If you associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with each instance of a SAE application, the instances can be accessed from the internet and can access other services over the internet. This topic describes how to associate and disassociate EIPs in the SAE console and how to view application events.
Prerequisites
You have confirmed that the number of available EIPs in the same region is greater than the number of SAE application instances.
Background information
Internet access solutions
The following two solutions provide public access to applications on SAE in a VPC.
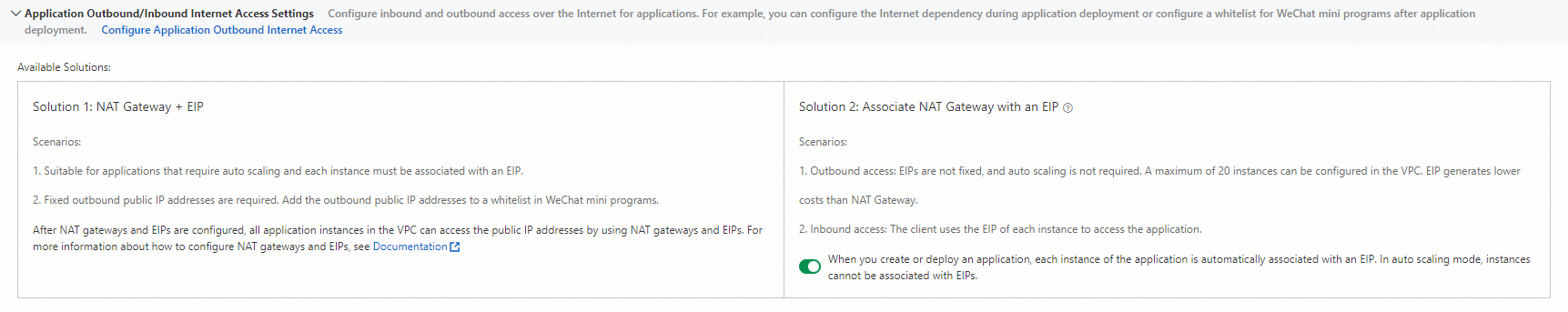
Solution 1: NAT Gateway + EIP
The source network address translation (SNAT) feature allows application instances that are deployed in a VPC to access the internet even when no public IP addresses are associated with them. If multiple applications in a VPC require internet access, you need to configure only one EIP. For more information, see Configure a NAT gateway for an SAE application to enable Internet access. This solution is suitable for the following scenarios:
The application uses an Auto Scaling policy, and you need a stable outbound IP address.
The application requires a fixed outbound public IP address. For example, you need to add the outbound public IP address to a whitelist in a WeChat mini program.
Solution 2: Associate an EIP with an application instance
If multiple applications in a VPC need to access the internet, at least one instance of each application must be associated with an EIP. This method is more cost-effective than using a NAT Gateway when you have 20 or fewer instances in the VPC. When you create or deploy an application, an EIP is automatically associated with each instance of the application. This solution is suitable for the following scenarios:
Accessing the internet (outbound traffic): This scenario applies when SAE services need to access external services over the internet. EIPs are not fixed, and Auto Scaling policies are not required.
Accessing the application from the internet (inbound traffic): Clients access the application by connecting to the EIP of each instance. However, this method is not suitable for external services that require a fixed IP address to access the SAE service because SAE uses new EIPs during deployment updates.
After you purchase EIPs, if you use Solution 2 to create or deploy an application, SAE automatically attaches an EIP to each instance of an application that requires an EIP. However, after the EIPs are attached, you can create an Auto Scaling policy, but you cannot enable or use it. If your application requires the Auto Scaling feature and internet access, we recommend that you use Solution 1.
Billing overview
You are charged for the EIPs that you purchase, but SAE does not incur additional fees. For more information, see Billing overview of EIP and Billing overview of SAE.
Usage notes
When you attach an EIP during application deployment, SAE first creates new instances and then releases the original instances. The original EIPs are not released during this process, so you must have an equivalent number of additional EIPs available.
