To monitor the availability of backend servers for Application Load Balancer (ALB), configure health checks for ALB server groups. Health checks detect unhealthy backend servers early and prevent service disruptions, improving service reliability.
Background information
ALB lets you define health check configurations for each server group. Health checks are enabled by default for all server groups.
When health checks are enabled, ALB automatically routes client requests to healthy backend servers and continuously monitors the health of all backend servers in the server group. A backend server must pass health checks for N consecutive times before it is declared healthy. N is the healthy threshold that you configure. Multiple checks help avoid false failures caused by network jitter.
If a backend server fails health checks, ALB stops sending new requests to that server.
After the server recovers, ALB automatically resumes sending traffic to it.
Health checks use short-lived connections. The connection closes after the check completes.
NoteBackend servers with a weight of 0 do not participate in health checks.
ALB uses specific IP addresses to communicate with backend servers and perform health checks. Ensure your backend servers do not block these IP addresses, including iptables rules or any third-party security software.
An upgraded ALB instance uses local IP addresses from its vSwitch CIDR block to communicate with backend servers. Log on to the ALB console and view the local IP addresses on the instance details page.
To ensure that the elastic capabilities of ALB upgrade instances are available, reserve at least eight IP addresses in each vSwitch where ALB instances reside and pre-authorize these vSwitch CIDR blocks.
A non-upgraded ALB instance uses IP addresses in the 100.64.0.0/10 CIDR block to communicate with backend servers.
If all backend servers in a server group fail health checks, ALB continues routing requests to the group based on the scheduling algorithm to minimize service impact. For more information, see How does ALB forward requests when all backend servers in a server group are unhealthy?.
Limits on HTTPS health checks
Standard Edition and higher ALB instances support HTTPS health checks. Basic Edition ALB instances do not support HTTPS health checks.
Create a health check
Method 1: Using the health check page
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the health check.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Health Check page, click Create Health Check.
In the Create Health Check dialog box, configure the parameters in the table below, then click Create.
Use the default values for health check parameters unless you have a specific need. This prevents frequent server switchovers caused by health check failures and helps maintain system availability.
Health check configuration
Description
Health check name
Enter a name for the health check.
Protocol
Select the protocol for health checks.
HTTP: ALB sends HEAD or GET requests to simulate browser behavior and check if the backend server is healthy.
HTTPS: ALB sends HEAD or GET requests to simulate browser behavior and check if the backend server is healthy. For limits, see Limits on HTTPS health checks.
TCP: ALB sends SYN packets to check if the backend server port is available.
gRPC: ALB sends POST or GET requests to check if the backend server is healthy.
Health check method
Select a health check method.
HEAD: HTTP health checks use HEAD by default. Make sure your backend servers support HEAD requests. If they do not, health checks may fail. In this case, use GET instead.
POST: gRPC health checks use POST by default. Make sure your backend servers support POST requests. If they do not, health checks may fail. In this case, use GET instead.
GET: If a response exceeds 8 KB, it is truncated. This does not affect the health check result.
NoteThis parameter applies only when the health check protocol is HTTP, HTTPS, or gRPC.
HTTP and HTTPS health checks support HEAD and GET. gRPC health checks support POST and GET.
HTTP Version
Select an HTTP version: HTTP1.0 or HTTP1.1.
NoteThis parameter applies only when the health check protocol is HTTP or HTTPS.
Port
Enter the port that ALB uses to probe the backend server.
By default, this field is empty. ALB uses the backend server’s port. To specify a custom port, enter a value from 1 to 65535. Enter only one port number.
Path
Enter the URL of the page to check. We recommend using a static page.
By default, ALB sends HTTP HEAD requests to the private IP address of a backend ECS instance. It targets the default homepage configured on the instance. If you use a different page, specify its path.
Domain name
Enter a domain name for health checks.
By default, ALB uses the private IP addresses of backend servers. You can specify a domain name instead.
Health Check Status Codes
Select the status codes that indicate healthy backend servers. An ALB backend server passes health checks only when the probe request succeeds and returns the specified status codes.
For HTTP or HTTPS, you can select http_2xx, http_3xx, http_4xx, or http_5xx. By default, http_2xx and http_3xx are selected.
For gRPC, valid values are 0 to 99. You can enter up to 20 ranges. Separate ranges with commas (,).
NoteThis parameter applies only when the health check protocol is HTTP, HTTPS, or gRPC.
WarningIncluding 4XX or 5XX in the health status codes may delay the removal of faulty instances. For example, if a backend server returns HTTP 500, but http_5xx is accepted, ALB treats the server as healthy and keeps sending traffic to it. Use this setting only after careful evaluation of your business scenario. Prefer returning correct 2XX or 3XX status codes from your backend services.
