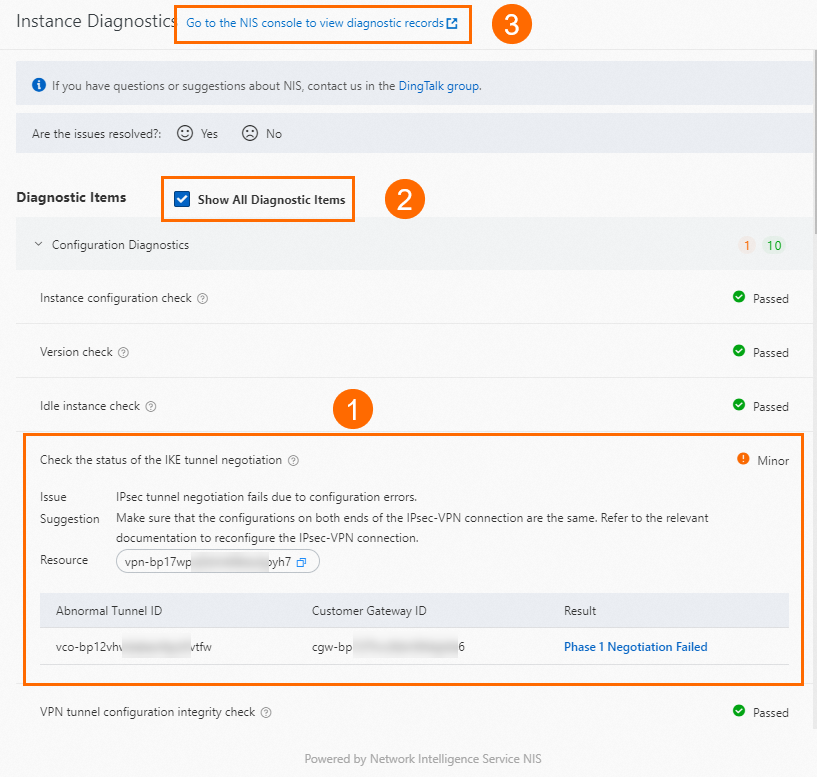
Section
Description
①
Anomalies are displayed in the Instance Diagnostics panel. You can view the diagnosis description, relevant resources, and suggestions.
②
You can view all diagnostic details about the VPN gateway by selecting Show All Diagnostic Items in the Diagnostic Items section.
③
You can go to the Overview page of the NIS console by clicking Go to the NIS console to view diagnostic records in the upper part of the Instance Diagnostics panel to view historical diagnostic reports about the VPN gateway. For more information, see Use features on the Overview page.
Diagnostic examples
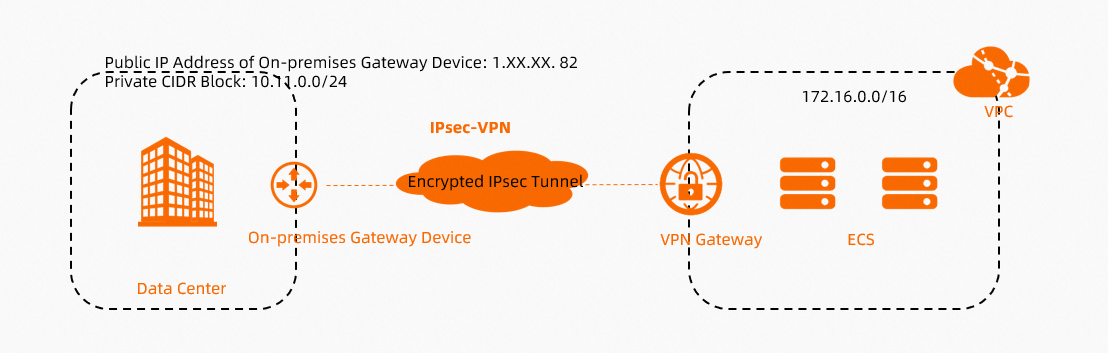
In scenarios in which a data center accesses resources in a VPC by using an IPsec-VPN connection, you can diagnose your VPN gateway to ensure that the IPsec-VPN connection works as expected before you use the connection to transmit service data.
Start a diagnostics on the VPN gateway. For more information, see the Start a diagnostics section of this topic.
In the Instance Diagnostics panel, view the diagnostic details.