After you associate EIPs with the application instances, check the security group to determine whether a port whitelist is configured. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
Configure EIPs when you create an application
In the SAE Application List, select the destination region and namespace from the top of the page, and then click Create Application.
In the Application Basic Information step of the configuration wizard, set the application parameters, and then click Next: Advanced Settings.
Expand the Application Outbound/Inbound Public Network Access Settings section, and turn on the Scenario 2. Associate With An Elastic IP switch.
If you do not enable this feature when you create the application, EIPs are not associated with instances that are added later through manual scaling. You must configure this setting when you deploy the application.
Click Create Application.
Verify the result.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click the Instance List tab to view the Elastic IP Address that is attached to the target instance.
Configure EIPs during an application deployment
After you redeploy an application, the application is restarted. To prevent unpredictable errors such as business interruptions, we recommend that you deploy applications during off-peak hours.
The procedure that can be performed to update an application varies based on the number of instances in the application. This section provides an example on how to configure the required features for an application in which the number of instances is greater than or equal to 1. For information about how to update an application in which the number of instances is 0, see Update an application.
In the SAE Application List, select the destination region and namespace from the top of the page, and then click the ID of the target Application to go to its details page.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click Deploy Application.
On the Deploy Application page, expand the Application Outbound/Inbound Public Network Access Settings section and configure the relevant parameters.

The deployment method is determined by the application's initial deployment method. Set the parameters based on the required deployment method.
Configure EIPs in the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: An Auto Scaling policy is not configured or enabled.
Associate EIPs.
Turn on the Option 2. Associate With An EIP switch.
Disassociate EIPs.
Turn off the Option 2. Associate With An EIP switch.
In the Disassociate From EIP dialog box that appears, click OK.
Scenario 2: An Auto Scaling policy is enabled.
In the Resume Auto Scaling After Deployment section, select Manual Resume.
NoteIf you select Automatic Resumption when you deploy the application, you cannot attach an EIP to the application.
Associate or disassociate EIPs.
Associate EIPs.
Turn on the Option 2. Associate With An EIP switch.
Disassociate EIPs.
Turn off the Option 2. Associate With An EIP switch.
In the Disassociate EIP dialog box that appears, click OK.
NoteAfter you attach an EIP to an application, SAE disables any enabled scaling policies, and you cannot enable the Auto Scaling feature. If your application requires the Auto Scaling feature and internet access, we recommend that you use the solution that integrates a NAT Gateway and an EIP. For more information, see Configure a NAT Gateway for an SAE application to enable Internet access.
After you complete the configuration, click Confirm.
Verify the result.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click the Instance List tab to view the Elastic IP Address that is attached to the target instance.
Configure EIPs when you roll back an application
If the application version that you want to roll back to has EIPs associated and an Auto Scaling policy was enabled before the rollback, perform the following steps.
In the SAE Application List, select the destination region and namespace from the top of the page, and then click the ID of the target Application to go to its details page.
In the upper-right corner of the Basic Information page, click Roll Back To Historical Version.
In the Roll Back To Previous Version panel, configure the settings, and then click OK.
In the Rollback Version section, select the target version.
NoteThe application version that you select in this step must have EIPs associated.
Optional: Click Select Batch/Grayscale Policy to configure the release policy.
Verify the result.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click the Instance List tab to view the Elastic IP Address that is attached to the target instance.
Configure EIPs during manual scaling
In the SAE application list, select the destination region and namespace from the top of the page, and then click the ID of the target Application to go to its details page.
In the upper-right corner of the Basic Information page, click Manual Scaling.
In the Application Scaling dialog box, configure the required parameters, and then click OK.
You can configure application scaling in the following scenarios. For more information, see Manual scaling.