Health Check Response Timeout
Set how long ALB waits for a health check response. If the backend ECS does not respond within this time, the health check fails.
Valid values: 1 to 300 seconds. Default: 5 seconds.
Health check interval
The interval between two consecutive health checks.
Valid values: 1 to 50 seconds. Default: 2 seconds.
Healthy threshold
Set how many consecutive successful health checks are required before ALB declares a backend server healthy.
Valid values: 2 to 10. Default: 3.
Unhealthy threshold
Set how many consecutive failed health checks are required before ALB declares a backend server unhealthy.
Valid values: 2 to 10. Default: 3.
Tags and Resource Group
Set the Tag key and Tag value.
After you set tags, filter health checks by tag on the Health Check page.
Resource Group: Select a resource group for the health check.
After you create a health check, select it in the Health Check Settings section when you create an ALB server group. For more information, see Create a server group.
Method 2: Through the Create Server Group Page
When you create a server group, save the health check configuration as a template. This makes it easy to reuse later.
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create a server group.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Server Groups page, click Create Server Group.
In the Create Server Group dialog box, configure the parameters, then click Create.
This section lists only parameters relevant to this topic. For other parameters, see Create and manage a server group.
Click Health Check Settings next to Modify. After you configure the settings, select Save the health check configurations as a template, which can facilitate health check creation and configurations, and enter a health check name.
Optional.Choose in the navigation pane on the left. On the Health Check page, view the saved health check template.
Modify a health check
Method 1: Through the Health Check page
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the health check.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Health Check page, find the health check you want to modify. In the Actions column, click Modify.
In the Modify Health Check Settings dialog box, update the parameters as needed, then click Save.
WarningAfter health checks are disabled, ALB no longer checks the health status of the backend servers. If a backend server is down, network traffic cannot be automatically switched to healthy backend servers.
If you specify a longer health check interval, more time is required for ALB to detect unhealthy backend servers.
Method 2: From the server group details page
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create a server group.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Server Groups page, find the server group you want to manage. In the Actions column, click Modify Health Check.
In the Modify Health Check dialog box, enable or disable health checks. Or click Health Check Settings next to Modify to update the settings.
WarningAfter health checks are disabled, ALB no longer checks the health status of the backend servers. If a backend server is down, network traffic cannot be automatically switched to healthy backend servers.
If you specify a longer health check interval, more time is required for ALB to detect unhealthy backend servers.
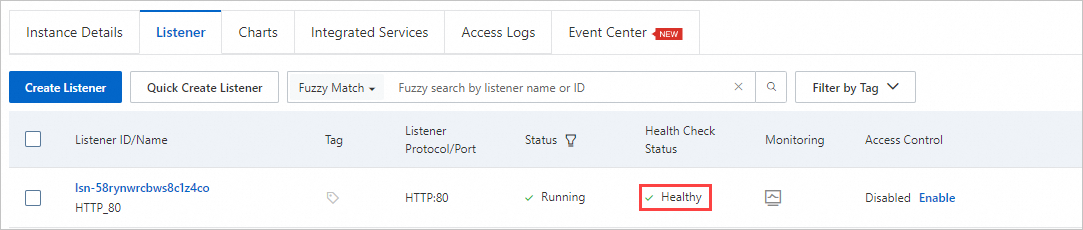
View health check status
If your ALB instance has a listener configured and health checks are enabled for its server groups, you can view the health check status of backend servers on the Listener tab.
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the ALB instance is deployed.
On the Instances page, find the ALB instance you want to manage and click its instance ID.
Click the Listener tab. In the Health Check Status column, view the health check status of backend servers.
Delete a health check
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the health check.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Health Check page, find the health check you want to delete. In the Actions column, click Delete.
In the Delete dialog box, confirm the message, then click OK.
Health check best practices
To ensure accuracy and reliability of health checks, follow these best practices:
Create a dedicated health check endpoint: Create a dedicated health check interface on your backend server, such as
/healthor/healthcheck. This interface should always return HTTP 200. Avoid using business paths for health checks because they may return 4XX status codes due to permission verification or missing resources.Fix backend services first: When health checks fail, troubleshoot and fix the backend service first. Ensure the health check path returns correct 2XX or 3XX status codes. Do not relax the status code requirements unless absolutely necessary.
Configure health check parameters carefully: Set appropriate values for health check interval, timeout, and thresholds based on your business needs. Poor settings can cause false positives or negatives.
Use curl to simulate health checks: When troubleshooting, use the following command to simulate ALB health checks:
curl -Iv -X HEAD --http1.0 -H "Host: your-domain.com" http://backend_ip:port/health_path