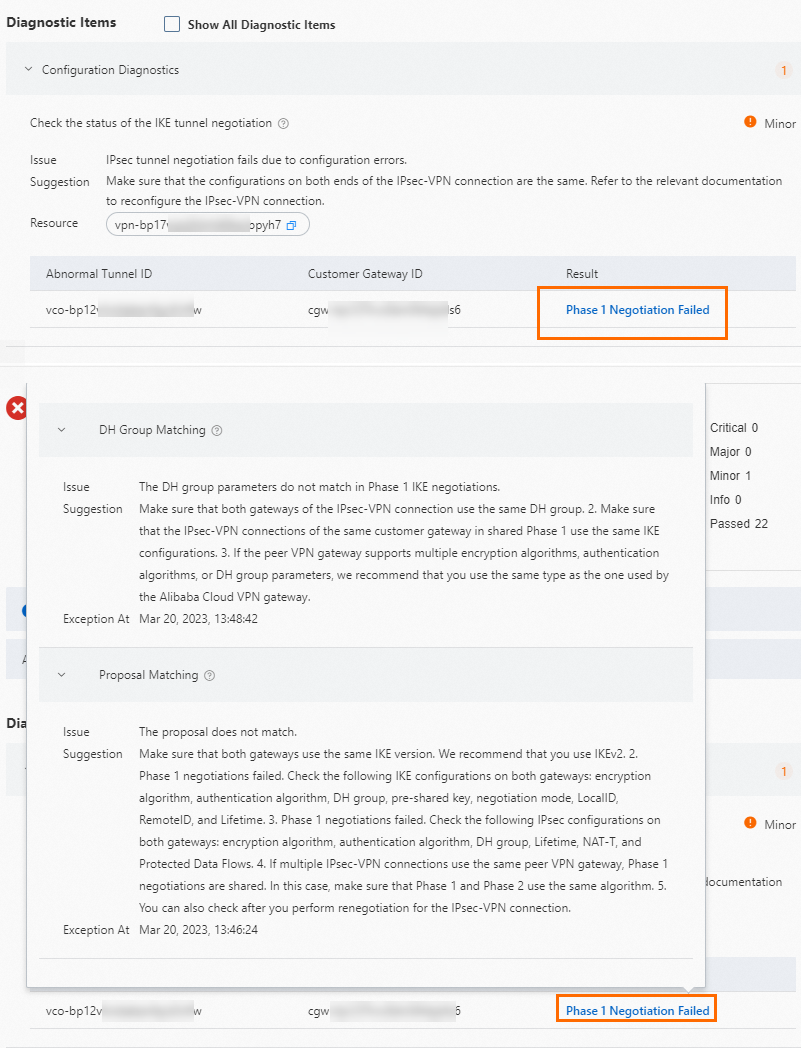
The preceding figure shows an example of a VPN gateway that fails the diagnostics because the Phase 1 negotiation of an IPsec-VPN connection fails. You can click Phase 1 Negotiation Failed in the Result column to view more details and troubleshoot issues.
You can also troubleshoot issues based on the error message on the IPsec Connections page. If the Phase 1 or Phase 2 negotiation of an IPsec-VPN connection fails, an error message is displayed on the IPsec Connections page. You can use the error message for troubleshooting. For more information, see Troubleshoot IPsec-VPN connection issues.
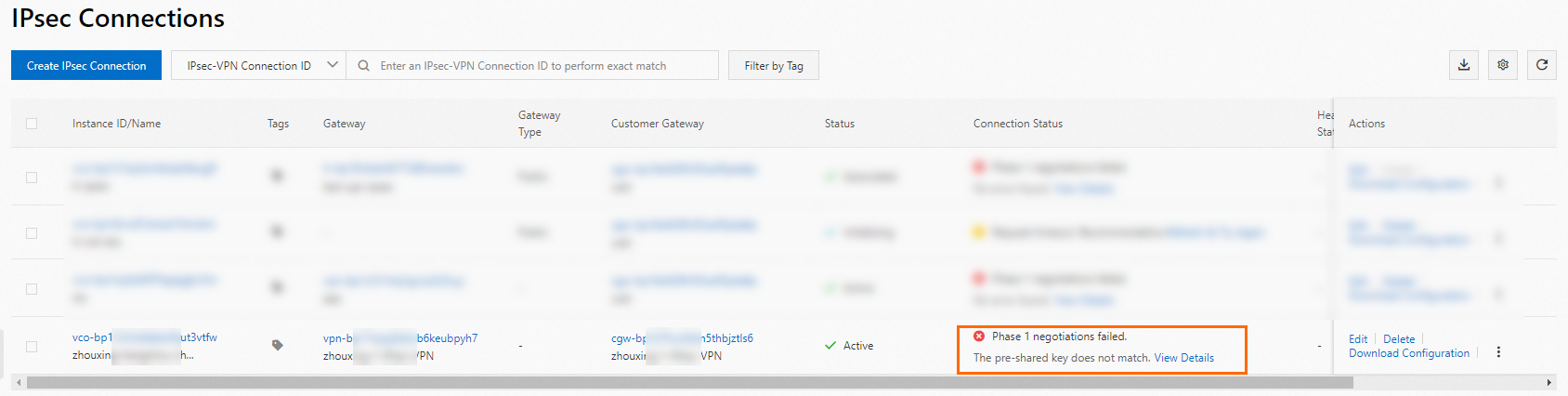
The preceding figure shows an example of the error message displayed on the IPsec Connections page due to failed Phase 1 negotiation of an IPsec-VPN connection. The IPsec-VPN connection fails because the pre-shared key is different on the VPN gateway and the peer gateway. To resolve this issue, make sure that both gateways use the same pre-shared key.
After you resolve the issue, diagnose the VPN gateway again. Make sure that the VPN gateway passes the diagnostics.
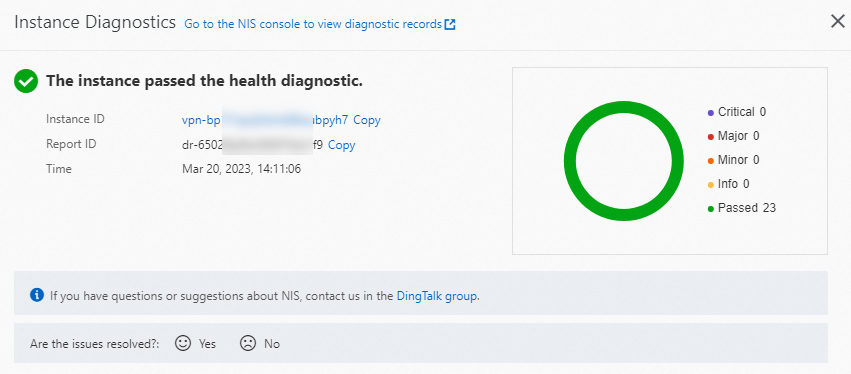
If the VPN gateway passes the diagnostics, but issues occur when you use the IPsec-VPN connection, such as communication failures between the data center and the VPC, see the FAQ topics of VPN Gateway for troubleshooting. For more information, see FAQ about IPsec-VPN connections.