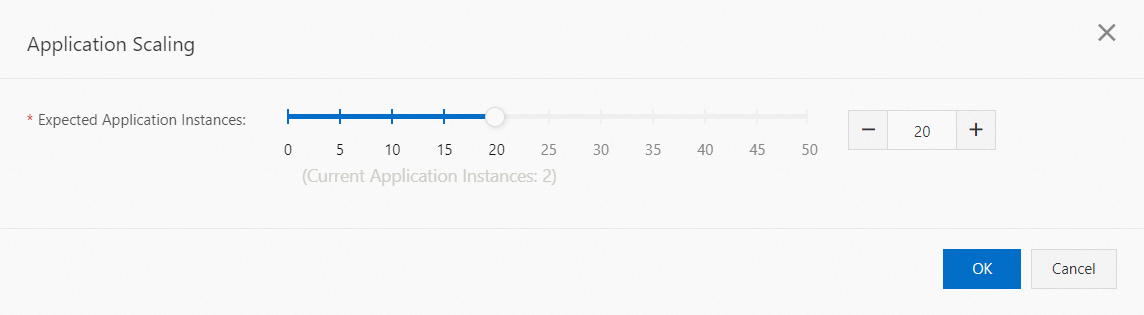
Scenario 1: An Auto Scaling policy is not deployed or enabled before scaling.
Use the slider to set the Target Number Of Application Instances.
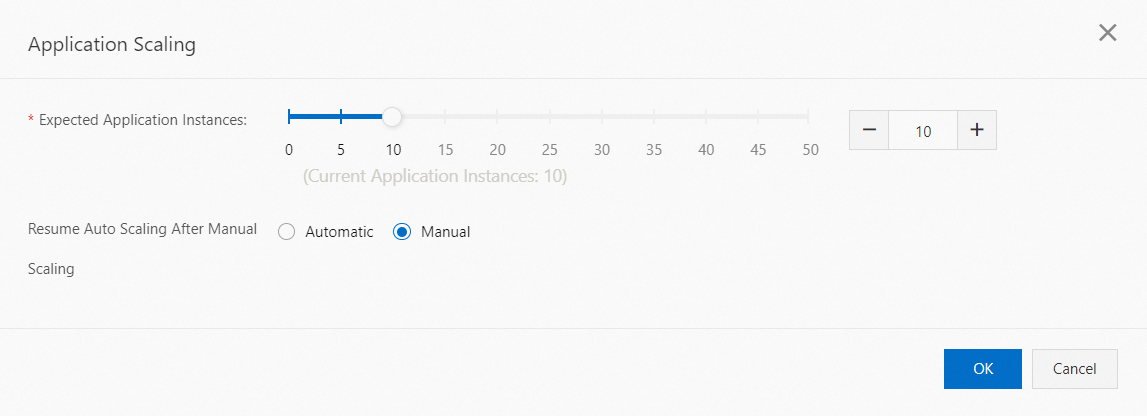
Scenario 2: An Auto Scaling policy is deployed and enabled before scaling.
Use the slider to set the Target Number Of Application Instances.
Select Manual Recovery.
 Note
NoteIf you select Automatic Resumption when you deploy the application, you cannot attach an EIP to the application.
Associate or disassociate EIPs.
For more information, see Configure EIPs during an application deployment.
Verify the result.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click the Instance List tab to view the Elastic IP Address that is attached to the target instance.
View application events
You can view error messages for application instances on the Application Events page.
In the SAE application list, select the destination region and namespace from the top of the page, and then click the ID of the target Application to go to its details page.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Application Events. From the Source Type drop-down list, select Application Instance (Pod). From the Event Level drop-down list, select Warning. You can then view the detailed error information for the application instance at the bottom of the page.
Troubleshoot the issue based on the Event Cause.
EipNotEnough: The number of available EIPs is insufficient. You can request more EIPs or scale in the application. For more information, see Request EIPs and Manual Scaling.
EipNotReady: The EIP failed to be attached or detached. Join the DingTalk group (Group ID: 32874633) and contact a product technical expert for assistance.