To facilitate API calls, we recommend that you integrate with Alibaba Cloud SDK in your project. SDKs simplify the development process, quickly integrate features, and greatly reduce the O&M cost. To integrate with Alibaba Cloud SDK, perform the following steps: install Alibaba Cloud SDK, configure an access credential, and use the SDK. This topic describes how to integrate with Alibaba Cloud SDK.
Prerequisites
Go 1.10.x or later is installed.
Import the SDK.
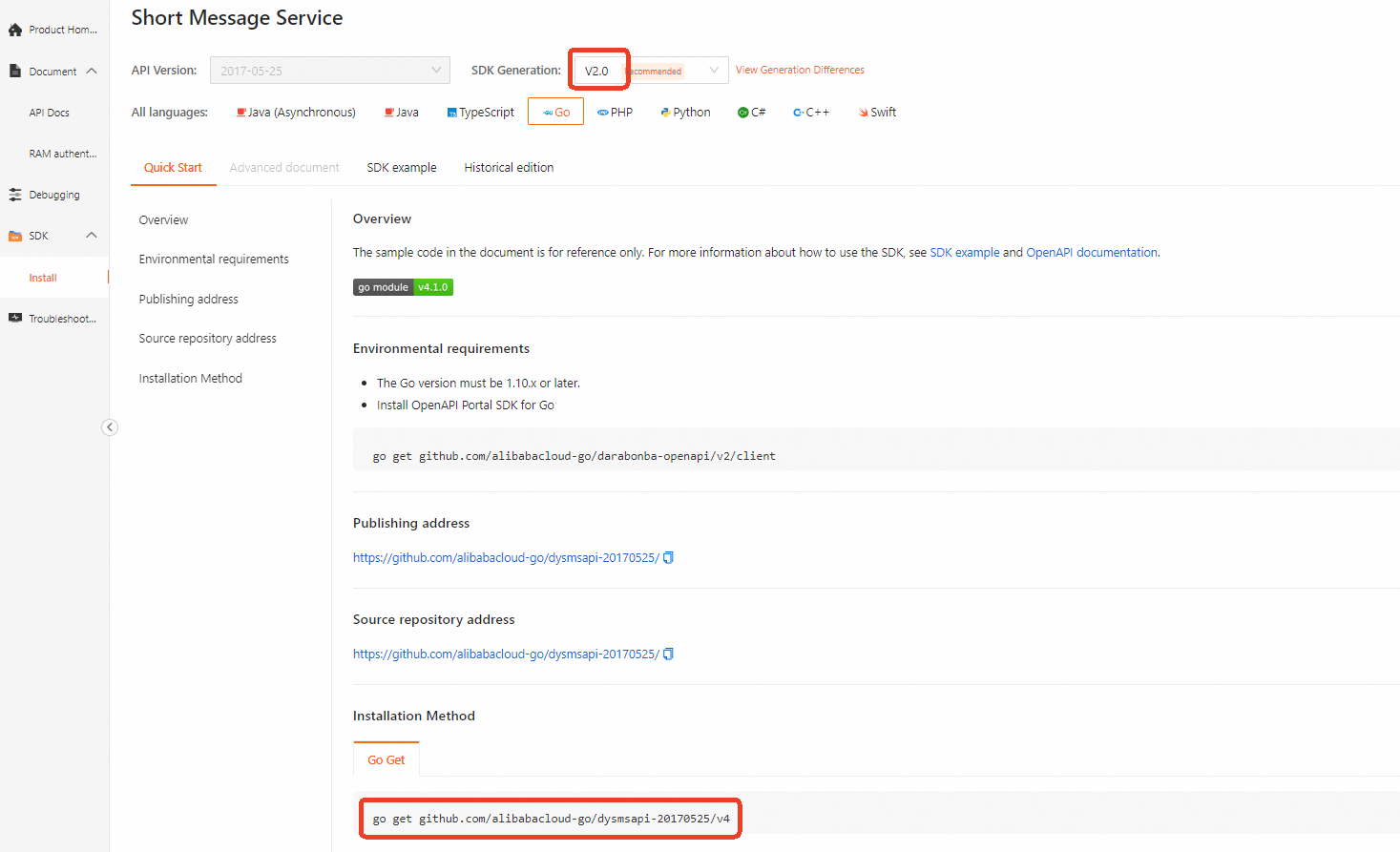
Log on to SDK Center and select the service whose SDK you want to use. In this example, Short Message Service (SMS) is selected.
On the Install page, and for All Languages, select Go. Then, on the Quick Start tab, you can find the SDK installation method for Short Message Service (SMS).
Configure an access credential
To call API operations of an Alibaba Cloud service, you must configure an access credential, such as an AccessKey pair or a Security Token Service (STS) token. To prevent AccessKey pair leaks, you can record the AccessKey pair in environment variables. For more information about other security solutions, see Credential security solutions. In this example, the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are used to record AccessKey pairs.
Configure environment variables in Linux and macOS
Configure environment variables by using the export command
The temporary environment variables configured by using the export command are valid only for the current session. After you exit the session, the configured environment variables become invalid. To configure permanent environment variables, you can add the export command to the startup configuration file of the corresponding operating system.
