Tablestore supports the pay-as-you-go billing method. You are charged based your actual resource usage. You are not charged for creating an instance.
Billable items
You are charged for the following items on an hourly basis:
Storage usage
Reserved read and write throughput
Metered read and write throughput
Outbound traffic over the Internet
Case 1: Calculate the total instance fee for 1 hour
During a 1-hour billing cycle: The storage usage is 50 GB, outbound traffic over the Internet is 10 GB, the reserved read throughput is increased from 1,000 to 1,200 and the reserved write throughput is decreased from 1,500 to 800 at the 20th minute for all tables in the instance, and 50,000 metered read capacity units (CUs) and 10,000 metered write CUs are consumed.
Note: The total instance fee for the billing cycle is the sum of the following fees:
Fee for storage usage:
50 GB x Unit price per GB-hour of storage usageFee for outbound traffic over the Internet:
10 GB x Unit price per GB of outbound traffic over the InternetFee for reserved read and write throughput:
Average reserved read throughput: (1,000 x 20 + 1,200 x 40)/60 = 1,133.3
Average reserved write throughput: (1,500 x 20 + 800 x 40)/60 = 1,033.3
Fee for reserved read and write throughput:
1,133.3 x Unit price per CU-hour of reserved read throughput + 1,033.3 x Unit price per CU-hour of reserved write throughputFee for metered read and write throughput:
50,000/10,000 x Unit price per 10,000 metered read CUs + 10,000/10,000 x Unit price per 10,000 metered write CUs
The billing for storage usage and reserved read and write throughput is accurate to minutes. The system calculates fees based on average storage usage and average reserved read and write throughput at the end of a billing cycle. The billing for metered read and write throughput is accurate to seconds. Fees are calculated based on the number of used CUs per second.
For example, the reserved read throughput within the first 20 minutes is 1,000 CUs. In 1 second, 2,100 read CUs are consumed. The metered read CUs are calculated as: Metered read CUs = 2,100 - 1,000. In this case, the metered read CUs for that second is 1,100.
Case 2: Calculate the total instance fee for one day
Scenario 1
This scenario describes the billing for resources purchased in a traditional way.
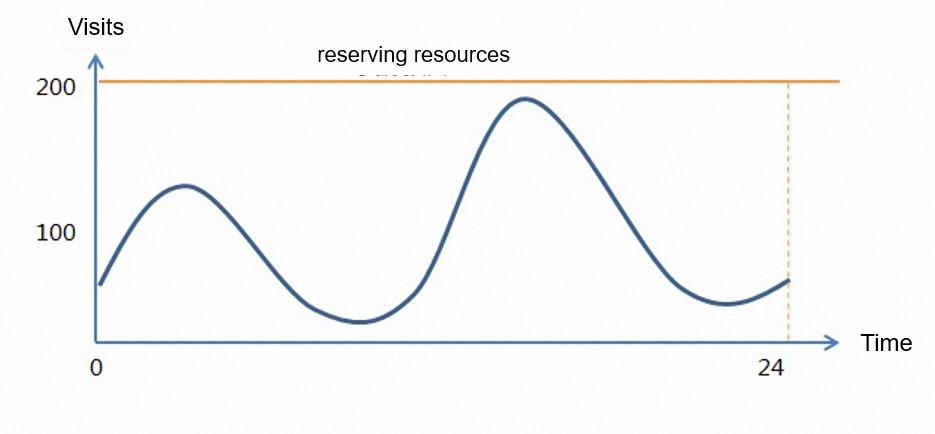
The preceding line chart simulates access to an application in one day. For easy understanding, assume that the visits generated by read and write requests to the application are the same. To ensure that the application has sufficient resources to provide read and write services during peak hours, purchase resources based on your business workloads at peak hours. For Tablestore, you must purchase 200 reserved read CUs and 200 reserved write CUs.
Note: Total daily fee of the instance =
200 × Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput x 24 + 200 × Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput x 24 + Storage usage fee for 24 hours + Fee for outbound traffic over the Internet for 24 hours=4,800 × Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput + 4,800 × Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput + Storage usage fee for 24 hours + Fee for outbound traffic over the Internet for 24 hours.Scenario 2
Tablestore has an operation that you can use to adjust the reserved read and write CUs of each table anytime. The adjustment takes effect within 1 minute and does not affect your business. You can call this operation to increase or decrease the reserved CUs to meet business requirements and minimize costs. The following figure shows the sample usage of Tablestore in one day.