Configure the AccessKey ID and press Enter.
# Replace <ACCESS_KEY_ID> with your AccessKey ID. export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID=yourAccessKeyIDConfigure the AccessKey secret and press Enter.
# Replace <ACCESS_KEY_SECRET> with your AccessKey secret. export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=yourAccessKeySecretCheck whether the configuration is successful.
Run the
echo $ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_IDcommand. If the valid AccessKey ID is returned, the environment variables are configured.
Configure environment variables in Windows
Use GUI
Procedure
If you want to use GUI to configure environment variables in Windows 10, perform the following steps:
On the Windows desktop, right-click This PC and select Properties. On the page that appears, click Advanced system settings. In the System Properties dialog box, click Environment Variables on the Advanced tab. In the Environment Variables dialog box, click New in the User variables or System variables section. Then, configure the variables described in the following table.
Variable
Example
AccessKey ID
Variable name: ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID
Variable value: LTAI****************
AccessKey Secret
Variable name: ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
Variable value: yourAccessKeySecret
Check whether the configuration is successful.
On the Windows desktop, click Start or press Win + R. In the Run dialog box, enter cmd. Then, click OK or press Enter. On the page that appears, run the
echo %ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID%andecho %ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET%commands. If the valid AccessKey pair is returned, the configuration is successful.
Use CMD
Procedure
Open a Command Prompt window as an administrator and run the following commands to add environment variables in the operating system:
setx ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID yourAccessKeyID /M setx ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET yourAccessKeySecret /M/Mindicates that the environment variable is of system level. You can choose not to use this parameter when you configure a user-level environment variable.Check whether the configuration is successful.
On the Windows desktop, click Start or press Win + R. In the Run dialog box, enter cmd. Then, click OK or press Enter. On the page that appears, run the
echo %ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID%andecho %ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET%commands. If the valid AccessKey pair is returned, the configuration is successful.
Use Windows PowerShell
In PowerShell, configure new environment variables. The environment variables apply to all new sessions.
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID', 'yourAccessKeyID', [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET', 'yourAccessKeySecret', [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)Configure environment variables for all users. You must run the following commands as an administrator.
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID', 'yourAccessKeyID', [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET', 'yourAccessKeySecret', [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)Configure temporary environment variables. The environment variables apply only to the current session.
$env:ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "yourAccessKeyID"
$env:ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET = "yourAccessKeySecret"In PowerShell, run the Get-ChildItem env:ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and Get-ChildItem env:ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET commands. If the valid AccessKey pair is returned, the configuration is successful.
Use the SDK
In this example, the SendMessageToGlobe API operation of Short Message Service (SMS) is called. For more information about SendMessageToGlobe, see SendMessageToGlobe.
1. Initialize a request client
In the V2.0 SDK, all OpenAPI calls are initiated through a client. Before you can call an OpenAPI operation, you must initialize the client. You can initialize the client in several ways. This example shows how to initialize the client using an AccessKey. For more information about other initialization methods, see Manage access credentials.
Client instances are thread-safe and can be used in multi-threaded environments. You do not need to create a separate instance for each thread.
In development projects, we recommend that you do not frequently create client objects. Otherwise, resource waste may increase and service perform may degrade. We recommend that you use a single instance to encapsulate the client. This ensures that only one Client instance is initialized for the same access credential and endpoint throughout the application lifecycle.
import (
openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client"
dysmsapi20180501 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/dysmsapi-20180501/v2/client"
util "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea-utils/v2/service"
"os"
)
func CreateClient () (_result *dysmsapi20180501.Client, _err error) {
config := &openapi.Config{
// Required, please ensure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID is set.
AccessKeyId: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")),
// Required, please ensure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET is set.
AccessKeySecret: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")),
}
config.Endpoint = tea.String("dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com")
_result = &dysmsapi20180501.Client{}
_result, _err = dysmsapi20180501.NewClient(config)
return _result, _err
}2. Create a Request struct instance
When you pass parameters for an OpenAPI call, you must use the Request struct that is provided by the SDK. The naming format for an OpenAPI Request struct is <OpenAPI operation name>Request. For example, the request struct for the `SendSms` operation is `SendSmsRequest`. For more information about the request parameters, see the corresponding API documentation. For the API documentation in this example, see SendMessageToGlobe.
If the API operation does not support request parameters, you do not need to create a request object. For example, the DescribeCdnSubList operation does not support request parameters.
// Create request object and set required input parameters
sendMessageToGlobeRequest := &dysmsapi20180501.SendMessageToGlobeRequest{
// Please replace with the actual recipient number.
To: tea.String("<YOUR_VALUE>"),
// Please replace with the actual SMS content.
Message: tea.String("<YOUR_VALUE>"),
}3. The client initiates the request.
When you use the client to call an OpenAPI operation, we recommend that you use the <Operation name>WithOptions function. This function takes two parameters: the first is a pointer to the API Request struct, and the second is a pointer to a runtime options struct. Runtime options are used to configure request behaviors, such as timeout settings and proxy configurations. For more information, see Advanced configuration.
If the API operation does not support request parameters, you do not need to specify a request object in the request. For example, you only need to specify the runtime parameter when you call the DescribeCdnSubList operation.
// You need to add 'util "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea-utils/v2/service"' to the import statement.
func _main() (_result *dysmsapi20180501.SendMessageToGlobeResponse, _err error) {
client, _err := CreateClient()
if _err != nil {
return nil, _err
}
// Create request object and set required input parameters
sendMessageToGlobeRequest := &dysmsapi20180501.SendMessageToGlobeRequest{
// Please replace with the actual recipient number.
To: tea.String("<YOUR_VALUE>"),
// Please replace with the actual SMS content.
Message: tea.String("<YOUR_VALUE>"),
}
runtime := &util.RuntimeOptions{}
// Copy the code to run, please print the return value of the API by yourself.
response, _err := client.SendMessageToGlobeWithOptions(sendMessageToGlobeRequest, runtime)
if _err != nil {
return nil, _err
}
return response, _err
}
4. Handle errors
Alibaba Cloud SDK V2.0 for Go classifies exceptions into the following types:
error: This type of exception is caused by non-business errors. For example, an error is thrown if the verification fails because the SDK source file is modified or if the parsing fails.
SDKError: In most cases, this type of exception is caused by business errors.
For more information about how to handle SDK exceptions, see Exception handling.
We recommend that you take proper exception handling measures, such as reporting exceptions, logging exceptions, and performing retries, to ensure the robustness and stability of your system.
For more information, see Sample code.
Special scenario: File upload through the Advance operation
When you use Image Search or Visual Intelligence API (VIAPI) to process images on an on-premises machine or upload images, the API of the Image Search or VIAPI described in the documentation does not support direct upload. To upload images, you need to use the Advance operation, which supports transmission of file streams. The cloud service temporarily stores the uploaded file in Object Storage Service (OSS), and reads the temporary file from OSS when necessary. The default region of OSS is cn-shanghai. The following example shows how to call the DetectBodyCount operation of VIAPI:
Temporary files in OSS are regularly cleared.
Initialize a request client
Make sure that both the
RegionIdparameter and theendpointof the cloud service are specified.RegionIdindicates the OSS region in which the temporary files are stored. If you do not configure theRegionIdparameter, the cloud service may use a different region than OSS, resulting in API timeouts.import ( "os" openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client" facebody20191230 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/facebody-20191230/v5/client" "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea/tea" ) func CreateClient() (_result *facebody20191230.Client, _err error) { config := &openapi.Config{ // Required. Make sure that the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID environment variable is set in your runtime environment. AccessKeyId: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")), // Required. Make sure that the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variable is set in your runtime environment. AccessKeySecret: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")), } // The endpoint and regionId must be set to the same region. config.RegionId = tea.String("cn-shanghai") config.Endpoint = tea.String("facebody.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com") _result, _err = facebody20191230.NewClient(config) return _result, _err }Create an AdvanceRequest struct instance
When you upload a local file, you must use the AdvanceRequest struct provided by the SDK to pass the file stream. The naming format for the AdvanceRequest struct is
<OpenAPI operation name>AdvanceRequest. To find the parameter name for passing the file stream, look for the parameter of theio.Readertype in the corresponding AdvanceRequest struct.// Replace with the file path. filePath := `<FILE_PATH>` // Open the file and create a stream. file, err := os.Open(filePath) if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("Failed to open file: %v", err) } defer file.Close() // Close the file. // Create an instance of the AdvanceRequest struct. detectBodyCountAdvanceRequest := &facebody20191230.DetectBodyCountAdvanceRequest{ ImageURLObject: file, }Initiate a request
Call the
<Operation name>Advancefunction to initiate the request. The input parameter is a pointer to the AdvanceRequest struct.// You need to add 'util "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea-utils/v2/service"' to the import statement. func _main() (response *facebody20191230.DetectBodyCountResponse, _err error) { client, _err := CreateClient() if _err != nil { return nil, _err } // Replace with the file path. filePath := `<FILE_PATH>` // Open the file and create a stream. file, err := os.Open(filePath) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to open file: %v", err) } defer file.Close() // Close the file. // Create a request object. detectBodyCountAdvanceRequest := &facebody20191230.DetectBodyCountAdvanceRequest{ ImageURLObject: file, } runtime := &util.RuntimeOptions{} // Initiate the request. response, _err = client.DetectBodyCountAdvance(detectBodyCountAdvanceRequest, runtime) if _err != nil { return nil, _err } return response, nil }
FAQ
How do I handle the "You are not authorized to perform this operation" error thrown by an API operation?
How do I handle the "SDKError: Message: Post "https://ecs-cn-XX.aliyuncs.com": dial tcp: lookup ecs-cn-XX.aliyuncs.com: no such host" error thrown by an API operation?
How do I handle the "SDKError: StatusCode: 404 Code: InvalidAccessKeyId.NotFound Message: code: 404, Specified access key is not found" error thrown by an API operation?
For more information about how to handle SDK errors, see FAQ.