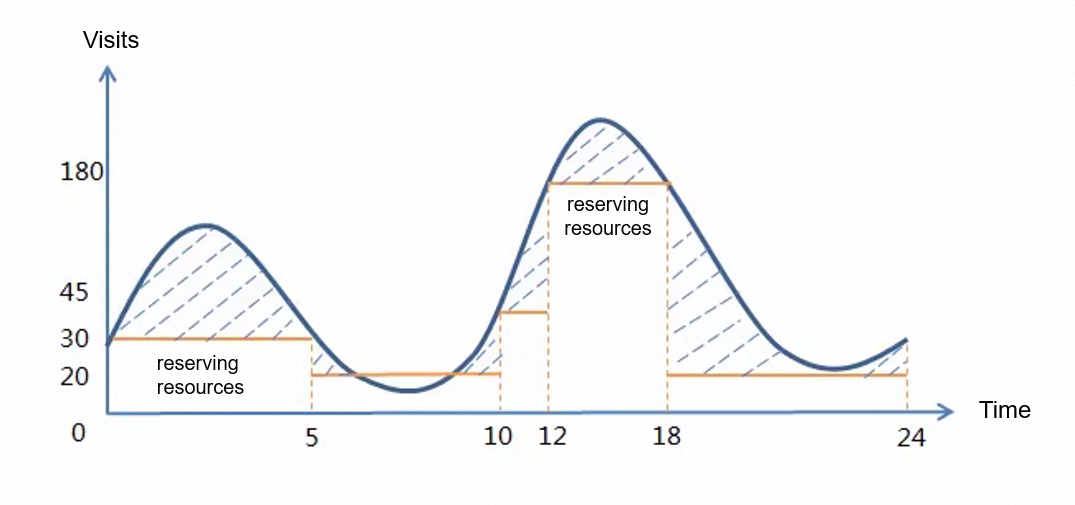
Settings and consumption of read and write CUs:
00:00:00 to 05:00:00: Set the reserved read and write throughput to 30 CUs, respectively. Within the 5 hours, the metered read and write throughput is both 100,000 CUs.
05:00:00 to 10:00:00: The number of application access requests decreases. Set the reserved read and write throughput to 20 CUs, respectively. Within the 5 hours, the metered read and write throughput is both 5,000 CUs.
10:00:00 to 12:00:00: The number of application access requests increases. Set the reserved read and write throughput to 45 CUs, respectively. Within the 2 hours, the metered read and write throughput is both 10,000 CUs.
12:00:00 to 18:00:00 (peak hours): Set the reserved read and write throughput to 180 CUs, respectively. Within the 6 hours, the metered read and write throughput is both 30,000 CUs.
18:00:00 to 24:00:00 (off-peak hours): Set the reserved read and write throughput to 20 CUs, respectively. Within the 6 hours, the metered read and write throughput is both 50,000 CUs.
For easy understanding, assume that the visits generated by read and write requests to the application are the same and that the reserved read and write throughput is changed to the same value by calling the operation.
Note: The following items describe the fees for read and write throughput for the day:
Fee for read throughput:
(30 x 5 hours + 20 x 5 hours + 45 x 2 hours + 180 x 6 hours + 20 x 6 hours) x Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput + (100,000 + 5,000 + 10,000 + 30,000 + 50,000) x Unit price of metered read throughput=1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput + 195,000 x Unit price of metered read throughput.Fee for write throughput:
(30 x 5 hours + 20 x 5 hours + 45 x 2 hours + 180 x 6 hours + 20 x 6 hours) x Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput + (100,000 + 5,000 + 10,000 + 30,000 + 50,000) x Unit price of metered write throughput=1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput + 195,000 x Unit price of metered write throughput.
Total daily fee of the instance =
1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput + 195,000 x Unit price of metered read throughput + 1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput + 195,000 x Unit price of metered write throughput + Storage usage fee for 24 hours + Fee for outbound traffic over the Internet for 24 hours.Savings compared with Scenario 1:
4,800 x Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput + 4,800 x Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput - 1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved read throughput - 19.5 x Unit price per 10,000 metered read CUs - 1,540 x Unit price per hour of reserved write throughput - 19.5 x Unit price per 10,000 metered write CUs.